(Press-News.org) The key to more accurate rainfall predictions may lie in the intricate dance of falling snowflakes, a new study has found.
The research, observing the physical motion of falling ice crystals, will help scientists better estimate where and when these crystals will melt into raindrops, a crucial stage in the formation of many types of rain.
Published today (Thursday 10 October) in the journal Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, the study involved scientists watching how fake snowflakes fell in a substance imitating the atmosphere.
Jennifer Stout, who led the research, said: "Watching snow gently falling can be mesmerising, so it has been a joy to uncover the ways in which different ice crystal shapes pirouette and zigzag on their downwards journey.
“Understanding the dance of a snowflake is not only beautiful but can help us understand the reflectivity of clouds. Each snow crystal in a cloud acts like a tiny mirror, reflecting and refracting the light that passes through it. By predicting the choreography of an entire cloud, we could better improve our understanding of the atmosphere and the processes which lead to rain and snow. This intricate coordination of snowflakes can also create a big visual impact, causing stunning phenomena such as sun dogs and ice halos."
3D printed snowflakes
The research team used 3D-printed "snowflakes" of various shapes and sizes, from simple hexagonal plates to complex multi-branched dendrites. These artificial crystals were dropped through a tank filled with a water-glycerine mixture, simulating atmospheric conditions. High-speed cameras captured their descent, allowing researchers to reconstruct their three-dimensional trajectories and orientations.
The study revealed four main types of ice crystal motion: stable (falling straight down), zigzag (swinging back and forth), transitional (a mix of zigzag and spin), and spiralling (rotating while falling). Surprisingly, complex shapes like dendrites remained stable in motion despite their tendency to create turbulence in their wake, while simpler shapes became unstable much earlier.
Improving rain forecasts
These discoveries have significant implications for weather forecasting. Weather radar, which plays a key role in observing oncoming rain, bounces signals off water and ice particles in the air. With better understanding of how different ice crystal shapes move and orient themselves, meteorologists can interpret these radar signals more accurately, and better estimate when ice becomes rain. This more detailed data can lead to improved predictions of when, where and how much rain will fall.
The study's findings may also potentially improve scientists’ understanding of how clouds reflect sunlight and trap heat in the atmosphere, with the potential to improve climate models and longer-term weather predictions.
END
Snowflake dance analysis could improve rain forecasts
2024-10-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ASPB welcomes Hong Ma as Society President
2024-10-09
ASPB is delighted to welcome its new President, Hong Ma, who was elected in 2023 as President-elect and served in this role starting October 1, 2023. He stepped into his role as ASPB President on October 1, 2024 following the end of now-Past President Leeann Thornton’s term.
“A top priority is to support and train young plant biologists toward becoming members of a community with greater diversity, to amplify the voices of diverse members of our society, and to promote diversity and representation in society leadership and society activities,” ...
Can advanced AI can solve visual puzzles and perform abstract reasoning?
2024-10-09
Artificial Intelligence has learned to master language, generate art, and even beat grandmasters at chess. But can it crack the code of abstract reasoning—those tricky visual puzzles that leave humans scratching their heads? Researchers at USC Viterbi School of Engineering Information Sciences Institute (ISI) are putting AI’s cognitive abilities to the test, pushing the multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) to solve visual problems once reserved for human IQ tests. The result? A glimpse into how far AI has come—and where it still stumbles.
USC Viterbi ISI Research ...
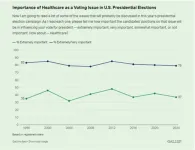
West Health-Gallup poll: Healthcare may be sleeper issue in U.S. presidential campaign
2024-10-09
WASHINGTON, D.C. – Oct. 9, 2024 – Though in this year’s presidential election healthcare has seemingly taken a back to other issues including the economy and democracy, nearly eight in 10 registered voters still say the issue that has been critical in nearly every presidential campaign in modern history, remains extremely (37%) or very important (42%) to whom they cast their vote, according to a new a West Health-Gallup poll of voters. This sentiment is consistent with what’s been expressed in most previous elections, although slightly more ...
