(Press-News.org) AN EXPERT on missing persons and unidentified human remains is hoping her research can help bring about a change in the law.
Work carried out by Emma Tilley, who is completing her PhD in Criminology and Policing at University of Staffordshire, is included in a Law Commission public consultation on burial and cremation.
Emma, who has starred in Locate International’s Channel 4 documentary series The Body Detectives, has been critically reviewing the cross-matching of unidentified human remains and missing persons reports in England and Wales.
She has identified that there are currently around 800 unsolved cases involving unidentified bodies or body parts. She has also revealed that while 27 per cent of local authorities typically bury the bodies or remains of unidentified people, around a third are likely to cremate them as part of their duties under the Public Health Act 1984.
The consultation document reads: “Tilley notes the immense impact on families of a missing person, as they fluctuate between hope and hopelessness in a state of “ambiguous loss”. In her view, there would be substantial benefits to requiring burial rather than cremation for unidentified bodies and partial remains, where practicable.
“Such a rule would allow for exhumations to confirm the identity of the unidentified deceased person. It would also enable family members whose identity was established at a later date to make decisions about the body of their relative.”
Although burials are more costly and place pressure on space, the consultation noted that laws which allow the cremation of unidentified human remains were passed before DNA profiling and advancement of forensic science. It also makes the point that a rule which insists that unidentified remains must be buried would err on the side of caution in terms of respecting religious rights.
Based on Emma’s research, which finds that DNA sampling isn’t always carried out on unidentified human remains, the Law Commission are also proposing [Consultation Question 48] that before any burial, a DNA sample should be taken for storage on the national central database held by the UK Missing Person’s Unit.
Emma said: “It feels surreal to have the opportunity to potentially use my PhD findings to change law. It is more than I could have ever imagined! I have also updated my network of this, and the families of missing people I am in contact with, who are also unanimously support this proposed change in law.”
Under the consultation proposals, old graves could be reused and closed burial grounds could be reopened to help manage the shortage of burial space. The consultation addresses a wide range of other issues including uncollected ashes, siting of crematoria and burials on private land.
The Law Commission is inviting views from the public, experts and those involved in the death care sector before 9 January 2025. They will be making final recommendations to Government at the end of 2025.
Professor Nick Hopkins, Commissioner for Property, Family and Trust Law said: “Our proposals provide a significant opportunity to reform burial and cremation law and secure burial space for future generations. This must be done sensitively and with wider public support, which is why we want to hear from those with a view.”
Alex Davies-Jones, Parliamentary Under-Secretary of State at the Ministry of Justice said,“The Government is supportive of the Law Commission’s work and would encourage the public to take the time to respond to this consultation paper. We await with interest the Law Commission’s recommendations, in due course, on the most appropriate framework to provide modern, consistent regulation for burial and cremation.”
END
Change in the law could help families of missing persons
AN EXPERT on missing persons and unidentified human remains is hoping her research can help bring about a change in the law
2024-10-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Subtle eye movements optimize vision
2024-10-29
Our ability to see starts with the light-sensitive photoreceptor cells in our eyes. A specific region of the retina, termed fovea, is responsible for sharp vision. Here, the color-sensitive cone photoreceptors allow us to detect even the smallest details. The density of these cells varies from person to person. Additionally, when we fixate on an object, our eyes make subtle, continuous movements, which also differ between individuals. Researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the University of Bonn have now investigated how sharp vision is linked to these tiny eye movements and ...
Maternal health expert professor Vicki Clifton reveals placenta's hidden role in mental health
2024-10-29
Brisbane, Queensland, Australia (October 29, 2024) - In a revealing Genomic Press Interview published in Brain Medicine on October 29, 2024, Professor Vicki Clifton shares transformative discoveries about the placenta's unexpected influence on maternal mental health, potentially revolutionizing our understanding of pregnancy-related anxiety and depression.
Professor Clifton's team at the Mater Research Institute-University of Queensland has identified 13 distinct glucocorticoid receptor isoforms in the placenta, with one particular variant ...
From concert piano to fear memory research: Dr. Raül Andero Galí bridges mouse-human studies
2024-10-29
Barcelona, Spain (October 29, 2024) - In a compelling new Genomic Press Interview published in Brain Medicine, Dr. Raül Andero Galí reveals how his early passion for classical piano shaped his unique approach to neuroscience research. As an ICREA Research Professor at the Autonomous University of Barcelona, Dr. Andero Galí leads groundbreaking studies that connect mouse and human fear responses, potentially revolutionizing treatments for PTSD and anxiety disorders.
