Researchers synthesize high-energy-density cubic gauche nitrogen at atmospheric pressure
2024-09-27
(Press-News.org)
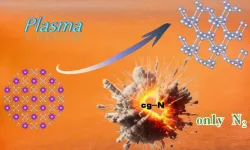
Recently, a research group led by Prof. WANG Xianlong from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, successfully synthesized high-energy-density materials cubic gauche nitrogen (cg-N) at atmospheric pressure by treating potassium azide (KN3) using the plasma-enhanced chemical vapour deposition technique (PECVD).
The research results were published in Science Advances.
Cg-N is a pure nitrogen material consisting of nitrogen atoms bonded by N-N single bonds, resembling the structure of diamond. It has attracted attention because it has a high-energy-density and produces only nitrogen gas when it decomposes. The development of efficient and safe synthesis method under atmospheric pressure is an important issue.
Since 2020, the research team has employed first-principles calculations as a theoretical guide to simulate the stability of the cg-N surface under various saturated states, pressures, and temperatures. The results revealed that surface instability led to the cg-N decomposition at low-pressures. They proposed that saturating the surface suspension bonds and transferring the charge could stabilize cg-N up to 750 K at atmospheric pressure.
In this research, choosing KN3 with lower toxicity and explosiveness as a precursor, due to the strong electron transfer capacity of potassium, the team successfully synthesized cg-N using PECVD technology without relying on the carbon nanotube-limiting effect. Thermogravimetric-differential scanning calorimetry (TG-DSC) measurements confirmed that the synthesized cg-N exhibits thermal stability up to 760 K, followed by rapid and intense thermal decomposition.
The study provides an efficient and convenient way to synthesis cg-N at atmospheric pressure, and also new ideas for the development of future high-energy-density materials, according to the team.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-27
University of Maryland scientists uncovered evidence of an ancient seafloor that sank deep into Earth during the age of dinosaurs, challenging existing theories about Earth’s interior structure. Located in the East Pacific Rise (a tectonic plate boundary on the floor of the southeastern Pacific Ocean), this previously unstudied patch of seafloor sheds new light on the inner workings of our planet and how its surface has changed over millions of years. The team’s findings were published in the journal Science Advances on September 27, 2024.
Led by geology postdoctoral researcher Jingchuan Wang, the team used innovative seismic imaging techniques to ...
2024-09-27
As Mark Hasegawa-Johnson combed through data from his latest project, he was pleasantly surprised to uncover a recipe for Eggs Florentine. Sifting through hundreds of hours of recorded speech will unearth a treasure or two, he said.
Hasegawa-Johnson leads the Speech Accessibility Project, an initiative at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign to make voice recognition devices more useful for people with speech disabilities.
In the project’s first published study, researchers asked an automatic ...
2024-09-27
NEW YORK, September 27, 2024 – Water scarcity, pollution, and the burden of waterborne diseases are urgent issues threatening global health and security. A recently published study in the journal Global Environmental Change highlights the pressing need for innovative economic strategies to bolster water security investments, focusing on the “enabling environment” that influences regional readiness for new business solutions.
Initiated and led by researchers at the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC), ...
2024-09-27
The study, published in Lancet Neurology, detailed the “head-to-head” trial implemented by the researchers to test two drugs, mexiletine and lamotrigine, on people with the condition.
The trial, which was conducted at the UCL Queen Square Multidisciplinary Centre for Neuromuscular Diseases and the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, UCLH, involved 60 adults with confirmed non-dystrophic myotonia.
Patients were randomly assigned to receive either mexiletine for eight weeks followed by lamotrigine for eight weeks, or the reverse order, with a seven-day ...
2024-09-27
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center has posthumously awarded Michael Frumovitz, M.D., with the Julie and Ben Rogers Award for Excellence in Patient Care. The annual award recognizes employees who consistently demonstrate excellence in their work and dedication to MD Anderson’s mission to end cancer. The award’s focus rotates among the areas of patient care, research, education, prevention and administration, with this year’s award focusing on patient care.
Frumovitz dedicated more than 20 years of service to MD Anderson, most recently as chief patient experience officer and professor in Gynecologic ...
2024-09-27
A University of Arizona College of Medicine – Phoenix researcher was recently awarded a $1.9 million National Institutes of Health grant to study the molecular mechanisms of how dilated cardiomyopathy progresses to heart failure, which could eventually lead to better preventive and treatment options for heart failure.
Heart failure is inextricably linked with dilated cardiomyopathy, or DCM, a disease characterized by the progressive enlargement of the heart and reduced contractility reflected by reduced ejection fraction. ...
2024-09-27
Clinical cancer research in the U.S. is increasingly dominated by pharmaceutical industry sponsors, study finds
Study underscores need for increased investment in federally funded cancer clinical trials
SEATTLE – September 27, 2024 – Researchers at Fred Hutch Cancer Center identified a substantial increase over the past decade in the proportion of patients with cancer in the U.S. who participate in pharmaceutical industry sponsored clinical trials compared to those conducted with federal government support. Published in The Journal of Clinical Oncology and presented at the ASCO Quality Care Symposium, these findings reveal trends of underinvestment in federally ...
2024-09-27
A new study published in the journal Science suggests that an ordinary old log could help refine strategies to tackle climate change.
A team of researchers led by University of Maryland Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Professor Ning Zeng analyzed a 3,775-year-old log and the soil it was excavated from. Their analysis, published on September 27, 2024, revealed that the log had lost less than 5% carbon dioxide from its original state thanks to the low-permeability clay soil that covered it.
“The wood is nice and solid—you could probably make a piece of furniture out of it,” Zeng noted.
Understanding the ...
2024-09-27
Preterm births have increased by more than 10 percent over the past decade, with racial and socioeconomic disparities persisting over time, according to a new study analyzing more than five million births.
The study, published in the journal JAMA Network Open, also found that some factors that increase the risk for preterm birth—such as diabetes, sexually transmitted infections, and mental health conditions—became much more common over the past decade, while other factors that protect against preterm birth declined.
“Our findings not only show that preterm births are on the rise, but provide clues as ...
2024-09-27
About The Study: The results of this cross-sectional study show that over the past 2 decades, menopausal hormone therapy use declined among U.S. postmenopausal women of all age and racial and ethnic groups. Women of racial and ethnic minority groups had lower prevalence of menopausal hormone therapy use compared to non-Hispanic white women.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Lin Yang, PhD, (lin.yang@ahs.ca) and Adetunji T. Toriola, MD, PhD, MPH, (a.toriola@wustl.edu).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.3128)
Editor’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers synthesize high-energy-density cubic gauche nitrogen at atmospheric pressure