Asymmetric placebo effect in response to spicy food
Positive expectations facilitate reward processing and negative expectations prime pain processing
2024-10-08
(Press-News.org) The expectations humans have of a pleasurable sensation asymmetrically shape neuronal responses and subjective experiences to hot sauce, according to a study published October 8th, in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Yi Luo from East China Normal University, Kenneth Kishida from Wake Forest School of Medicine, U.S., and colleagues.
Expectations shape our perception, profoundly influencing how we interpret the world. Positive expectations about sensory stimuli can alleviate distress and reduce pain through what’s known as the placebo effect, while negative expectations may heighten anxiety and exacerbate pain. In the new study, Luo, Kishida, and colleagues investigated the impact of the hedonic aspect of expectations on subjective experiences.
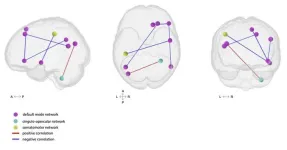
Specifically, the researchers measured neurobehavioral responses to the taste of hot sauce among individuals with a wide range of taste preferences. In total, 47 participants completed the tasks while undergoing functional magnetic resonance imaging scanning. The researchers identified participants who liked versus those who strongly disliked spicy flavors and provided contextual cues about the spiciness of the sauce to be tasted. That way, they were able to dissociate the effects of positive and negative expectations from sensory stimuli (i.e., visual and taste stimuli), which were the same across all participants.
The results showed that positive expectations lead to modulations in the intensity of subjective experience. These modulations were accompanied by increased activity in brain regions previously linked to pleasure, information integration, and the placebo effect, including the anterior insula, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, and dorsal anterior cingulate cortex. By contrast, negative expectations decreased hedonic experience and increased neural activity in the Neurological Pain Signature network.
Taken together, these findings demonstrate that hedonic aspects of one’s expectations asymmetrically shape how the brain processes sensory input and associated behavioral reports of one’s subjective experiences of intensity, pleasure, and pain. The results suggest a dissociable impact of hedonic information. While positive expectations facilitate higher-level information integration and reward processing, negative expectations prime lower-level processes related to pain and emotions. According to the authors, this study demonstrates the powerful role of hedonic expectations in shaping subjective reality and suggests potential avenues for consumer and therapeutic interventions targeting expectation-driven neural processes.
The authors add, “Our study highlights how hedonic expectations shape subjective experiences and neural responses, offering new insights into the mechanisms behind pain perception.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002818
Author Interview: https://plos.io/4dds8bC
Citation: Luo Y, Lohrenz T, Lumpkin EA, Montague PR, Kishida KT (2024) The expectations humans have of a pleasurable sensation asymmetrically shape neuronal responses and subjective experiences to hot sauce. PLoS Biol 22(10): e3002818. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002818
Author Countries: China, United States
Funding: see manuscript
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-08
In a rare, longitudinal study, researchers from Aalto University and the University of Oulu tracked one person’s brain and behavioral activity for five months using brain scans and data from wearable devices and smartphones.
‘We wanted to go beyond isolated events,’ says research leader Ana Triana. ‘Our behaviour and mental states are constantly shaped by our environment and experiences. Yet, we know little about the response of brain functional connectivity to environmental, physiological, and behavioral changes on different ...
2024-10-08
LA JOLLA (October 8, 2024)—The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has selected Salk Associate Professor Nicola Allen to receive a 2024 NIH Director’s Pioneer Award. The award recognizes exceptionally creative scientists pursuing highly innovative research and groundbreaking approaches to major challenges in biomedical, behavioral, or social sciences.
Allen will receive $3.5 million over five years to support her latest research, which investigates how plasticity in the adult brain could be enhanced. ...
2024-10-08
Proteins control most of the body’s functions, and their malfunction can have severe consequences, such as neurodegenerative diseases or cancer. Therefore, cells have mechanisms in place to control protein quality. In animal and human cells, chaperones of the Hsp70 class are at the heart of this control system, overseeing a wide array of biological processes. Yet, despite their crucial role, the precise molecular mechanism of Hsp70 chaperones has remained elusive for decades. Using a cutting-edge nanopore single-molecule technique, a team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), in collaboration with EPFL, has now made a significant breakthrough in determining how Hsp70 chaperones ...
2024-10-08
DataSeer and the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) are pleased to announce two new pilot programs designed to support high-quality reporting across scientific disciplines. The first will generate pre-filled MDAR reports for authors – saving them time and boosting the quality of methods reporting – for AAAS’ flagship journal Science. The second will establish an Open Science Indicators baseline dataset, quantifying how and when authors at Science share their ...
2024-10-08
Students don’t have to be friends, but they should be friendly. In other words, they should learn to be respectful of one another while sharing the same space. For Chad Rose, a nationally renowned bullying prevention expert at the University of Missouri, this idea is central to his efforts to reduce school bullying, and in turn, school violence.
Bullying is a risk factor for violence, said Rose, the director of Mizzou’s Bully Prevention Lab who has spent the past 18 years researching the subject.
“After the Safe Schools initiative was launched in 1999 by the U.S. Department of Education, we began to see that children and teens who have experienced prolonged ...
2024-10-08
Researchers at Concordia have developed a novel method of 3D printing that uses acoustic holograms. And they say it’s quicker than existing methods and capable of making more complex objects.
The process, called holographic direct sound printing (HDSP), is described in a recent article in the journal Nature Communications. It builds on a method introduced in 2022 that described how sonochemical reactions in microscopic cavitations regions — tiny bubbles — create extremely high temperatures and pressure for trillionths of a second to harden resin into complex ...
2024-10-08
“ATT may be more sensitive to age-related decline than CBF, and therefore useful for early detection and management of cerebrovascular impairment.”
BUFFALO, NY- October 8, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 18 on September 18, 2024, entitled, “Determinants of cerebral blood flow and arterial transit time in healthy older adults.”
This research paper highlights that brain health deteriorates with ...
2024-10-08
The cells in your pancreas, like people, can only handle so much stress before they start to break down. Certain stressors, such as inflammation and high blood sugar, contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes by overwhelming these cells.
Researchers at The Jackson Laboratory (JAX) have now discovered that DNA sequence changes known to increase a person’s risk for diabetes are linked to how well pancreatic cells can handle two different kinds of molecular stress. In people with these DNA changes, the insulin-producing ...
2024-10-08
About The Study: In this systematic review and meta-analysis, aerobic physical activity was associated with modest short-term and long-term reductions of depression among adults with cancer. Future studies should discern the effectiveness of aerobic physical activity in combination with other strategies for managing depression across various populations of patients with cancer.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Sapna Oberoi, M.D., M.Sc., email soberoi@cancercare.mb.ca.
To access the embargoed study: ...
2024-10-08
About The Study: In this cohort study of a large primary care population served by an integrated health system, alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS) hospitalizations were common, especially in male patients, younger age groups, and individuals with high-risk alcohol use. During hospitalizations, the burden of AWS was similar to or exceeded complications of other chronic diseases that receive greater medical attention.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Tessa L. Steel, M.D., M.P.H., email tessita@uw.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Asymmetric placebo effect in response to spicy food
Positive expectations facilitate reward processing and negative expectations prime pain processing