UC Irvine scientists track and analyze lofted embers that cause spot fires
2024-10-09
Irvine, Calif., Oct. 9, 2024 — In the chaos of a wildfire, heat, wind, flames and fuel interact to produce embers that are lofted into surrounding areas, starting new spot fires and spreading destruction and property loss in California’s wildland-urban interface. Researchers at the University of California, Irvine have conducted first-of-their-kind field experiments to better understand the physics of these firebrands, and their results can help authorities better model the outcomes of disasters that are happening with greater frequency in a warming climate.
In a paper published recently in the journal Physics of Fluids, UC Irvine team members describe their ...
Uncovering pandemic inequities
2024-10-09
More than four years after the COVID-19 pandemic caused the world to come to a standstill, lessons in pandemic response are still being learned. What we know: the global pandemic disproportionately affected racial and ethnic minority groups across the U.S., with Black and Hispanic individuals being three to four times more likely to die from COVID compared to white individuals.
Daniel Harris, Assistant Professor of Epidemiology in the University of Delaware's College of Health Sciences (CHS), took a deep dive into rarely obtained COVID-19 ...
Microbiome researcher awarded NIH Transformative Research Award to pursue personalized treatment for gut diseases
2024-10-09
Baylor University researcher Aaron Wright, Ph.D., has earned a $5.6 million National Institutes of Health (NIH) Director’s Transformative Research Award for a project that he and collaborators hope could lead to personalized – and revolutionary – treatments for gut microbiome diseases like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s, Ulcerative Colitis and more. Wright, a nationally recognized microbiome researcher and chemical biologist who serves as The Schofield Endowed Chair in Biomedical Science in Baylor’s Department of Biology, will partner on the project with colleagues from Weill ...
Teresa Bowman, Ph.D., named Chair of Developmental & Molecular Biology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine
2024-10-09
October 9, 2024—(BRONX, NY)—Stem cell researcher Teresa Bowman, Ph.D., has been appointed chair of the department of developmental & molecular biology (DMB) at Albert Einstein College of Medicine after a comprehensive national search. Dr. Bowman will begin her new role on December 1, following the longtime leadership of Richard Stanley, Ph.D.
“Dr. Bowman has demonstrated her leadership abilities, commitment to mentorship, and dedication to the College of Medicine since she ...
Legal system fails to protect people from malicious copyright cases at the cost of sexual privacy, study warns
2024-10-09
Changes need to be made to the UK legal system to protect people from exploitative litigation designed to prey on vulnerabilities, a new study warns.
Reforms need to be made to protect adults from unfairness during copyright enforcement legal proceedings. This would also help to prevent children being exposed to adult pornography online.
The malicious litigation typically involves copyright holders or their agents of online pornographic works obtaining contact details of internet users via a court order to ...
Ancient climate analysis reveals unknown global processes
2024-10-09
According to highly cited conventional models, cooling and a major drop in sea levels about 34 million years ago should have led to widespread continental erosion and deposited gargantuan amounts of sandy material onto the ocean floor. This was, after all, one of the most drastic climate transitions on Earth since the demise of the dinosaurs.
Yet a new Stanford review of hundreds of studies going back decades contrastingly reports that across the margins of all seven continents, little to no sediment has ever been found dating back to this transition. The discovery of this globally extensive gap in the geologic record was published this week in Earth-Science Reviews.
“The ...
Gene therapy shows long-term benefit for patients with a rare pediatric brain disease
2024-10-09
Cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy (CALD) is a rare progressive, genetic brain disease that primarily presents in young boys, causing loss of neurological function and ultimately leading to early death. Researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, Boston Children’s Hospital, and collaborators have shown that six years after treatment with the first gene therapy approved for CALD, 94 percent of patients have had no decline in neurological functioning, with over 80 percent remaining free of major disability. Findings, published in two articles in the New England Journal of Medicine, describe long-term outcomes ...