Researchers close in on understanding possible cause of Alzheimer’s disease
Awarded four-year, $3.3M grant from National Institutes of Health
2024-09-30
(Press-News.org) CLEVELAND—With a four-year, $3.3 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), researchers from Case Western Reserve University will study whether certain brain proteins may play a role in the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s disease is a brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills. According to the Alzheimer’s Association, nearly 7 million Americans 65 and older are living with the disease and there are more deaths from Alzheimer’s than breast and prostate cancer combined.
Previous research has found evidence that Alzheimer’s begins when the brain’s protective barrier—called the blood-brain barrier (BBB)—weakens. This weakening allows harmful substances to enter the brain, which could lead to the onset of Alzheimer’s.
The NIH-backed study will examine the potential function of epitope (Eph) receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. Eph receptors are proteins initially investigated by Bing-Cheng Wang, a professor of pharmacology at Case Western Reserve’s School of Medicine, for their role in brain development and cancer. They mediate various cell-to-cell interactions.
These proteins, according to Matthias Buck, a professor of physiology and biophysics at the School of Medicine, and his colleagues, may be involved in the BBB’s disintegration, which is crucial for protecting the brain from damage during strokes and the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. The new study expands on Buck’s 15 years of Eph research.
Working with Buck’s lab, which is studying a part of the Eph receptor protein using advanced imaging and computational techniques, researchers from Texas Tech University and the University of Tennessee will study how this protein behaves in living cells. And scientists at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center are using crystallography to understand the protein’s structure.
“Alzheimer’s is very complex, which is why this project requires a collaboration of special skills,” Buck said. “Since some infectious agents can pass through the blood-brain barrier and Eph receptors are helpful, we plan to enlist the assistance of more local and national partners as this research gains momentum. We anticipate this research will result in discoveries that will one day make it possible to treat an illness that impacts millions of people worldwide.”
###
Case Western Reserve University is one of the country's leading private research institutions. Located in Cleveland, we offer a unique combination of forward-thinking educational opportunities in an inspiring cultural setting. Our leading-edge faculty engage in teaching and research in a collaborative, hands-on environment. Our nationally recognized programs include arts and sciences, dental medicine, engineering, law, management, medicine, nursing and social work. About 6,000 undergraduate and 6,300 graduate students comprise our student body. Visit case.edu to see how Case Western Reserve thinks beyond the possible.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-30
HOUSTON – (Sept. 30, 2024) – Rice University engineers have developed an innovative way to make covalent organic frameworks (COFs), special materials that can be used to trap gases, filter water and speed up chemical reactions. COFs have the potential to address significant environmental challenges, including energy storage and pollution control. An example of that is their potential use in the decontamination of “forever chemicals” or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
Rice chemical engineer Rafael Verduzco and his team have described a new way to synthesize high-quality ...
2024-09-30
Researchers from West China Hospital, Sichuan University, have conducted a study revealing a significant association between COVID-19 and acute kidney disorders (AKD), including acute kidney injury (AKI), that varies over time. The study, led by Dr. Li Chunyang and Dr. Zeng Xiaoxi from the West China Biomedical Big Data Center, was recently published in the journal Health Data Science.
COVID-19, known for its impact on the respiratory system, also affects other organs, including the kidneys. The study aimed to investigate the time-dependent effects of COVID-19 on acute kidney disorders. Using data from the ...
2024-09-30
A new hand-held scanner developed by UCL researchers can generate highly detailed 3D photoacoustic images in just seconds, paving the way for their use in a clinical setting for the first time and offering the potential for earlier disease diagnosis.
In the study, published in Nature Biomedical Engineering, the team show their technology can deliver photoacoustic tomography (PAT) imaging scans to doctors in real time, providing them with accurate and intricate images of blood vessels, helping inform patient care.
Photoacoustic ...
2024-09-30
Kunming, China - A team of researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences has uncovered compelling evidence of a genetic link between bipolar disorder type I (BD-I) and epilepsy, potentially revolutionizing our understanding of these complex neuropsychiatric conditions. The study, published in Genomic Psychiatry on September 30, 2024, reveals shared genetic variants and a causal relationship between the two disorders, opening new avenues for research and treatment.
Led by Dr. Ming Li from the Kunming ...
2024-09-30
Lead researcher Dr Sarah Nason, from Bangor University’s School of History, Law and Social Sciences explained: “Debt, benefits, special educational needs, healthcare issues, these are everyday problems that many of us face, and it’s only natural to turn to people you know and trust for help and advice. However, we found that having to talk to more people or support services was an indicator that the problem was more complex and difficult to resolve.”
The team studied four distinct areas across England and Wales: Bryngwran, a village on Anglesey in North Wales; Deeplish, a district of Rochdale in Greater ...
2024-09-30
Aging societies and population decline have been on the rise globally, but in Japan, the situation has exasperated tenfold. A staggering 36.21 million people, or 28.9% of the populace, are 65 and over. Further, 74.6% of Japan’s 1,747 cities are categorized as shrinking, with urban policies struggling to keep up with the decline. However, the factors that correlate with population changes in cities of varying sizes have not been clarified.
Dr. Haruka Kato, a junior associate professor at Osaka Metropolitan University, ...
2024-09-30
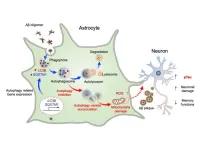
A research team led by Dr. Hoon Ryu from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Sang-Rok Oh) Brain Disease Research Group, in collaboration with Director Justin C. Lee of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS, President Do-Young Noh) and Professor Junghee Lee from Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, has uncovered a new mechanism involving astrocytes for treating Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and proposed a novel therapeutic target. In this study, the researchers revealed that autophagy pathway ...
2024-09-30
Media contacts:
Lisa Robinson, lrobinson@aap.org
Alex Hulvalchick, ahulvalchick@aap.org
American Academy of Pediatrics Announces its First Clinical Practice Guideline for Opioid Prescriptions
Pediatricians should prescribe opioids for pain when necessary, with recommended precautions in place to increase safety, according to a clinical practice guideline released during the AAP 2024 National Conference & Exhibition
ORLANDO, Fla.--The American Academy of Pediatrics has published its first clinical ...
2024-09-30
Drivers of electric vehicles (EVs) are more likely to be involved in at-fault road traffic accidents than drivers of petrol and diesel cars, research by Lero, the Research Ireland Centre for Software, at University of Limerick and Universitat de Barcelona, reveals.
In the analysis of insurance claims and data from onboard sensors, due to be published in the November issue of the journal Accident Analysis & Prevention, the Lero researchers reveal a number of key findings:
Electric and hybrid drivers exhibit different behaviours ...
2024-09-30
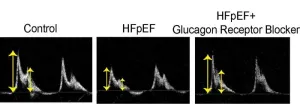
Duke-NUS scientists and their collaborators have discovered a potential new treatment for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), a type of heart disease that is notoriously difficult to treat. The team discovered that the diseased heart cells had high levels of glucagon activity, a pancreatic hormone that raises blood sugar (glucose) levels. Armed with this novel insight, the scientists demonstrated that a drug that blocks the hormone’s activity, can significantly improve heart ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers close in on understanding possible cause of Alzheimer’s disease
Awarded four-year, $3.3M grant from National Institutes of Health