(Press-News.org) Waterborne diseases affect over 7 million people in the U.S. every year, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and cost our health care system over $3 billion. But they don’t impact all people equally.
A campuswide collaboration is using sewage surveillance as a vital strategy in the fight against diseases that spread through the water such as legionella and shigella. The ones that are most difficult to combat are diseases with antimicrobial resistance, which means they are able to survive against antibiotics that are intended to kill them.
A recent paper in Nature Water offers an encouraging insight: Monitoring sewage for antimicrobial resistance indicators is proving to be more efficient and more comprehensive than testing individuals. This approach not only detects antimicrobial resistance more effectively but also reveals its connection to socioeconomic factors, which are often key drivers of the spread of resistance.
The paper’s corresponding author is Peter Vikesland, the Pryor Professor of Engineering in the civil and environmental engineering department. The full list of authors at Virginia Tech, in addition to Vikesland, are:
Suraj Gupta, computer science
Xiaowei Wu, statistics
Liqing Zhang, computer science
Amy Pruden, civil and environmental engineering
The team is collaborating across Virginia Tech with experts such as Leigh-Anne Krometis in biological systems engineering and Alasdair Cohen and Julia Gohlke in population health sciences to focus on serving rural communities where the issues are most acute.
The significance
Globally, low-to middle-income communities bear the brunt of infectious diseases and the challenges of antimicrobial resistance. Sewage surveillance could be a game changer in addressing these disparities. This method not only captures a snapshot of antimicrobial resistance at the community level, but also reveals how socioeconomic factors drive the issue.
The study
The National Science Foundation Research Traineeship focuses on advancing sewage surveillance to combat antimicrobial resistance. The work is integral to broader efforts led by Vikesland and the Fralin Life Sciences Institute program for technology enabled environmental surveillance and control to sense and monitor waterborne health threats.
The study analyzed data from 275 human fecal samples across 23 countries and 234 urban sewage samples from 62 countries to investigate antibiotic resistance gene levels. Socio-economic data, including health and governance indicators from World Bank databases, were incorporated to explore links between antibiotic resistance genes and socio-economic factors. The group utilized machine learning to assess antibiotic resistance gene abundance in relation to socio-economic factors, revealing significant correlations. Statistical methods supported the finding that within country antibiotic resistance gene variation was lower than between countries.
Big picture, the team's findings show sewage surveillance is emerging as a powerful tool in the fight against antimicrobial resistance. It even has the potential to protect vulnerable communities more effectively.
END
Sewage surveillance proves powerful in combating antimicrobial resistance
Research from an interdisciplinary team at Virginia Tech shows public health promise
2024-11-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Natural environment is declining: are companies doing their part to save it?
2024-11-06
The natural environment across the globe is deteriorating, leading to crises like climate change, biodiversity loss, and water scarcity. Companies and industries play a major role in this decline, and they are expected to take responsibility for their environmental impact. A recent study by Probal Dutta from the University of Vaasa, Finland, suggests that companies can meet these expectations by openly sharing reliable, credible information about their activities, environmental performance, and effects on nature.
Probal Dutta’s doctoral dissertation at the University ...
New study sheds light on the role of sound and music in gendered toy marketing
2024-11-06
A groundbreaking study from Queen Mary University of London reveals that the music and soundscapes used in toy commercials are reinforcing rigid gender norms, shaping the way children perceive masculinity and femininity. The research uncovers how gender stereotypes are not only conveyed through visuals and language but are also deeply embedded in the sound and music used in advertisements targeted at children.
For more than 40 years, research has shown how gender polarisation in children’s ...
Pathogens which cling to microplastics may survive wastewater treatment
2024-11-06
Wastewater treatment fails to kill several human pathogens when they hide out on microplastics in the water, reports a new study led by Ingun Lund Witsø of the Norwegian University of Life Sciences, published November 6, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
Wastewater treatment plants are designed to remove contaminants from wastewater, but microplastics persist and can become colonized by a sticky microbial biofilm. Previous research has suggested that these microbial communities, called plastispheres, include potential pathogens, and thus might pose a risk to human health and the environment when treated wastewater and sludge are released.
In the new study, researchers ...
Effects of preterm birth extend into adulthood, study finds
2024-11-06
By analyzing all live births in Canada over a six-year period and following children for more than two decades, researchers found that preterm births and the related cognitive, development and physical health impacts of prematurity are associated with lower income, employment and university enrollment
Individuals born before 37 weeks of gestation, considered to be preterm infants, have, on average, lower employment income, university enrollment and educational attainment through age 28, according to ...
