(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science were recently awarded $2.8 million of a $5.8 million grant from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Climate Program Office to support a groundbreaking four-year project aimed at developing best practices for decision-ready climate projection information. This work will address increased demand by public and private sectors for reliable, long-term extreme weather climate information.
This initiative, led by the Rosenstiel School and including partners from the National Center for Atmospheric Research, Colorado State University, and Florida International University, will engage a wide array of stakeholders across five key themes: western water resources, heat waves, coastal flood risk, wildfire risk, and extreme wind events. It aims to provide access to crucial datasets and analysis procedures while promoting education for the next generation of climate projection translators.
"This is a challenging research project that brings a large team of scientists together focused on developing climate change projections of extreme heat, rainfall, flooding, fire risk, and other environmental hazards for the mid-century and beyond that can be used to support local adaptation and resilience planning by governmental organizations, businesses, and individuals,” said the project’s principal investigator Ben Kirtman, the William R. Middelthon III Endowed Chair of Earth Sciences at the Rosenstiel School. Kirtman is also the director of the University’s NOAA Cooperative Institute for Marine and Atmospheric Studies and the deputy director of the Frost Institute for Data Science and Computing.
Climate change is already affecting communities across the U.S., with impacts expected to intensify in the coming decades. Mid-to-long-range forecasts on coastal inundation, extreme heat, flooding, and drought are crucial for infrastructure planning and anticipating climate effects. Demand for this information is rising among governmental and private entities, yet it is often met through disjointed researcher-stakeholder relationships or generic online graphics that fail to address specific needs.
The project, titled “Developing Decadal Climate Projection Services Through Stakeholder Guidance and Foundational Science,” will develop the scientific understanding to underpin authoritative climate projection services. The team led by Kirtman will conduct the research necessary to support reliable and scientifically robust climate projection services, ensuring that approaches are state-of-the-art, thoroughly and transparently documented, and developed in collaboration with stakeholders.
Project updates and results will be communicated to a broad audience via a website, blogs, and interaction with NOAA’s climate.gov.
About the University of Miami and Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science
The University of Miami is a private research university and academic health system with a distinct geographic capacity to connect institutions, individuals, and ideas across the hemisphere and around the world. The University’s vibrant and diverse academic community comprises 12 schools and colleges serving more than 19,000 undergraduate and graduate students in more than 180 majors and programs. Located within one of the most dynamic and multicultural cities in the world, the University is building new bridges across geographic, cultural, and intellectual borders, bringing a passion for scholarly excellence, a spirit of innovation, a respect for including and elevating diverse voices, and a commitment to tackling the challenges facing our world. With more than $413 million in research and sponsored program expenditures annually, the University of Miami is a member of the prestigious Association of American Universities (AAU).
Founded in 1943, the Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science is one of the world’s premier research institutions in the continental United States. The school’s basic and applied research programs seek to improve understanding and prediction of Earth’s geological, oceanic, and atmospheric systems by focusing on four key pillars:
*Saving lives through better forecasting of extreme weather and seismic events.
*Feeding the world by developing sustainable wild fisheries and aquaculture programs.
*Unlocking ocean secrets through research on climate, weather, energy and medicine.
*Preserving marine species, including endangered sharks and other fish, as well as protecting and restoring threatened coral reefs.
www.earth.miami.edu
END
NOAA awards grant to enhance decision-ready climate projections for diverse stakeholders
University of Miami scientists will lead a four-year, first-of-its-kind collaborative project
2024-10-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Why using a brand nickname in marketing is not a good idea
2024-10-08
Researchers from Western University, Stockton University, and University of Massachusetts Amherst published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines if firms benefit from adopting popular nicknames in their branding efforts.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “BMW is Powerful, Beemer is Not: Nickname Branding Impairs Brand Performance” and is authored by Zhe Zhang, Ning Ye, and Matthew Thomson.
Many brands have popular nicknames that have become a part of ...
Asymmetric placebo effect in response to spicy food
2024-10-08
The expectations humans have of a pleasurable sensation asymmetrically shape neuronal responses and subjective experiences to hot sauce, according to a study published October 8th, in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Yi Luo from East China Normal University, Kenneth Kishida from Wake Forest School of Medicine, U.S., and colleagues.
Expectations shape our perception, profoundly influencing how we interpret the world. Positive expectations about sensory stimuli can alleviate distress and reduce pain through what’s ...
Echoes in the brain: Why today’s workout could fuel next week’s bright idea
2024-10-08
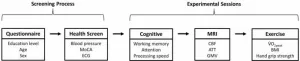
In a rare, longitudinal study, researchers from Aalto University and the University of Oulu tracked one person’s brain and behavioral activity for five months using brain scans and data from wearable devices and smartphones.
