Advanced liver fibrosis predicts liver outcomes in biopsy-proven metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
2024-10-25
(Press-News.org) Background and Aims
Data regarding risk factors and long-term outcomes of U.S. patients with biopsy-proven metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) are limited. This study aimed to investigate the role of clinical and histologic risk factors on long-term outcomes in patients with MASLD.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study of 451 adults with biopsy-proven MASLD was conducted at a U.S. academic hospital from 2012 to 2020. An experienced pathologist evaluated the index liver biopsy. Patients with a prior liver transplant or alternative etiologies of chronic liver disease were excluded. The duration of the risk exposure was determined from the date of the index liver biopsy to an outcome event or the last follow-up examination. Outcome events of interest included incident liver-related events, liver decompensation, and all-cause mortality.
Results
In the final cohort of 406 patients followed for a median of 3.7 years (interquartile range: 4.8 years), 35 patients died, 41 developed hepatic decompensation, and 70 experienced a liver-related event. Among histologic risk factors, stage 3 (adjusted Hazard ratio (aHR) 2.68, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.18–6.11) and stage 4 (aHR 6.96, 95% CI 3.55–13.64) fibrosis were associated with incident liver-related events compared to stage 0–1 fibrosis. Stage 4 (aHR 8.46, 95% CI 3.26–21.99) fibrosis alone was associated with incident liver decompensation events compared to stage 0–1 fibrosis. Among clinical risk factors, hypertension (aHR 2.58, 95% CI 1.05–6.34) was associated with incident liver decompensation.
Conclusions
In a U.S. single-center cohort of patients with biopsy-proven MASLD, advanced fibrosis was the primary risk factor for incident liver decompensation and liver-related events.
Full text
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2310-8819/JCTH-2024-00189
The study was recently published in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology.
The Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology (JCTH) is owned by the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University and published by XIA & HE Publishing Inc. JCTH publishes high quality, peer reviewed studies in the translational and clinical human health sciences of liver diseases. JCTH has established high standards for publication of original research, which are characterized by a study’s novelty, quality, and ethical conduct in the scientific process as well as in the communication of the research findings. Each issue includes articles by leading authorities on topics in hepatology that are germane to the most current challenges in the field. Special features include reports on the latest advances in drug development and technology that are relevant to liver diseases. Regular features of JCTH also include editorials, correspondences and invited commentaries on rapidly progressing areas in hepatology. All articles published by JCTH, both solicited and unsolicited, must pass our rigorous peer review process.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-25
Water is synonymous with life, but the dynamic, multifaceted interaction that brings H2O molecules together – the hydrogen bond – remains mysterious. Hydrogen bonds result when hydrogen and oxygen atoms between water molecules interact, sharing electronic charge in the process. This charge-sharing is a key feature of the three-dimensional ‘H-bond’ network that gives liquid water its unique properties, but quantum phenomena at the heart of such networks have thus far been understood only through theoretical simulations.
Now, researchers led by Sylvie Roke, head of the Laboratory for Fundamental BioPhotonics in EPFL’s School of Engineering, ...
2024-10-25
Subtle temperature differences at the ocean surface allow more carbon dioxide (CO₂) to be absorbed, new research shows.
Scientists studied the “ocean skin” – a sliver less than 2 mm deep at the ocean surface that is fractionally cooler than the rest.
Theoretical and lab work have suggested this temperature difference should increase the amount of CO₂ absorbed by the ocean – but this had never been successfully observed at sea before.
The new study – led by researchers from the University of Exeter’s Penryn Campus in Cornwall – used precision measurements to confirm that the ...
2024-10-25
URBANA, Ill. — Invasive silver carp have been spreading throughout the Mississippi River Basin since their introduction a half-century ago. Yet, try as they might, the fish have not advanced beyond a particular stretch of the Illinois River north of Kankakee. Research from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign shows the fish are likely avoiding contaminants from the Chicago Area Waterway, which flows south before petering out around Kankakee.
A new study, published today in Scientific Reports, shows silver carp change their behavior and metabolism when introduced to water from the Illinois River north of Kankakee, representing Chicago-area water.
“When animals ...
2024-10-25
Imagine trying to settle into a new home while constantly being attacked. That’s what the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa faces when it infects the lungs, and it can’t both spread and protect itself from antibiotics at the same time. Nonetheless, it’s one of the top culprits in hospital-acquired infections and it’s notorious for causing long-lasting, antibiotic-resistant infections, causing damage especially in people with lung diseases like cystic fibrosis, COPD, or bronchiectasis.
To survive tough conditions, P. aeruginosa forms colonies ...
2024-10-25
University of Oxford researchers have made a significant step towards realising miniature, soft batteries for use in a variety of biomedical applications, including the defibrillation and pacing of heart tissues. The work has been published today in the journal Nature Chemical Engineering.
The development of tiny smart devices, smaller than a few cubic millimeters, demands equally small power sources. For minimally invasive biomedical devices that interact with biological tissues, these power sources must be fabricated from soft materials. Ideally, these should ...
2024-10-25
FINDINGS
UCLA scientists have identified the protein GPNMB as a critical regulator in the heart’s healing process after a heart attack.
Using animal models, they demonstrate that bone marrow-derived immune cells called macrophages secrete GPNMB, which binds to the receptor GPR39, promoting heart repair. These findings offer a new understanding of how the heart heals itself and could lead to new treatments aimed at improving heart function and preventing the progression to heart failure.
BACKGROUND
Every 40 seconds, ...
2024-10-25
News coverage of the 2024 election season has often centered on how partisan division has affected our politics. But a new analysis shows that political polarization also poses significant health risks—by obstructing the implementation of legislation and policies aimed at keeping Americans healthy, by discouraging individual action to address health needs, such as getting a flu shot, and by boosting the spread of misinformation that can reduce trust in health professionals.
“Compared to other high-income countries, the United States has a disadvantage when it comes to the health of its citizens,” ...
2024-10-25
**EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL OCT. 25 AT 5 A.M. ET**
A newly described stage of a lymph node-like structure seen in liver tumors after presurgical immunotherapy may be vital to successfully treating patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, according to a study by researchers from the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
The study, published Oct. 25 in Nature Immunology, provides new information about lymph node-like structures called tertiary lymphoid structures. These structures, which are highly organized ...
2024-10-25
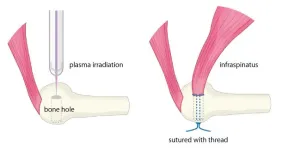
The human body, filled with muscles and moving parts, is far from indestructible. Injuries are common, especially where tendons and bones connect. In Japan, rotator cuff tears affect approximately 1 in 4 people over age 50, and reports state that even after surgery, about 20% of cases result in re-tears. To combat this, new healing methods to bolster current clinical practices are needed.
Graduate student Katsumasa Nakazawa, Associate Professor Hiromitsu Toyoda, and then Professor Hiroaki Nakamura at Osaka Metropolitan University’s ...
2024-10-25
San Diego, CA (October 24, 2024) — Investigators recently uncovered key insights into newly defined rejection entities in kidney transplantation that may offer improved patient risk categorization post-transplant. The research will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2024 October 23– 27.
Kidney transplant rejection continues to threaten the long-term success of kidney transplants, with microvascular inflammation (inflammation within capillaries) playing a pivotal role in graft failure. Due to its complex nature, this inflammation poses a major challenge in clinical practice. In response, the international Banff classification—the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Advanced liver fibrosis predicts liver outcomes in biopsy-proven metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease