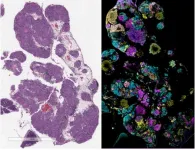
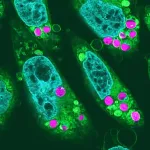
The study, published in the October 30 online issue of Cell [DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.10.006], used a cutting-edge spatial genomics technology and preclinical animal models, with tumor specimens from ovarian cancer patients further validating the findings.
The researchers found that ovarian cancer cells produce a molecule called Interleukin-4 (IL-4), which is typically associated with asthma and the skin condition eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis. The study went on to find that the cancer cells used IL-4 to create a protective environment that kept away killer immune cells, making the tumors resistant to immunotherapy. A drug, dupilumab, which blocks IL-4’s activity, has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and is already used to treat asthma and eczema. This new study suggests dupilumab or similar drugs could be repurposed to enhance immunotherapy for ovarian cancer.
Ovarian cancer is one of the most deadly cancers; 50 percent of patients die within five years of diagnosis. While immunotherapy drugs such as pembrolizumab, which target the PD-1 molecule, have demonstrated efficacy in treating melanoma and lung cancer, they have not significantly improved survival rates in ovarian cancer. This is partly because ovarian tumors have fewer mutations, making them harder for the immune system to recognize. Additionally, research suggests that these tumors may resist immunotherapy by creating barriers that prevent immune cells from infiltrating their borders. The critical question, say the investigators, has been: how do tumors establish these protective environments?
To address this question, the research team, led by Alessia Baccarini, PhD, Assistant Professor of Immunology and Immunotherapy, and Brian D. Brown, PhD, Director of the Icahn Genomics Institute at Icahn Mount Sinai, used a novel genomics technology known as Perturb-map. Perturb-map enhances traditional gene-editing CRISPR screening—where hundreds of genes are simultaneously “perturbed”—by incorporating state-of-the-art spatial imaging. This enables each gene’s role in controlling the tumor environment to be elucidated. Their experiments revealed that removing the IL-4 gene from ovarian cancer cells rendered the tumors susceptible to anti-PD-1 therapy.
“Surprisingly, the IL-4-deficient cancer cells were eliminated by the immune system even when mixed within tumors containing IL-4-producing cancer cells, a phenomenon known as intratumoral heterogeneity, which also contributes to drug resistance in cancer,” says Dr. Brown, who is Mount Sinai Professor of Genetic Engineering and senior author of the study.
The researchers then tested a combination of anti-PD-1 and IL-4 receptor-blocking drugs in mice with aggressive metastatic ovarian cancer and found that this combination treatment significantly extended their survival.
Additional preclinical studies demonstrated that ovarian cancer uses IL-4 to program macrophages, a type of immune cell, into protectors of the cancer cells. The IL-4-programmed macrophages prevented T cells from killing the cancer cells. However, when IL-4 was blocked, the local environment surrounding the cancer cells changed, and this left the malignant cells susceptible to being eliminated by the immune system.
To further validate their findings, the team examined specimens from human ovarian tumor resections and saw that the patients’ cancer cells also produced IL-4. Moreover, analysis of single-cell RNA sequencing data from patient tumors—which examines how genes are expressed in cells—revealed that the macrophages displayed a strong IL-4 signature, suggesting that IL-4 is playing a similar role in human ovarian cancer and may be one of the reasons patients have not benefited from immunotherapy.
“Ovarian cancer has almost been written off as non-responsive to existing immunotherapy, so it was quite stunning to us that by just blocking this one molecule, IL-4, and altering the tumor’s microenvironment, we could make these difficult-to-treat tumors more treatable,” adds Dr. Brown. “This is further evidence that targeting the tumor’s neighborhood, not just the cancer cells, can be beneficial.”
While these findings are encouraging, the investigators stress that clinical trials are essential to determine whether targeting IL-4 can enhance patient outcomes. Given that dupilumab is already FDA-approved for asthma and eczema, there is potential for swift clinical testing alongside immunotherapy to enhance survival in ovarian cancer patients. Thomas Marron, MD, PhD, Director of the Early Phase Trial Unit at Mount Sinai and a colleague of Drs. Brown and Baccarini, has already been running a clinical study to test whether dupilumab can improve anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in patients with lung cancer, and several patients have shown beneficial responses.
“Ovarian cancer is a disease that’s so hard to catch early and once diagnosed, it’s often too late. I am excited that these findings may make a difference in patients’ lives. The IL-4 pathway is already targeted for diseases like eczema, and I am hopeful that if we target it in ovarian cancer, we can help women facing this terrible disease,” says Dr. Baccarini.
The paper is titled “Ovarian cancer-derived IL-4 promotes immunotherapy resistance.”
To view details on the remaining authors and competing interests, see: [DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.10.006].
The work was supported by NIH awards R01AT011326, R01CA254104, R01CA257195, U2C-CA233262, U01CA284207, U01CA282114, and funding from the Cancer Research Institute, the Feldman Foundation, the Applebaum Foundation, and Ludwig Cancer Research.
-####-
About the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai is internationally renowned for its outstanding research, educational, and clinical care programs. It is the sole academic partner for the eight- member hospitals* of the Mount Sinai Health System, one of the largest academic health systems in the United States, providing care to a large and diverse patient population.
Ranked 13th nationwide in National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding and among the 99th percentile in research dollars per investigator according to the Association of American Medical Colleges, Icahn Mount Sinai has a talented, productive, and successful faculty. More than 3,000 full-time scientists, educators, and clinicians work within and across 44 academic departments and 36 multidisciplinary institutes, a structure that facilitates tremendous collaboration and synergy. Our emphasis on translational research and therapeutics is evident in such diverse areas as genomics/big data, virology, neuroscience, cardiology, geriatrics, as well as gastrointestinal and liver diseases.
Icahn Mount Sinai offers highly competitive MD, PhD, and Master’s degree programs, with current enrollment of approximately 1,300 students. It has the largest graduate medical education program in the country, with more than 2,000 clinical residents and fellows training throughout the Health System. In addition, more than 550 postdoctoral research fellows are in training within the Health System.
A culture of innovation and discovery permeates every Icahn Mount Sinai program. Mount Sinai’s technology transfer office, one of the largest in the country, partners with faculty and trainees to pursue optimal commercialization of intellectual property to ensure that Mount Sinai discoveries and innovations translate into healthcare products and services that benefit the public.
Icahn Mount Sinai’s commitment to breakthrough science and clinical care is enhanced by academic affiliations that supplement and complement the School’s programs.
Through the Mount Sinai Innovation Partners (MSIP), the Health System facilitates the real-world application and commercialization of medical breakthroughs made at Mount Sinai. Additionally, MSIP develops research partnerships with industry leaders such as Merck & Co., AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, and others.
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai is located in New York City on the border between the Upper East Side and East Harlem, and classroom teaching takes place on a campus facing Central Park. Icahn Mount Sinai’s location offers many opportunities to interact with and care for diverse communities. Learning extends well beyond the borders of our physical campus, to the eight hospitals of the Mount Sinai Health System, our academic affiliates, and globally.
-------------------------------------------------------
* Mount Sinai Health System member hospitals: The Mount Sinai Hospital; Mount Sinai Beth Israel; Mount Sinai Brooklyn; Mount Sinai Morningside; Mount Sinai Queens; Mount Sinai South Nassau; Mount Sinai West; and New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai.
END