‘We wanted to go beyond isolated events,’ says research leader Ana Triana. ‘Our behaviour and mental states are constantly shaped by our environment and experiences. Yet, we know little about the response of brain functional connectivity to environmental, physiological, and behavioral changes on different ...
Salk Institute’s Nicola Allen receives 2024 NIH Director’s Pioneer Award
2024-10-08
LA JOLLA (October 8, 2024)—The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has selected Salk Associate Professor Nicola Allen to receive a 2024 NIH Director’s Pioneer Award. The award recognizes exceptionally creative scientists pursuing highly innovative research and groundbreaking approaches to major challenges in biomedical, behavioral, or social sciences.
Allen will receive $3.5 million over five years to support her latest research, which investigates how plasticity in the adult brain could be enhanced. ...
The secret strength of our cell guards
2024-10-08
Proteins control most of the body’s functions, and their malfunction can have severe consequences, such as neurodegenerative diseases or cancer. Therefore, cells have mechanisms in place to control protein quality. In animal and human cells, chaperones of the Hsp70 class are at the heart of this control system, overseeing a wide array of biological processes. Yet, despite their crucial role, the precise molecular mechanism of Hsp70 chaperones has remained elusive for decades. Using a cutting-edge nanopore single-molecule technique, a team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), in collaboration with EPFL, has now made a significant breakthrough in determining how Hsp70 chaperones ...
DataSeer and AAAS partner to boost reporting standards
2024-10-08
DataSeer and the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) are pleased to announce two new pilot programs designed to support high-quality reporting across scientific disciplines. The first will generate pre-filled MDAR reports for authors – saving them time and boosting the quality of methods reporting – for AAAS’ flagship journal Science. The second will establish an Open Science Indicators baseline dataset, quantifying how and when authors at Science share their ...
Mizzou researchers awarded $8 million in grants to discover new bullying prevention strategies
2024-10-08
Students don’t have to be friends, but they should be friendly. In other words, they should learn to be respectful of one another while sharing the same space. For Chad Rose, a nationally renowned bullying prevention expert at the University of Missouri, this idea is central to his efforts to reduce school bullying, and in turn, school violence.
Bullying is a risk factor for violence, said Rose, the director of Mizzou’s Bully Prevention Lab who has spent the past 18 years researching the subject.
“After the Safe Schools initiative was launched in 1999 by the U.S. Department of Education, we began to see that children and teens who have experienced prolonged ...
Holographic 3D printing has the potential to revolutionize multiple industries, say Concordia researchers
2024-10-08
Researchers at Concordia have developed a novel method of 3D printing that uses acoustic holograms. And they say it’s quicker than existing methods and capable of making more complex objects.
The process, called holographic direct sound printing (HDSP), is described in a recent article in the journal Nature Communications. It builds on a method introduced in 2022 that described how sonochemical reactions in microscopic cavitations regions — tiny bubbles — create extremely high temperatures and pressure for trillionths of a second to harden resin into complex ...
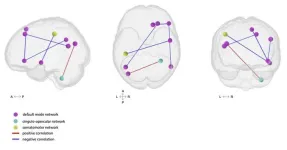
Cerebral blood flow and arterial transit in older adults
2024-10-08
“ATT may be more sensitive to age-related decline than CBF, and therefore useful for early detection and management of cerebrovascular impairment.”
BUFFALO, NY- October 8, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 18 on September 18, 2024, entitled, “Determinants of cerebral blood flow and arterial transit time in healthy older adults.”
This research paper highlights that brain health deteriorates with ...
How diabetes risk genes make cells less resilient to stress
2024-10-08
The cells in your pancreas, like people, can only handle so much stress before they start to break down. Certain stressors, such as inflammation and high blood sugar, contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes by overwhelming these cells.
Researchers at The Jackson Laboratory (JAX) have now discovered that DNA sequence changes known to increase a person’s risk for diabetes are linked to how well pancreatic cells can handle two different kinds of molecular stress. In people with these DNA changes, the insulin-producing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New PET imaging study reveals how ketamine relieves treatment-resistant depression
New study reveals differences between anime bamboo muzzle and actual bamboo
The ‘Great Texas Freeze’ killed thousands of purple martins; biologists worry recovery could take decades
Cancer has a unique nuclear metabolic fingerprint
Tiny thermometers offer on-chip temperature monitoring for processors
New compound stops common complications after intestinal surgery
Breaking through water treatment limits with defect-free, high-efficiency next-generation ceramic filters!
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
[Press-News.org] NOAA awards grant to enhance decision-ready climate projections for diverse stakeholdersUniversity of Miami scientists will lead a four-year, first-of-its-kind collaborative project