(Press-News.org) The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, and defense technology company Lockheed Martin announced the signing of a new five-year master research agreement Oct. 31, reinforcing a longstanding partnership that helps UT take its research capabilities from the lab to the field.
“This partnership allows UT researchers to conduct true translational research,” said James Andes, director of national security research initiatives for UT. “Our research concepts are matured by working with technical champions at Lockheed Martin, and as a result our technologies get scaled up and out into defense applications.”
Linda O’Brien of Lockheed Martin, left, and Chancellor Donde Plowman
As a global security, innovation and aerospace company, Lockheed Martin carries out the majority of its business with the U.S. Department of Defense and other federal agencies. In addition, Sikorsky — a Lockheed Martin Company — provides military and rotary-wing aircraft to all five branches of the U.S. armed forces as well as to military services and commercial operators in 40 nations.
While Lockheed Martin does not have a physical presence on any of UT’s campuses, the master research agreement serves as a prenegotiated contract so the university can quickly respond when UT’s capabilities align with Lockheed Martin’s needs, Andes explained.
“Lockheed Martin is an important strategic partner,” said Deb Crawford, UT vice chancellor for research, innovation and economic development, “We’re excited to renew our partnership to advance technological solutions to national security challenges while also preparing the aerospace workforce of the future.”
Historically UT’s work with Lockheed Martin has centered around hypersonics solutions, helping evaluate and test prototypes that will travel at eight or nine times the speed of sound, Andes said. However, the research agreement extends beyond hypersonics technologies, allowing UT to support Lockheed Martin in other mission areas such as advanced materials and manufacturing, energy and power systems, and trusted artificial intelligence and machine learning — areas that align with UT’s innovation gateways and core research strengths.
“Our partnership with Lockheed Martin is not specific to any one academic unit but covers a broad spectrum of both fundamental and applied research, from engineering to agriculture,” Andes said. “There are very few areas they have a concern for that we don’t have an expert in.”
Marc Gibson, associate vice chancellor, speaks before a group of people from Lockheed Martin and UT
The 2019-2024 master research agreement produced six Lockheed Martin-funded projects totaling more than $3 million. It also included the company’s annual sponsorship of Tickle College of Engineering senior design projects, one of which resulted in a paper presented at the University Consortium for Applied Hypersonics fall 2024 symposium. Students from other UT colleges also reap the benefits of the partnership.
“Experiential learning is at the heart of our mission at the College of Emerging and Collaborative Studies,” said Vice Provost and Founding Dean Ozlem Kilic. “We’re not only enriching our students’ education across campus but also equipping them with the adaptability, critical thinking and collaborative skills that cut through disciplines essential for the careers of the future that revolve around emerging technologies. We are thrilled that this new master research agreement between UT and Lockheed Martin will allow us to continue providing students access to real-world experiences and also expand our ability to offer more students these opportunities.”
UT has played an important workforce development role for Lockheed Martin as well, Andes said, by providing quality students for internships and co-ops at Lockheed Martin and well-prepared graduates for employment. At last count, Lockheed Martin employed more than 350 UT alumni.
“Our partnership with UT is key to solving some of the most complex challenges in the aerospace domain,” said Linda O’Brien, vice president and chief engineer for Lockheed Martin Aeronautics and a UT mechanical engineering graduate. “It’s personally exciting to see the sophistication and relevance of the research, as well as the caliber of talent, from my own alma mater.”
END
University of Tennessee, Lockheed Martin expand Master Research Agreement
2024-11-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Testing thousands of RNA enzymes helps find first ‘twister ribozyme’ in mammals
2024-11-05
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The “RNA world” hypothesis proposes that the earliest life on Earth may have been based on RNA — a single-stranded molecule similar in many ways to DNA — like some modern viruses. This is because, like DNA, RNA can carry genetic information, but, like a protein, it can also act as an enzyme, initiating or accelerating reactions. While the activity of a few RNA enzymes — called ribozymes — have been tested on a case-by-case basis, there are thousands more that have been computationally predicted to exist in organisms ranging from bacteria to plants and animals. Now, ...
Groundbreaking study provides new evidence of when Earth was slushy
2024-11-05
At the end of the last global ice age, the deep-frozen Earth reached a built-in limit of climate change and thawed into a slushy planet.
Results from a Virginia Tech-led study provide the first direct geochemical evidence of the slushy planet — otherwise known as the “plumeworld ocean” era — when sky-high carbon dioxide levels forced the frozen Earth into a massive, rapid melting period.
