(Press-News.org) Anecdotes abound of wildlife behaving “drunk” after eating fermented fruits, but despite this, nonhuman consumption of ethanol has been assumed to be rare and accidental. Ecologists challenge this assumption in a review publishing October 30 in the Cell Press journal Trends in Ecology & Evolution. They argue that since ethanol is naturally present in nearly every ecosystem, it is likely consumed on a regular basis by most fruit- and nectar-eating animals.
“We're moving away from this anthropocentric view that ethanol is just something that humans use,” says behavioral ecologist and senior author Kimberley Hockings (@KJHockings) of the University of Exeter. “It's much more abundant in the natural world than we previously thought, and most animals that eat sugary fruits are going to be exposed to some level of ethanol.”
Ethanol first became abundant around 100 million years ago, when flowering plants began producing sugary nectar and fruits that yeast could ferment. Now, it’s present naturally in nearly every ecosystem, though concentrations are higher, and production occurs year-round in lower-latitude and humid tropical environments compared to temperate regions. Most of the time, naturally fermented fruits only reach 1%-2% alcohol by volume (ABV), but concentrations as high as 10.2% ABV have been found in over-ripe palm fruit in Panama.
Animals already harbored genes that could degrade ethanol before yeasts began producing it, but there is evidence that evolution fine-tuned this ability for mammals and birds that consume fruit and nectar. In particular, primates and treeshrews have adapted to efficiently metabolize ethanol.
“From an ecological perspective, it is not advantageous to be inebriated as you're climbing around in the trees or surrounded by predators at night—that's a recipe for not having your genes passed on,” says molecular ecologist and senior author Matthew Carrigan of the College of Central Florida. “It’s the opposite of humans who want to get intoxicated but don’t really want the calories—from the non-human perspective, the animals want the calories but not the inebriation.”
It’s unclear whether animals intentionally consume ethanol for ethanol’s sake, and more research is needed to understand its impact on animal physiology and evolution. However, the researchers say that ethanol consumption could carry several benefits for wild animals. First and foremost, it’s a source of calories, and the odorous compounds produced during fermentation could guide animals to food sources, though the researchers say it’s unlikely that animals can detect ethanol itself. Ethanol could also have medicinal benefits: fruit flies intentionally lay their eggs in substances containing ethanol, which protects their eggs from parasites, and fruit fly larvae increase their ethanol intake when they become parasitized by wasps.
“On the cognitive side, ideas have been put forward that ethanol can trigger the endorphin and dopamine system, which leads to feelings of relaxation that could have benefits in terms of sociality,” says behavioral ecologist and first author Anna Bowland of the University of Exeter. “To test that, we'd really need to know if ethanol is producing a physiological response in the wild.”
There are a lot of unanswered questions regarding the significance of ethanol consumption to wild animals. In their future research, the team plans to investigate the behavioral and social implication of ethanol consumption in primates and to more deeply examine the enzymes involved in alcohol metabolism.
###
This research was supported by the Primate Society of Great Britain, the Wenner-Gren Foundation, the Canada Research Chairs program, and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Trends in Ecology & Evolution, Bowland et al., “The evolutionary ecology of ethanol” https://cell.com/trends/ecology-evolution/fulltext/S0169-5347(24)00240-4
Trends in Ecology & Evolution (@Trends_Ecol_Evo), published by Cell Press, is a monthly review journal that contains polished, concise, and readable reviews and opinion pieces in all areas of ecology and evolutionary science. It aims to keep scientists informed of new developments and ideas across the full range of ecology and evolutionary biology—from the pure to the applied, and from molecular to global. Visit http://www.cell.com/trends/ecology-evolution. To receive Cell Press media alerts, please contact press@cell.com.
END
While pancreatic cancer rates are rising in people under age 50, a new survey conducted by The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James) shows most people continue to believe that pancreatic disease affects only the elderly – and that there is nothing they can do to reduce their risk.
For this survey, respondents were asked about risk factors for pancreatic cancer. More than half (53%) of adults under age 50 said they would not recognize the early signs or symptoms of the disease, and more than one third (37%) believe there is ...