Salmon frequently mislabeled in Seattle grocery stores and sushi restaurants
2024-11-06
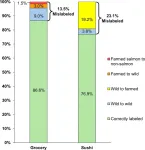
In a study of salmon samples from Seattle, Washington, grocery stores and sushi restaurants, DNA analysis revealed that 18 percent were mislabeled. Tracie Delgado and colleagues at Seattle Pacific University, WA, U.S., present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on November 6, 2024.
Washington State is one of the top suppliers of wild salmon eaten in the United States. The price of salmon depends on the species and whether it is farmed or wild caught. Prior studies have revealed frequent mislabeling of salmon in Washington markets and restaurants. In 2013, the state made it illegal to mislabel salmon, citing negative ...
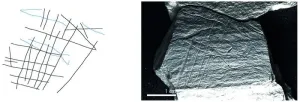
15,800-year-old engraved plaquettes from modern-day Germany depict fishing techniques, including the use of nets, not previously known in the Upper Paleolithic
2024-11-06
15,800-year-old engraved plaquettes from modern-day Germany depict fishing techniques, including the use of nets, not previously known in the Upper Paleolithic
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0311302
Article Title: Upper Palaeolithic fishing techniques: Insights from the engraved plaquettes of the Magdalenian site of Gönnersdorf, Germany
Author Countries: Germany, U.K.
Funding: Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft DFG (Germany) - AHRC (UK) Memorandum of Understanding Grant DFG-Projekt GZ: GA 683/13-1 (AOBJ: 647648); AHRC (UK) AH/V002899/1) Kunst und Haushalt im Paläolithikum: ...
How plants evolved multiple ways to override genetic instructions
2024-11-06
Biologists at Washington University in St. Louis have discovered the origin of a curious duplication that gives plants multiple ways to override instructions that are coded into their DNA. This research could help scientists exploit a plant’s existing systems to favor traits that make it more resilient to environmental changes, like heat or drought stress.
The study led by Xuehua Zhong, a professor of biology in Arts & Sciences, was published Nov. 6 in Science Advances.
Zhong’s new research focuses on DNA methylation, a normal biological process in living cells wherein small chemical groups called methyl ...
Nasal swab tests predict COVID-19 disease severity, Emory study finds
2024-11-06
A wide variety of COVID-19 symptoms exist, ranging from mild to severe, and while current strains of the virus generally cause milder symptoms, those with co-morbidities are still at an exponentially greater risk of severe disease. Now, new research from Emory University is providing a more precise prediction of COVID-19 severity that can be found by looking at autoantibodies in the nasal cavity, leading to more personalized treatment plans. For high-risk individuals, this could provide critical information to inform immediate treatment options, including ...
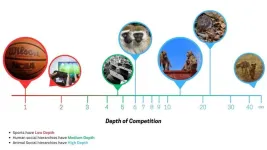
'Shallow' sports and 'deep' social hierarchies: Not all pecking orders are created equal
2024-11-06
University of Michigan researchers have added a new dimension to the mathematics used to predict the outcomes of all manner of competitions, including sports, games and social hierarchies in both humans and animals.
This dimension, which they call "depth of competition," can be integrated into a variety of important and lucrative fields. It could, for instance, help project winners of match-ups in sports, forecast consumer preferences, rank universities and evaluate hiring practices.
But it also ...
New PFAs testing method created at UMass Amherst
2024-11-06
AMHERST, Mass. — University of Massachusetts Amherst researchers have discovered a new way to detect per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in water. This marks an important step forward in creating testing devices that are simpler, more cost-effective, faster and generally more accessible than existing methods.
PFAS, the so-called forever chemicals, have been recognized as a concerning pollutant.
These chemicals persist in the environment because they resist breaking down and pose significant health threats. Exposure to these chemicals is linked to various cancers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
Housing displacement, employment disruption, and mental health after the 2023 Maui wildfires
GLP-1 receptor agonist use and survival among patients with type 2 diabetes and brain metastases
Solid but fluid: New materials reconfigure their entire crystal structure in response to humidity
New research reveals how development and sex shape the brain
New discovery may improve kidney disease diagnosis in black patients
What changes happen in the aging brain?
Pew awards fellowships to seven scientists advancing marine conservation
Turning cancer’s protein machinery against itself to boost immunity
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
Adults with concurrent hearing and vision loss report barriers and challenges in navigating complex, everyday environments
Breast cancer stage at diagnosis differs sharply across rural US regions
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
[Press-News.org] Sewage surveillance proves powerful in combating antimicrobial resistanceResearch from an interdisciplinary team at Virginia Tech shows public health promise