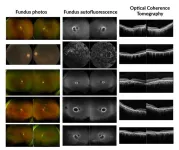
These fish use legs to taste the seafloor
2024-09-26
(Press-News.org) Sea robins are unusual animals with the body of a fish, wings of a bird, and walking legs of a crab. Now, researchers show that the legs of the sea robin aren’t just used for walking. In fact, they are bona fide sensory organs used to find buried prey while digging. This work appears in two studies published in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on September 26.
“This is a fish that grew legs using the same genes that contribute to the development of our limbs and then repurposed these legs to find prey using the same genes our tongues use to taste food—pretty wild,” says Nicholas Bellono (@NBellono) of Harvard University in Cambridge, MA.
Bellono, along with David Kingsley of Stanford University and their colleagues, didn’t set out to study sea robins at all. They came across these creatures on a trip to the Marine Biological Laboratory in Woods Hole, MA. After learning that other fish follow the sea robins around, apparently due to their skills in uncovering buried prey, the researchers became intrigued and took some sea robins back to the lab to find out more. They confirmed that the sea robins could indeed detect and uncover ground-up and filtered mussel extract and even single amino acids.
As reported in one of the two new studies, they found that sea robins’ legs are covered in sensory papillae, each receiving dense innervation from touch-sensitive neurons. The papillae also have taste receptors and show chemical sensitivity that drives the sea robins to dig.
“We were originally struck by the legs that are shared by all sea robins and make them different from most other fish,” Kingsley says. “We were surprised to see how much sea robins differ from each other in sensory structures found on the legs. The system thus displays multiple levels of evolutionary innovation from differences between sea robins and most other fish, differences between sea robin species, and differences in everything from structure and sensory organs to behavior.”
Through further developmental studies, the researchers confirmed that the papillae represent a key evolutionary innovation that has allowed the sea robins to succeed on the seafloor in ways other animals can’t. In the second study, they looked deeper into the genetic basis of the fish’s unique legs. They used genome sequencing, transcriptional profiling, and study of hybrid species to understand the molecular and developmental basis for leg formation.
Their analyses identified an ancient and conserved transcription factor, called tbx3a, as a major determinant of the sea robins’ sensory leg development. Genome editing confirmed that they depend on this regulatory gene to develop their legs normally. The same gene also plays a critical role in the formation of sea robins’ sensory papillae and their digging behavior.
“Although many traits look new, they are usually built from genes and modules that have existed for a long time,” Kingsley said. “That’s how evolution works: by tinkering with old pieces to build new things.”
The findings show that it’s now possible to expand our detailed understanding of complex traits and their evolution in wild organisms, not just in well-established model organisms, according to the researchers. They are now curious to learn more about the specific genetic and genomic changes that led to sea robins’ evolution.
###
Funding information about these studies can be found in the text of the papers.
Current Biology, Allard, Herbert, Krueger, et al., “Evolution of novel sensory organs in fish with legs” https://cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(24)01126-6
Current Biology, Herbert, Allard, McCoy, et al., “Ancient developmental genes underlie evolutionary novelties in walking fish” https://cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(24)01157-6
Current Biology (@CurrentBiology), published by Cell Press, is a bimonthly journal that features papers across all areas of biology. Current Biology strives to foster communication across fields of biology, both by publishing important findings of general interest and through highly accessible front matter for non-specialists. Visit http://www.cell.com/current-biology. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-26
Sea robins are ocean fish particularly suited to their bottom-dwelling lifestyle: Six leg-like appendages make them so adept at scurrying, digging, and finding prey that other fish tend to hang out with them and pilfer their spoils.
A chance encounter in 2019 with these strange, legged fish at Cape Cod’s Marine Biological Laboratory was enough to inspire Corey Allard to want to study them.
“We saw they had some sea robins in a tank, and they showed them to us, because they know we like weird animals,” said Allard, a ...
