(Press-News.org) Seven New Frog Species Discovered in Madagascar: Sounds Like Something from Star Trek
An international team of researchers have discovered seven new species of tree frogs that make otherworldly calls in the rainforests of Madagascar. Their strange, high-pitched whistling calls sound more like sound effects from the sci-fi series Star Trek. As a result, the researchers have named the new species after seven of the series' most iconic
If you think all frogs croak, you’d be wrong. Seven newly discovered species from the tree frog genus Boophis, found across the rainforests of Madagascar, emit special bird-like whistling sounds in their communication with other frogs.
These whistling sounds reminded the research team, led by Professor Miguel Vences of the Technische Universität Braunschweig, Germany, of Star Trek, where similar whistle-like sound effects are frequently used.
“That’s why we named the frogs after Kirk, Picard, Sisko, Janeway, Archer, Burnham, and Pike—seven of the most iconic captains from the sci-fi series,” says Professor Vences.
“Not only do these frogs sound like sound-effects from Star Trek, but it seems also fitting that to find them, you often have to do quite a bit of trekking! A few species are found in places accessible to tourists, but to find several of these species, we had to undertake major expeditions to remote forest fragments and mountain peaks. There’s a real sense of scientific discovery and exploration here, which we think is in the spirit of Star Trek,” explains Assistant Professor Mark D. Scherz from the Natural History Museum of Denmark at the University of Copenhagen, who was senior author on the study.
To Drown Out the Sound of Water
The otherworldly calls of these frogs are known as "advertisement calls"—a type of self-promotion that, according to the researchers, may convey information about the male frog’s suitability as a mate to females. This particular group live along fast-flowing streams in the most mountainous regions of Madagascar—a loud background that may explain why the frogs call at such high pitches.
For fans of Star Trek, some of the frog calls might remind them of sounds from the so-called ‘boatswain whistle’ and a device called the ‘tricorder.’ To others, they might sound like a bird or an insect.
“If the frogs just croaked like our familiar European frogs, they might not be audible over the sound of rushing water from the rivers they live near. Their high-pitched trills and whistles stand out against all that noise,” explains Dr Jörn Köhler, Senior Curator of Vertebrate Zoology at the Hessisches Landesmuseum Darmstadt, Germany, who played a key role in analyzing the calls of the frogs.
“The appearance of the frogs has led to them being confused with similar species until now, but each species makes a distinctive series of these high-pitched whistles, that has allowed us to tell them apart from each other, and from other frogs,” he says.
The calls also lined up with the genetic analysis the team performed.
Vulnerable to Climate Change
Madagascar is renowned for its immense biodiversity, and research in its rainforests continues to uncover hidden species, making it a true paradise for frogs. Madagascar, an island roughly the size of France, is home to about 9% of all the world’s frog species.
“We’ve only scratched the surface of what Madagascar’s rainforests have to offer. Every time we go into the forest, we find new species, and just in terms of frogs, there are still several hundred species we haven’t yet described,” says Professor Andolalao Rakotoarison of the Université d’Itasy in Madagascar. Just in the last ten years, she and the rest of this team have described around 100 new species from the island.
The researchers behind the discovery hope that this new knowledge will strengthen conservation efforts in Madagascar’s rainforests. The species often live in close geographic proximity but at different altitudes and in different microhabitats. This division makes them particularly vulnerable to changes in climate or the environment.
Thus, the research team urges greater awareness around the conservation of Madagascar’s biodiversity to ensure that these unique species and their habitats are preserved for the future. But they also hope to continue exploring, to seek out new species in forests where no scientist has gone before.
END
Seven new frog species discovered in Madagascar: sounds like something from Star Trek
An international team of researchers have discovered seven new species of tree frogs that make otherworldly calls in the rainforests of Madagascar. Their strange, high-pitched whistling calls sound more like sound effects from the sci-fi series Star Trek.
2024-10-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New temperatures in two thirds of key tropical forest
2024-10-15
Two thirds of Key Biodiversity Areas (KBAs) in tropical forests are experiencing new temperature conditions as our climate changes, research shows.
KBAs identify the most important places on Earth for species and their habitats.
The new study – by Exeter, Manchester Metropolitan and Cambridge universities – assessed 30 years of temperature conditions below the forest canopy in KBAs in tropical forests worldwide.
It found that 66% of KBAs in tropical forests have recently transitioned to new “temperature regimes” (more than 40% of temperature measurements being outside the range previously recorded ...
Fearful memories of others seen in mouse brain
2024-10-15
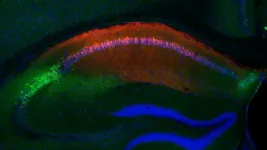
NEW YORK, NY — How do we distinguish threat from safety? It’s a question important not just in our daily lives, but for human disorders linked with fear of others, such as social anxiety or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The microscope image accompanying this press release, from the laboratory of Steven A. Siegelbaum, PhD, at Columbia’s Zuckerman Institute, displays a powerful technique scientists used to help us find an answer.
The scientists were investigating the hippocampus, a brain area that plays a key role in memory in humans and mice. Specifically, they focused on the CA2 region, which is ...
