(Press-News.org) Like people, birds have fewer friends as they age, but the reasons why are unclear. New research suggests they may just have no drive to.
In humans, it’s often been assumed that older people have fewer friends because they’re pickier about who they spend their time with. There’s also the issue that there are fewer people of their own age around.
But it’s hard to pick apart the various potential causes for humans, so researchers have turned to animals. The team behind the new research, led by Imperial College London, studied an isolated population of sparrows on the island of Lundy, in the Bristol Channel.
By mapping the ages and social networks of all the birds, they found that older sparrows do tend to have fewer friends, as with humans. The reason could be that there is no ‘evolutionary pressure’ to do so: while friendliness helps younger birds survive and breed more successfully, the same isn’t true for older birds.
Lead researcher Dr Julia Schroeder, from the Department of Life Sciences (Silwood Park) at Imperial, said: “This evolutionary mechanism may also be at work in humans – it could be that older people are less inclined to new friends as they age. Combined with fewer same-age potential friends available, this could be a factor in the loneliness crisis among older people.”
Co-author Dr Jamie Dunning, now at the University of Leeds, explained: “Our study is one of the first to suggest that birds, like mammals, also reduce the size of their social network as they age. Specifically, the number of friendships, and how central a bird is to the wider social network, declined with age.”
The study is published today in Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, in a special issue of the journal on understanding age and society using natural populations.
Changing with age
Lundy Island hosts a ‘closed’ population of sparrows, meaning that no individuals leave or arrive on the island. This allows the team to collect lots of accurate data on the inhabitants, including their ages, breeding success, and social networks, which have been recorded for 25 years.
Previous research from the team showed that being friendly (especially with the opposite sex) helps sparrows on the island breed successfully, showing that when they’re young, having a good social network is an advantage.
In the new study, the researchers looked at the other end of life, to see if friendliness is still a benefit. They found that, rather than having a benefit, the lack of friendliness simply seems to be of no cost.
Dr Schroeder explained: “’Friendliness’, at least for sparrows, may change with age. When they’re young, it helps them to make friends, giving them an evolutionary ‘benefit’. But once they’ve reproduced, it seems like being unfriendly has no evolutionary ‘cost’ – there are no downsides that mean those genes wouldn’t be passed on.”
There are parallels in humans for age-related conditions like Parkinson’s – while diseases like this clearly do have a cost for the individual, since they only occur after reproduction, they are passed on to offspring anyway, so there is no mechanism for evolution to lose those genes.
Dr Schroeder said: “Ultimately, the study of friendliness with age – whether it be in sparrows or humans – may help us understand how to help older people make new friends, and reduce the burden of loneliness.”
END
No incentive for older birds to make new friends
2024-10-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Development and validation of a new prognostic model for predicting survival outcomes in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure
2024-10-27
Background and Aims
Early determination of prognosis in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is crucial for optimizing treatment options and liver allocation. This study aimed to identify risk factors associated with ACLF and to develop new prognostic models that accurately predict patient outcomes.
Methods
We retrospectively selected 1,952 hospitalized patients diagnosed with ACLF between January 2010 and June 2018. This cohort was used to develop new prognostic scores, which were subsequently validated in external groups.
Results
The study included 1,386 ACLF patients and identified six independent ...
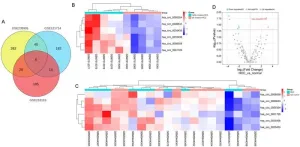
Identification and validation of the Hsa_circ_0001726/miR-140-3p/KRAS axis in hepatocellular carcinoma based on microarray analyses and experiments
2024-10-27
Background and Aims
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most fatal malignancies. Epigenetic mechanisms have revealed that noncoding RNAs, such as microRNAs (miRNAs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs), are involved in HCC progression. This study aimed to construct a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in HCC and validate one axis within the network.
Methods
HCC-related transcriptome data were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus, and HCC-related genes were sourced from GeneCards to identify differentially expressed circRNAs and miRNAs. ...
New study warns that melting Arctic sea-ice could affect global ocean circulation
2024-10-27
“Our finding that enhanced melting of Arctic sea-ice likely resulted in significant cooling in northern Europe in the earth’s past is alarming,” says Mohamed Ezat from the iC3 Polar Research Hub, lead author of the new study. “This reminds us that the planet’s climate is a delicate balance, easily disrupted by changes in temperature and ice cover.”
Ice-free summer conditions are expected to occur in the Arctic Ocean from the year 2050 onwards.
Earlier this ...
