(Press-News.org) Three teams led by Weill Cornell Medicine scientists have received awards from the Starr Cancer Consortium in its 17th and final annual grant competition. The grants will fund research on the deep mechanisms of common cancers and related treatment strategies.
The Starr Cancer Consortium, established in 2006 with generous support from The Starr Foundation, includes The Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, The Rockefeller University and Weill Cornell Medicine. The consortium’s goal has been to encourage highly collaborative and transformative research on cancer biology and novel treatment strategies. Its grants have targeted early-career scientists and have been intended mainly as seed funding for ambitious, long-term projects.
“Collaborative research, combining diverse areas of expertise and knowledge, is at the heart of successful biomedical breakthroughs,” said Dr. Jedd Wolchok, the Meyer Director of the Sandra and Edward Meyer Cancer Center at Weill Cornell Medicine. “We extend our gratitude to The Starr Foundation for fostering these vital combined efforts to advance cancer prevention and treatment.”
Weill Cornell Medicine researchers are the principal investigators for three of this year’s ten funded projects and co-principal investigators for another four of the projects.
“We’re extremely grateful to The Starr Foundation for its generous support over the years, which has enabled our investigators to pursue transformative ideas in cancer research,” said Dr. Hugh Hemmings, senior associate dean for research and chair of the Department of Anesthesiology at Weill Cornell Medicine. “The collective impact of this funding has been extraordinary in supporting innovative and collaborative projects from interinstitutional teams of investigators.”
Dr. Ekta Khurana
Associate Professor of Physiology and Biophysics; Co-Leader of the Cancer Genetics and Epigenetics Program at the Meyer Cancer Center, member of the Englander Institute for Precision Medicine
Prostate cancer non-neuroendocrine lineage plasticity: detection using multimodal integration and immunotherapeutic targeting
Prostate cancer is driven initially by androgen (testosterone) receptor signaling, but commonly develops resistance to androgen-blocking treatments so that it maintains its growth despite low or zero androgen levels. This “castration-resistant” prostate cancer (CRPC) represents the key challenge for oncologists in this field. Dr. Khurana and colleagues recently discovered and defined a relatively common, stem-cell like subtype of CRPC. In their newly funded project, they plan to develop an AI-based method for readily identifying this subtype from biopsied tissue slides. Based on evidence that this stem-cell-like subtype creates an immune-suppressive environment around itself, they also hope to find an effective treatment strategy that reverses this immune suppression to unleash anticancer immunity.
Co-Principal Investigators: Dr. Francisco Sanchez-Vega (Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center), Dr. Yu Chen (Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center), Dr. Roberta Zappasodi (Weill Cornell Medicine)
Dr. Jacob Geri
Assistant Professor of Pharmacology, member of the Meyer Cancer Center
Elucidating and targeting the resistant leukemia stem cell niche using high-resolution in situ protein interactomics and surfaceomics in human bone marrow tissue
Acute myeloid leukemia is hard to cure; the five-year survival rate for patients over 60 years old is only about 20 percent. A key source of treatment resistance is a type of cell called a leukemia stem cell, which can hide in bone marrow, avoiding damage from chemotherapy by staying in a quiescent, non-dividing state. In principle, treatments that could destroy leukemia stem cells as they hide in bone marrow would greatly improve patient outcomes, but scientists so far don’t know enough about these cells to target them selectively in bone marrow. Drs. Geri and Kentsis and their colleagues propose to develop methods to enable that targeting, using a photocatalytic technique for spatially mapping protein interactions within bone marrow. They hope that this approach ultimately will be a general tool for studying cancers and uncovering therapeutic targets.
Co-Principal Investigator: Dr. Alex Kentsis (Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center).
Dr. Anna S. Nam
Assistant Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, member of the Meyer Cancer Center
Modulating inflammation to eradicate clonal stem cells
Most cancers arise not suddenly but gradually: A healthy, normal cell develops a mutation or other state-change that modestly boosts its growth or survival rate, and the progeny of that cell start to locally replace slower-growing cells of that type. Further mutations in these clonally expanded cells can then trigger faster proliferation and full malignancy. Dr. Nam and her colleagues have been studying how this process in blood-cell-making or “hematopoietic” stem cells (HSCs) of the bone marrow can lead to blood cancers. They have shown in particular how one immune-related signal may be manipulated to trigger the destruction of clonal premalignant HSCs, while another can protect these HSCs from destruction, making malignancy more likely. Part of these findings were recently published by co-principal investigator Dr. Leonard Zon and Dr. Nam in Science. In their new project, they plan to apply advanced single-cell analysis methods to better understand these signals, with the ultimate goal of harnessing them to treat or even prevent blood cancers.
Co-Principal Investigator: Dr. Leonard Zon (The Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard).
END
New Starr Cancer Consortium grants awarded to Weill Cornell Medicine researchers
2024-10-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers aim to spark action to address rising homelessness among older people
2024-10-30
Homelessness among people over the age of 50 is on the rise, a phenomenon formal housing strategies often overlook -- but researchers from the University of Toronto and McGill hope to prevent this oversight in the future.
