(Press-News.org) A pitiful sound from tinny speakers, sad virtual eyes, trembling robot arms: it doesn’t take much to feel sorry for a robot. This is the conclusion of a study by Marieke Wieringa, who will be defending her PhD thesis at Radboud University on 5 November. But she warns that our human compassion could also be exploited: just wait until companies find a revenue model for emotional manipulation by robots.
Objectively, we know that a robot cannot experience pain. Still, under certain circumstances, people can be slightly more inclined to believe that a robot is in pain, provided they are manipulated in the right way. “If a robot can pretend to experience emotional distress, people feel guiltier when they mistreat the robot”, Wieringa explains.
Boring task or shaking robots
Through several tests, Wieringa and her colleagues studied how people respond to violence against robots. “Some participants watched videos of robots that were either mistreated or treated well. Sometimes, we asked participants to give the robots a shake themselves. We tried out all variations: sometimes the robot didn’t respond, sometimes it did – with pitiful sounds and other responses that we associate with pain.” In the tests, it soon appeared that the tormented robot triggered more pity: participants were less willing to shake the robot again. “If we asked the participants to shake a robot that showed no emotion, then they didn’t seem to have any difficulty with it at all.”
In one of the tests, the participants were asked to choose: complete a boring task or give the robot a shake. If participants chose to shake the robot for longer, it meant that they didn’t have to carry out the task for as long. “Most people had no problem shaking a silent robot, but as soon as the robot began to make pitiful sounds, they chose to do the boring task instead.”
Tamagotchi
Wieringa warns that it is just a question of time before organisations exploit emotional manipulation. “People were obsessed with Tamagotchis for a while: virtual pets that successfully triggered emotions. But what if a company made a new Tamagotchi that you had to pay to feed as a pet? That’s why I am calling for governmental regulations that establish when it’s appropriate for chatbots, robots and other variants to be able to express emotions.”
But Wieringa doesn’t think that a complete ban on emotions would be good either. “It’s true that emotional robots would have some advantages. Imagine therapeutic robots that could help people to process certain things. In our study, we saw that most participants found it good when the robot triggered pity: according to them, it signalled that violent behaviour is not OK. Still, we need to guard against risks for people who are sensitive to ‘fake’ emotions. We like to think we are very logical, rational beings that don’t fall for anything, but at the end of the day, we are also led by our emotions. And that’s just as well, otherwise we’d be robots ourselves.”
END
Can you feel sorry for a robot?
A pitiful sound from tinny speakers, sad virtual eyes, trembling robot arms: it doesn’t take much to feel sorry for a robotic buddy, research by Marieke Wieringa shows
2024-10-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Oceanographers record the largest predation event ever observed in the ocean
2024-10-29
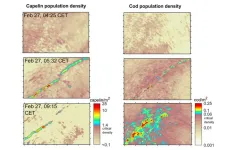
There is power in numbers, or so the saying goes. But in the ocean, scientists are finding that fish that group together don’t necessarily survive together. In some cases, the more fish there are, the larger a target they make for predators.
This is what MIT and Norwegian oceanographers observed recently when they explored a wide swath of ocean off the coast of Norway during the height of spawning season for capelin — a small Arctic fish about the size of an anchovy. Billions of capelin migrate each February from the edge of the Arctic ...
A molecular switch reshapes a dividing cell in minutes
2024-10-29
A living cell is a bustling metropolis, with countless molecules and proteins navigating crowded spaces in every direction. Cell division is a grand event which completely transforms the landscape. The cell starts behaving like the host of an international competition, reconfiguring entire streets, relocating buildings and rerouting its transportation systems.
For decades, researchers have been captivated by the cell's ability to organise such a dramatic transformation. Central to the process is the microtubule cytoskeleton, a network of fibres which provides structural support and facilitates movement within the cell, ensuring that chromosomes ...
Have we found all the major Maya cities? Not even close, new research suggests
2024-10-29
Using laser-guided imaging to peer through dense jungle forests, Tulane University researchers have uncovered vast unexplored Maya settlements in Mexico and a better understanding of the ancient civilization's extent and complexity.
The new research, published in the journal Antiquity, was led by Tulane University anthropology doctoral student Luke Auld-Thomas and his advisor, Professor Marcello A. Canuto.