Researchers test imlifidase enzyme versus plasma exchange in removing donor-specific antibodies in kidney transplant rejection trial
2024-10-27
San Diego, CA (October 26, 2024) — For kidney transplant recipients experiencing antibody-mediated rejection, the current standard of care involves removing donor-specific antibodies (DSAs) through plasmapheresis (PLEX)—a procedure that removes antibodies from the plasma portion of the blood. Results from a recent clinical trial reveal that an investigational drug called imlifidase, which cleaves and inactivates the type of antibodies that include DSAs, is more effective than PLEX. The research will be presented at ASN Kidney ...
Preclinical studies test novel gene therapy for treating IgA nephropathy
2024-10-26
San Diego, CA (October 26, 2024) — IgA nephropathy is an autoimmune kidney disease, and complement, a component of the innate immune system, plays a role in the condition’s pathogenesis. Investigators have developed and tested a novel gene therapy that enters kidney cells and enables them to block complement activation. The research will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2024 October 23– 27.
The gene therapy, called PS-002, uses a modified virus to treat kidney cells called podocytes. Administration of PS-002 in a mouse model of IgA nephropathy reduced signs of kidney dysfunction, lowered complement ...
Trial assesses antibody therapy for chronic active antibody-mediated kidney transplant rejection
2024-10-26
San Diego, CA (October 26, 2024) — Chronic active antibody-mediated rejection (caAMR) is a common cause of allograft loss after transplantation, with no approved therapies. Clazakizumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6), stabilized kidney transplant recipients’ kidney function in a phase 2 trial. Investigators now have data from a phase 3 trial with clazakizumab. The findings from the Phase 3 IMAGINE trial, the largest placebo-controlled study in kidney transplant recipients with caAMR, will be ...
High-impact clinical trials generate promising results for improving kidney health: Part 2
2024-10-26
The results of numerous high-impact phase 3 clinical trials that could affect kidney-related medical care will be presented in-person at ASN Kidney Week 2024 October 23–27.
Hyponatremia, or a chronically low blood salt level, is the most common electrolyte disorder in hospitalized patients, and is associated with higher risks of death and re-hospitalization. In a recent trial, 2,173 hospitalized patients with hyponatremia from 9 centers across Europe were assigned to undergo either targeted correction of blood salt levels according to guidelines or to receive routine care for hyponatremia. The primary outcome was the combined ...
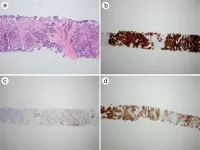
Expression of carbonic anhydrase IX as a novel diagnostic marker for differentiating pleural mesothelioma from non-small cell lung carcinoma
2024-10-26
Background and objectives
Mesothelioma is an aggressive tumor with a poor prognosis. Histological diagnosis of mesothelioma using limited tissue samples can be challenging. Carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) is a transmembrane protein that is overexpressed in a variety of solid tumors. This study aimed to investigate the clinical utility of CAIX expression in the differential diagnosis of pleural mesothelioma from non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC).
Methods
Unstained tissue microarray slides composed of 56 cases of pleural mesothelioma and 82 cases of NSCLC were subjected to immunohistochemical staining using a mouse anti-human antibody against CAIX.
Results
Of the 38 epithelioid mesothelioma ...
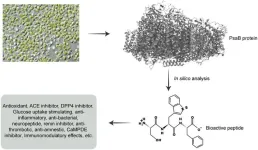
In silico assessment of photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A2 (PsaB) from Chlorella vulgaris (green microalga) as a source of bioactive peptides
2024-10-26
Background and objectives
Chlorella vulgaris is a green, photosynthetic microalga in the phylum Chlorophyta. The goal of our study was to perform a bioinformatics analysis of Photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A2, one of its photosynthesis-related proteins, and to hunt for potent bioactive peptides.
Methods
To generate peptides and estimate the safety and efficacy of each bioactive peptide, we employed the tools BIOPEP-UWM™, PeptideRanker, DBAASP, and ToxinPred. PepDraw was used to understand the physicochemical properties ...
Association between TLR10 rs10004195 gene polymorphism and risk of Helicobacter pylori infection
2024-10-26
Background and objectives
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection can cause multiple secondary digestive disorders. Some studies have found that polymorphisms in Toll-like receptor (TLR) genes, including TLR10 rs10004195, may be associated with increased susceptibility to H. pylori infection. Despite conflicting reports, we conducted a meta-analysis to clarify the relationship between these factors.
Methods
We conducted an exhaustive review, encompassing all relevant literature up to February 2024, using databases ...