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Oct. 30, 2024)—Many studies suggest that an earlier age at menopause is more detrimental to a woman’s health, leading to an increased risk for adverse health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, osteoporosis, and depression, among others. However, a new study is linking a later age at natural menopause with a greater risk for asthma. Results of the study are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
Asthma is a common, chronic disease affecting more than 300 million people worldwide. The prevalence of asthma ...
EMBARGOED: NOT FOR RELEASE UNTIL 00.05 (UK TIME) WEDNESDAY 30 OCTOBER 2024
An international team of paleobiologists have found that the sinuses of ocean dwelling relatives of modern-day crocodiles prevented them from evolving into deep divers like whales and dolphins.
A new paper published today [30 October] in Royal Society Open Science suggests that thalattosuchians, which lived at the time of the dinosaurs, were stopped from exploring the deep due to their large snout sinuses.
Whales and dolphins (cetaceans) ...
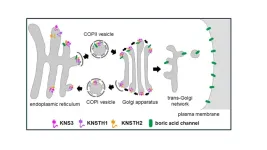
Botanists have come to understand the channels and transporters involved in the uptake and transport of nutrients, yet how are they positioned where they need to be?
For example, plants need boron, which is taken into the cells by molecules known as the boric acid channel. But how do the proteins that form the channel make it to the plasma membrane?
A research group led by Professor Junpei Takano of Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Agriculture identified a mutant line of Arabidopsis thaliana in which the boric acid channels are not properly transported to the plasma membrane. The cause was a deficiency in the protein KAONASHI3 (KNS3); the name ...
University of Cambridge media release
Britain’s brass bands older than we thought and invented by soldiers from the Napoleonic Wars, new study reveals
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 00:01 AM (UK TIME) ON WEDNESDAY 30TH OCTOBER 2024
Military musicians returning from the Napoleonic wars established Britain’s first brass bands earlier than previously thought, new research reveals. The study undermines the idea that brass bands were a civilian and exclusively northern creation.
It is widely believed that brass bands originated with coal miners and other industrial communities ...
The Lancet: Health threats of climate change reach record-breaking levels, as experts call for trillions of dollars spent on fossil fuels to be redirected towards protecting people’s health, lives and livelihoods
New global findings in the 8th annual indicator report of the Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change reveal that people in every country face record-breaking threats to health and survival from the rapidly changing climate, with 10 of 15 indicators tracking health threats reaching ...
Just one or two sessions of physical activity at the weekend—a pattern of exercise dubbed ‘weekend warrior’---may be just as likely to lower the risk of cognitive decline, which can often precede dementia, as more frequent sessions, concludes research published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
And it may be more convenient and achievable for busy people as well, suggest the researchers.
It’s important to identify potentially modifiable risk factors for dementia because a 5-year delay in onset might halve its prevalence, they say, adding that nearly all the evidence to date comes from studies ...
Physical activity of any intensity after a diagnosis of dementia is associated with around a 30% lower risk of death, finds research published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
The findings prompt the researchers to conclude that those affected should be encouraged to keep up or start an exercise routine, especially as average life expectancy after a diagnosis of dementia may be only around 4-5 years.
Previously published research has linked physical activity with a lower risk of death in people with the disease, but these studies have focused on a single point in time. So it’s not clear if changes in the amount or intensity of physical ...
Lifetime cannabis use is associated with several changes in brain structure and function in later life, suggests an observational study, but these associations may not be causal, finds a genetic analysis of the same data, published in the open access journal BMJ Mental Health.
Some other unidentified factors may explain the differences found, say the researchers, who nevertheless emphasise that further research is needed to fully understand the effects of heavy use and cannabis potency on the brain.
Cannabis use has increased worldwide following its ...
A new paper published today, led by Chicago’s Shedd Aquarium, reveals how volunteers across Illinois, Wisconsin and Michigan enabled researchers to gather seven years of data on the spawning migrations of suckers, an understudied yet essential group of freshwater fishes. Using observations collected by trained members of the public, the collaborative team of researchers have discovered that temperature is the primary trigger for sucker spawning migration, which can help inform conservation strategies in light of a changing climate.
“We believe that conservation of native, non-game fishes ...