A new study published in The Gerontologist now provides a clear definition of late life homelessness informed by the lives and experiences of older adults. Drawing on interviews with older people who are unhoused and community workers in Montreal, Canada, the researchers aim to spark ...
Comparative metabolism of the humantenirine in liver microsomes from pigs, goats, and humans
2024-10-30
Background and objectives
Gelsemium elegans Benth (G. elegans) is a traditional medicinal plant; however, it is highly toxic, and toxicity varies significantly between species. The cause of this difference has not been clarified. Humantenirine is an important toxic alkaloid in G. elegans, and its metabolism has been poorly studied. This study aimed to compare the different metabolites formed by human liver microsomes, pig liver microsomes, and goat liver microsomes.
Methods
High-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry was used to study the metabolism of humantenirine in human liver microsomes, ...
Some wildfire suppressants contain heavy metals and could contaminate the environment
2024-10-30
In fire-prone areas, water isn’t the only thing used to quell blazes. Wildland firefighters also apply chemical or synthetic suppressants. Researchers reporting in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters explored whether these suppressants could be a source of elevated metal levels sometimes found in waterways after wildfires are extinguished. Several products they investigated contained high levels of at least one metal, including chromium and cadmium, and could contribute to post-fire increases in the environment.
“Wildfires ...
McMahon receives NIH grant to help build TTUHSC research capacity
2024-10-30
As a leader in academic health and biomedical research training, the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC) covers the West Texas region that comprises half of the state’s land mass and is home to 10% of its population. Research at TTUHSC drives innovation and discovery, changing the lives of those it serves and attracting talented faculty, staff and students.
During the latest reporting period (2020-2022), TTUHSC received an average of $12,539,679 annually in National Institutes ...
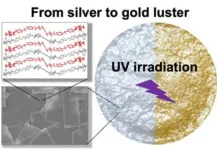
Turning silver to gold: A diacetylene derivative-based metallic luster materials
2024-10-30
Societies of the past and present have given high regard to precious metals like gold and silver. Both metals remind us of nobility and luxury. However, they are quite expensive, which restricts their applications. Therefore, materials with attractive but artificial gold- and silver-like metallic lusters are popular, finding use in jewelry, reflective materials, inks, and cosmetics.
Unfortunately, typical metallic luster materials cause environmental harm, rendering them unsustainable. Thus, scientists are actively searching for metal-free alternatives. In this direction, the research fraternity ...
Faster space communication with record-sensitive receiver
2024-10-30
In space exploration, long-distance optical links can now be used to transmit images, films and data from space probes to Earth using light. But in order for the signals to reach all the way and not be disturbed along the way, hypersensitive receivers and noise-free amplifiers are required. Now, researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, in Sweden, have created a system that, with a silent amplifier and record-sensitive receiver, paves the way for faster and improved space communication.
Space communication systems are increasingly based on optical laser beams rather than radio waves, as the signal loss has been shown to be less when light is used ...
New study shows that university students experienced increased psychological distress during COVID-19, but utilized fewer support services
2024-10-30
Embargoed Until 10/30/24 at 7 am
PhD in Public Health candidate Elaine Russell and her mentor Kenneth Griffin, professor in the department of Global and Community Health, in George Mason University’s College of Public Health, worked with Tolulope Abidogun, also a PhD in Public Health student, and former Global and Community Health professor Lisa Lindley, now of Lehigh University, to analyze data from the American College Health Association National College Health Assessment (ACHA-NCHA III) in an effort to understand how university ...
Camera trap study reveals a “vital sanctuary” for wildlife and endangered species in Cambodia’s Central Cardamom Mountains
2024-10-30
PHNOM PENH, Cambodia (October 30, 2024) – The first-ever camera trap study of the Central Cardamom Mountains Landscape has recorded 108 species, 23 of which are listed at risk (Vulnerable or above) on the IUCN Red List, underscoring the significance of the region as a global stronghold for biodiversity and rare and threatened species.
Editors please note: Use these links to access camera trap footage and the full report.
The report, released today by the Cambodian Ministry of Environment (MoE), the United States Agency ...
Buried Alive: Carbon dioxide release from magma deep beneath ancient volcanoes was a hidden driver of Earth’s past climate
2024-10-30
An international team of geoscientists led by a volcanologist at Rutgers University-New Brunswick has discovered that, contrary to present scientific understanding, ancient volcanoes continued to spew carbon dioxide into the atmosphere from deep within the Earth long past their period of eruptions.
In doing so, the research team has solved a long-standing mystery over what caused prolonged episodes of warming during turning points in Earth’s climate history. The work is detailed in today’s issue of the journal Nature Geoscience.
“Our ...
New genetic web tool to help restore climate-resilient marine ecosystems
2024-10-30
In the face of increased human pressures and climate change, a team of Australian scientists led by Dr Georgina Wood at Flinders University have launched a new online tool to assist marine managers and restoration experts to bolster the resilience of marine habitat-forming species.
The ‘Reef Adapt’ initiative, developed by experts from the NSW Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development (NSW DPIRD), Flinders University and The University of Western Australia (UWA), aims to expand the tools available to promote diverse, adaptable and resilient ecosystems.
Described in a new article in Communications Biology, Reef Adapt harnesses genetic data ...