2024-09-26
The number of days per year that are simultaneously extremely hot, dry, and have a high fire risk have as much as tripled since 1970 in some parts of South America. The results are published in a study in Communications Earth & Environment.
South America is warming at a similar rate to the global average. However, some regions of the subcontinent are more at risk of the co-occurrence of multiple climate extremes. These compound extremes can have amplified impacts on ecosystems, economy, and human health.
Raúl Cordero and colleagues calculated the number of days per year that each approximately 30 by 30 km grid ...
2024-09-26
About The Study: This cross-sectional study found increased rates of both sudden unexpected infant death (SUID) and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) during the COVID-19 pandemic, with a significant shift in epidemiology from the pre-pandemic period noted in June to December 2021. These findings support the hypothesis that off-season resurgences in endemic infectious pathogens may be associated with SUID rates, with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) rates in the U.S. closely approximating this shift. Further investigation into the role ...
2024-09-26
About The Study: This study highlights the wide variation of nonprofit hospitals’ tax benefit across states, its high concentration among a small number of hospitals, and the primary role played by state and local taxes. Policy efforts to strengthen nonprofit hospitals’ taxpayer accountability are likely to be more effective when pursued at the local level.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ge Bai, PhD, CPA, email gbai@jhu.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
2024-09-26
Scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and their colleagues have identified a gene responsible for some inherited retinal diseases (IRDs), which are a group of disorders that damage the eye’s light-sensing retina and threatens vision. Though IRDs affect more than 2 million people worldwide, each individual disease is rare, complicating efforts to identify enough people to study and conduct clinical trials to develop treatment. The study’s findings published today in JAMA Ophthalmology.
In a small study of six unrelated participants, researchers linked the gene UBAP1L to different forms of ...
2024-09-26
In some mammals, the timing of the normally continuous embryonic development can be altered to improve the chances of survival for both the embryo and the mother. This mechanism to temporarily slow development, called embryonic diapause, often happens at the blastocyst stage, just before the embryo implants in the uterus. During diapause, the embryo remains free-floating and pregnancy is extended. This dormant state can be maintained for weeks or months before development is resumed, when conditions are favorable. Although not all mammals use this reproductive ...
2024-09-26
In both the natural world and human society, there commonly exist complex systems such as climate systems, ecological systems, and network systems. Due to the involvement of numerous interacting elements, complex systems can stay in multiple different states, and their overall behavior generally exhibits randomness and high disorder. For example, due to the complex interactions between factors such as solar radiation, terrain, and ocean currents, the climate system can exhibit various states like sunny, cloudy, and rainy. The dynamic changes and mutual influences of these factors make the behavior of the climate highly uncertain and difficult to predict accurately. For instance, the formation ...
2024-09-26
Washington, September 26, 2024—The number of educational opportunities that children accrue at home, in early education and care, at school, in afterschool programs, and in their communities as they grow up are strongly linked to their educational attainment and earnings in early adulthood, according to new research. The results indicate that the large opportunity gaps between low- and high-income households from birth through the end of high school largely explain differences in educational and income achievement ...
2024-09-26
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE
Thursday, September 26, 2024 - 9 a.m. EDT
Contact:
NIH Office of Communications and Public Liaison
NIH News Media Branch
301-496-5787
Statement by NIH on Research Misconduct Findings
Following an investigation, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has made findings of research misconduct against Eliezer Masliah, M.D., due to falsification and/or fabrication involving re-use and relabel of figure panels representing different experimental results in two publications. NIH will notify the two journals of its findings so that appropriate action can be taken. NIH initiated its research misconduct review process ...
2024-09-26
WASHINGTON—Pregnant women who do not get enough sleep may be at higher risk of having children with neurodevelopmental delays, according to new research published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Short sleep duration (SSD) is defined as sleeping less than seven hours per night. Pregnant woman may have trouble sleeping due to hormonal changes, pregnancy discomfort, frequent urination, and other factors.
It’s been reported that almost 40% of pregnant women have SSD. These women may have ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] These fish use legs to taste the seafloor