The intersection of stress and memory has captured Dr. Andero Galí's attention throughout his career. "All ...
Arctic whales research collaboration is signed by Heriot-Watt University and HX Expeditions (Hurtigruten Expeditions)
2024-10-29
Pioneering research to protect and conserve Arctic whale populations is to begin under a new five-year collaboration between Heriot-Watt University in Edinburgh, Scotland and HX Expeditions (Hurtigruten Expeditions), a world leader in travel exploration.
The partners have signed a five-year Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), beginning in 2024, to research challenges facing marine life in the high Arctic – the most northern part of the Arctic region and one of the world’s most fragile ecosystems.
The agreement will see Heriot-Watt University and HX work together on the Whales & Arctic Vessels Project (WAVE), ...
Scientists develop tool to predict sepsis in apparently healthy newborns
2024-10-29
A genetic signature in newborns can predict neonatal sepsis before symptoms even start to show, according to a new study.
The study, led by UBC and SFU researchers in collaboration with the Medical Research Council (MRC) Unit The Gambia, has the potential to help healthcare workers diagnose babies earlier, including in lower- and middle-income countries (LMICs) where neonatal sepsis is of particular concern. The research, published today in eBiomedicine, is funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
“Neonatal sepsis is caused by the body’s irregular response ...
AI algorithm accurately detects heart disease in dogs
2024-10-29
Researchers have developed a machine learning algorithm to accurately detect heart murmurs in dogs, one of the main indicators of cardiac disease, which affects a large proportion of some smaller breeds such as King Charles Spaniels.
The research team, led by the University of Cambridge, adapted an algorithm originally designed for humans and found it could automatically detect and grade heart murmurs in dogs, based on audio recordings from digital stethoscopes. In tests, the algorithm detected heart murmurs with a sensitivity ...
What animal societies can teach us about ageing
2024-10-29
Red deer may become less sociable as they grow old to reduce the risk of picking up diseases, while older house sparrows seem to have fewer social interactions as their peers die off, according to new research which shows humans are not the only animals to change our social behaviour as we age.
A collection of 16 studies, including six from the University of Leeds, have been published today as part of a special issue of the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, investigating ageing and society across the natural world.
One study into red deer shows that ...
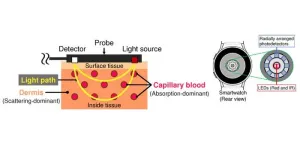
Enhancing the accuracy of wearables that measure blood glucose levels
2024-10-28
Diabetes is an increasingly pervasive disease, currently affecting over 500 million adults worldwide. Since there is as yet no cure for type 1 or type 2 diabetes, patients must regularly monitor their BGLs to keep them in check. Though BGL-measuring devices relying on painful finger pricks have been the gold standard for decades, modern technology is slowly opening doors to better alternatives.
Many researchers have proposed noninvasive methods to monitor BGLs using widely available wearable devices, such as smartwatches. For example, by placing the LEDs ...
Increasing social supports for new mothers with opioid use disorder
2024-10-28
Opioid use disorder (OUD) is a growing public health problem among pregnant and parenting people in the U.S. Between 1999 and 2014, the number of pregnant women with OUD increased by more than four times. This trend also coincides with a rise in pregnancy-associated maternal overdose mortality.
Researchers at Thomas Jefferson University, led by Meghan Gannon, PhD, MSPH, investigated how community-based supports, like doulas, can be integrated into health care for mothers who use opioids. Using a social network analysis, ...
Mitigating the neurotoxic effects of lead exposure
2024-10-28
Lead exposure is a risk to any human, but children are most vulnerable to the element’s neurotoxicity, which can lead to developmental delays, learning difficulties and mood changes among other symptoms. There has been some progress in reducing exposure and preventing neurotoxicity, but hundreds of thousands of American children are still affected.
A new study by Thomas Jefferson University neuroscientist Jay Schneider, PhD, suggests that the toxic effects of lead can be mitigated by attentive maternal care and an enriched environment ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Change in the law could help families of missing personsAN EXPERT on missing persons and unidentified human remains is hoping her research can help bring about a change in the law