“Our results have important implications for understanding how Earth's climate and ocean chemistry changed after the extreme conditions of the last global ...
International survey of more than 1600 biomedical researchers on the perceived causes of irreproducibility of research results
2024-11-05
International survey of more than 1600 biomedical researchers on the perceived causes of irreproducibility of research results
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002870
Article Title: Biomedical researchers’ perspectives on the reproducibility of research
Author Countries: Canada, Australia, United States
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Integrating data from different experimental approaches into one model is challenging – this study presents a community-based, full-scale in silico model of the rat hippocampal CA1 region that integra
2024-11-05
Integrating data from different experimental approaches into one model is challenging – this study presents a community-based, full-scale in silico model of the rat hippocampal CA1 region that integrates diverse experimental data from synapse to network
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002861
Article Title: Community-based reconstruction ...
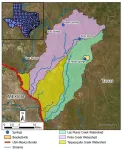
SwRI awarded grant to characterize Las Moras Springs watershed
2024-11-05
SAN ANTONIO — November 5, 2024 — Hydrologists at Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) will begin a 12-month targeted water-sampling campaign of the Las Moras Springs system near Brackettville, Texas. The project will analyze and characterize the system of springs and their relationship to the Pinto Creek watershed to improve water management and conservation efforts.
“Las Moras, like many other Texas spring systems, are at-risk and prone to going dry. It is important to clear up uncertainties about their source and relationship with ...
Water overuse in MATOPIBA could mean failure to meet up to 40% of local demand for crop irrigation
2024-11-05
Considered one of the fastest-growing agricultural frontiers in Brazil, and the area with the highest greenhouse gas emissions in the Cerrado, Brazil’s savanna-type biome, the region known as MATOPIBA risks facing water shortages in the years ahead. Water overuse may mean that between 30% and 40% of demand for crop irrigation cannot be met in the period 2025-40. MATOPIBA is a portmanteau of the names of four states – Maranhão, Tocantins, Piauí, and Bahia (all but Tocantins located in Brazil’s Northeast ...
An extra year of education does not protect against brain aging
2024-11-05
Thanks to a 'natural experiment' involving 30,000 people, researchers at Radboud university medical center were able to determine very precisely what an extra year of education does to the brain in the long term. To their surprise, they found no effect on brain structure and no protective benefit of additional education against brain aging.
It is well-known that education has many positive effects. People who spend more time in school are generally healthier, smarter, and have better jobs and higher incomes than those with less education. However, whether prolonged education actually causes changes in brain structure over the long term ...
Researchers from Uppsala and Magdeburg obtain an ERC Synergy Grant to advance cancer immunotherapy
2024-11-05
Targeting and customizing blood vessels in tumors to increase T cell infiltration and maintain their function may represent the next breakthrough in cancer therapy. The European Research Council has recognized this by awarding a prestigious Synergy Grant to the project VASC-IMMUNE, where three researchers, each possessing complementary expertise in this research topic, will synergize to advance the field. Professors Anna Dimberg and Magnus Essand are both from the Department of Immunology, Genetics and Pathology, Uppsala University and Professor Thomas Tüting is from the Department of Dermatology, University Hospital Magdeburg.
The successful implementation ...
Deaf male mosquitoes don’t mate
2024-11-05
Mosquitoes are much more blunt. Mating occurs for a few seconds in midair. And all it takes to woo a male is the sound of a female’s wingbeats. Imagine researchers’ surprise when a single change completely killed the mosquitoes’ libidos.
Now a study out of UC Santa Barbara reveals that this is really all there is to it. Researchers in Professor Craig Montell’s lab created deaf mosquitoes and found that the males had absolutely no interest in mating. “You could leave them together with the females ...
Recognizing traumatic brain injury as a chronic condition fosters better care over the survivor’s lifetime
2024-11-05
INDIANAPOLIS – A commentary, published in the Journal of Neurotrauma, calls for traumatic brain injury to be recognized as a chronic condition as are diabetes, asthma, depression and heart failure.
To provide comprehensive care for traumatic brain injury throughout individuals’ lifespans, the authors propose that coordinated care models they and others have developed, tested and applied to various populations -- including older adults, individuals living with depression and post-intensive care unit survivors -- be adapted to improve communication and integration between brain injury specialists -- including ...