The team used lidar, a laser-based detection system, to survey 50 square miles of land in Campeche, Mexico, an area largely overlooked by archaeologists. Their findings included evidence of more than 6,500 pre-Hispanic structures, including a previously unknown ...
Change in the law could help families of missing persons
2024-10-29
AN EXPERT on missing persons and unidentified human remains is hoping her research can help bring about a change in the law.
Work carried out by Emma Tilley, who is completing her PhD in Criminology and Policing at University of Staffordshire, is included in a Law Commission public consultation on burial and cremation.
Emma, who has starred in Locate International’s Channel 4 documentary series The Body Detectives, has been critically reviewing the cross-matching of unidentified human remains ...
Subtle eye movements optimize vision
2024-10-29
Our ability to see starts with the light-sensitive photoreceptor cells in our eyes. A specific region of the retina, termed fovea, is responsible for sharp vision. Here, the color-sensitive cone photoreceptors allow us to detect even the smallest details. The density of these cells varies from person to person. Additionally, when we fixate on an object, our eyes make subtle, continuous movements, which also differ between individuals. Researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the University of Bonn have now investigated how sharp vision is linked to these tiny eye movements and ...
Maternal health expert professor Vicki Clifton reveals placenta's hidden role in mental health
2024-10-29
Brisbane, Queensland, Australia (October 29, 2024) - In a revealing Genomic Press Interview published in Brain Medicine on October 29, 2024, Professor Vicki Clifton shares transformative discoveries about the placenta's unexpected influence on maternal mental health, potentially revolutionizing our understanding of pregnancy-related anxiety and depression.
Professor Clifton's team at the Mater Research Institute-University of Queensland has identified 13 distinct glucocorticoid receptor isoforms in the placenta, with one particular variant ...
From concert piano to fear memory research: Dr. Raül Andero Galí bridges mouse-human studies
2024-10-29
Barcelona, Spain (October 29, 2024) - In a compelling new Genomic Press Interview published in Brain Medicine, Dr. Raül Andero Galí reveals how his early passion for classical piano shaped his unique approach to neuroscience research. As an ICREA Research Professor at the Autonomous University of Barcelona, Dr. Andero Galí leads groundbreaking studies that connect mouse and human fear responses, potentially revolutionizing treatments for PTSD and anxiety disorders.
The intersection of stress and memory has captured Dr. Andero Galí's attention throughout his career. "All ...
Arctic whales research collaboration is signed by Heriot-Watt University and HX Expeditions (Hurtigruten Expeditions)
2024-10-29
Pioneering research to protect and conserve Arctic whale populations is to begin under a new five-year collaboration between Heriot-Watt University in Edinburgh, Scotland and HX Expeditions (Hurtigruten Expeditions), a world leader in travel exploration.
The partners have signed a five-year Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), beginning in 2024, to research challenges facing marine life in the high Arctic – the most northern part of the Arctic region and one of the world’s most fragile ecosystems.
The agreement will see Heriot-Watt University and HX work together on the Whales & Arctic Vessels Project (WAVE), ...
Scientists develop tool to predict sepsis in apparently healthy newborns
2024-10-29
A genetic signature in newborns can predict neonatal sepsis before symptoms even start to show, according to a new study.
The study, led by UBC and SFU researchers in collaboration with the Medical Research Council (MRC) Unit The Gambia, has the potential to help healthcare workers diagnose babies earlier, including in lower- and middle-income countries (LMICs) where neonatal sepsis is of particular concern. The research, published today in eBiomedicine, is funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
“Neonatal sepsis is caused by the body’s irregular response ...
AI algorithm accurately detects heart disease in dogs
2024-10-29
Researchers have developed a machine learning algorithm to accurately detect heart murmurs in dogs, one of the main indicators of cardiac disease, which affects a large proportion of some smaller breeds such as King Charles Spaniels.
The research team, led by the University of Cambridge, adapted an algorithm originally designed for humans and found it could automatically detect and grade heart murmurs in dogs, based on audio recordings from digital stethoscopes. In tests, the algorithm detected heart murmurs with a sensitivity ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
[Press-News.org] Can you feel sorry for a robot?A pitiful sound from tinny speakers, sad virtual eyes, trembling robot arms: it doesn’t take much to feel sorry for a robotic buddy, research by Marieke Wieringa shows