Rangers lead ground-breaking effort to monitor Uganda's lion population in critical stronghold
2024-10-15
In a new study published in Nature Communications Biology, wildlife rangers from the Uganda Wildlife Authority have demonstrated their ability to generate precise and reliable data on lion populations in Uganda’s Nile Delta, a critical stronghold for African lions.
The study reveals that wildlife rangers, a critical component of global conservation efforts but often underutilised in scientific research, can play a pivotal role in the conservation science surrounding the world’s most beloved big cat.
Rangers are effective at monitoring lions and are an underutilised resource
The study showed rangers ...
Modern mass extinction in an Ecuadorean cloud forest found to be a mirage
2024-10-15
One of the most notorious mass extinction events in modern times occurred on a hilltop in coastal Ecuador in the 1980s. Ninety species of plants known from nowhere else on Earth—many of them new to science and not yet given a name—went extinct when the last cloud forests of the Centinela range were cleared for agriculture. The cautionary tale of Centinela has long been a driving force in the fight to save the world’s rainforests. But did it really happen?
In a new study published in Nature Plants, an international team of botanists reveals that, indeed, it did not happen. The researchers – who spent years of scouring natural history museums, biodiversity databases, ...
HLA-DRB1*01:03 and severe ulcerative colitis
2024-10-15
About The Study: Among individuals with ulcerative colitis, the allele HLA-DRB1*01:03 was associated with severe ulcerative colitis requiring major operation, hospitalization, and systemic corticosteroid use compared with less severe disease. HLA-DRB1*01:03 has previously been linked to ulcerative colitis incidence. This study supports earlier, targeted genetic studies comparing patients with healthy controls reporting an association with total disease and severe disease requiring colectomy.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Marie Vibeke Vestergaard, MSc, email marievv@dcm.aau.dk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our ...
Quantum leap in suicide prevention: Professor Philippe Courtet's visionary approach unveiled in Genomic Press Interview
2024-10-15
Montpellier, France – 15 October 2024. In a captivating Genomic Press Interview published on October 15, 2024, in the peer-reviewed journal Genomic Psychiatry (Genomic Press), Professor Philippe Courtet shares groundbreaking perspectives on suicide prevention and mental health care. As an influential PU-PH (Professeur des Universités-Praticien Hospitalier), he is a Professor of Psychiatry at the University of Montpellier, France, and head of emergency psychiatry at the University Hospital of, Professor Courtet stands at the forefront of ...
Need for streamlined miscarriage care in Canada
2024-10-15
Miscarriage, or early pregnancy loss, can have devastating emotional effects, but it is poorly managed in Canada. A review published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231489 provides guidance to physicians on how to diagnose and manage this condition and calls for referral to outpatient early pregnancy assessment clinics (EPACs) as well as a compassionate approach.
October 15 is Pregnancy and Infant Loss Remembrance Day.
Data suggest that 15%–20% of all confirmed pregnancies result in miscarriage, with ...
Traces of ancient immigration patterns to Japan found in 2000-year-old genome
2024-10-15
A joint research group led by Jonghyun Kim and Jun Ohashi of the University of Tokyo has demonstrated that the majority of immigration to the Japanese Archipelago in the Yayoi and Kofun periods (between 3000 BCE and 538 CE) came from the Korean Peninsula. The researchers analyzed the complete genome of a “Yayoi” individual and found that, among the non-Japanese populations, the results bore the most similarity to Korean populations. Although it is widely accepted that modern Japanese populations have a dual ancestry, the discovery provides insight into the details of immigration patterns to the ...
Countries that choose to do so can reduce premature death by half, researchers say
2024-10-14
DURHAM, N.C. -- Since 1970, 37 countries have cut the probability of their citizens dying before they reach age 70 in half, a milestone that signals the remarkable progress many countries have made in preventing and treating disease. But a new report argues that this goal isn’t out of reach for any country that chooses to cut its premature mortality, even those afflicted by war or poverty.
The report, published Oct. 14 by The Lancet Commission on Investing in Health, lays out a roadmap for every nation that chooses to do so to cut ...
50 by 50—How can we reduce the probability of dying before age 70 by 50% globally by 2050?
2024-10-14
A team of 50 leading international experts, the Lancet Commission on Investing in Health (CIH), explored this question, resulting in clear, actionable, and achievable measures for achieving this ambitious goal worldwide. Six of the 50 commission members are affiliated with the Bergen Centre for Ethics and Priority Setting in Health (BCEPS), a Norwegian Centre of Excellence based at the University of Bergen, Norway, including BCEPS Director and Professor Ole Frithjof Norheim, BCEPS PhD Research Fellow Sarah Bolongaita, and BCEPS-affiliated researchers Angela Chang (University ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
[Press-News.org] Seven new frog species discovered in Madagascar: sounds like something from Star TrekAn international team of researchers have discovered seven new species of tree frogs that make otherworldly calls in the rainforests of Madagascar. Their strange, high-pitched whistling calls sound more like sound effects from the sci-fi series Star Trek.