(Press-News.org) Baton Rouge, November 4, 2024 – Novel research just published in the American Ornithological Society journal, Ornithological Applications, has revealed noteworthy insights into how Barred Owls (Strix varia) interact with urban environments, with implications for both wildlife conservation and urban planning. This study, conducted by a team of biologists from Louisiana State University and other institutions, highlights the connection between owl habitat selection and an urban landscape, underscoring the broader ecological and socio-economic impacts of urban landscapes.
Key findings:
Day vs. night habitat use: Barred Owls’ home ranges were significantly larger at night than during the day, indicating different habitat needs between their active and resting periods. The research emphasizes that preserving green spaces in urban areas can have profound effects on nocturnal and diurnal wildlife.
Energy efficiency in preferred habitats: Owls expended less energy in their preferred nocturnal habitats, suggesting that these areas provide higher-quality resources.
Affluent neighborhoods attract Barred Owls: Barred Owls in Baton Rouge, Louisiana, showed a marked preference for habitats in affluent neighborhoods, supporting the “luxury effect”—the tendency for wealthier areas to harbor greater biodiversity.
Implications for urban design: The study advocates for providing and protecting habitat for Barred Owls to keep this important species, other forest-associated species, and the ecosystem services they provide present and functioning in urban areas. The study also advocates for the equitable distribution of green spaces in cities, especially in less affluent areas, to promote biodiversity throughout the urban landscape.
The importance of studying the entire diel cycle
This research highlights the need to study the entire diel cycle—the full 24-hour period—in animal ecology, rather than focusing solely on their active phases. For example, while owls are typically active at night, understanding their behavior during the day, when they are resting, is equally important for a complete picture of their habitat needs. This approach can be likened to inferring human priorities by only tracking their activities during work hours and neglecting what happens at home during the evening and night. Just as human well-being is shaped by both work and home life, animal survival and fitness are influenced by both active and inactive periods. By examining these patterns holistically, scientists can develop more effective conservation strategies.
Capturing the owls: a hands-on learning experience
The research team faced unique challenges in capturing Barred Owls. The team deployed a variety of strategies, including a stuffed owl toy named Judas. “Judas was supposed to lure territorial owls into our nets,” explains coauthor Dr. Vitek Jirinec. “He was hit a few times, but most owls weren’t fooled. We had better success with a broadcast of owl calls next to 12-meter (40-foot) tall nets.”
Dr. Jirinec recalls the experience as both thrilling and humbling. “Most of my previous experience comes from working with small songbirds, but these owls are a different kind of beast who can make use of their sharp beaks and claws, if one is not careful.” As proof he has photographic evidence of his hands, torso, and head.
Once captured, the owls were fitted with GPS and accelerometer loggers, allowing the team to track their movements and energy expenditures with high precision. This data collection was important in revealing the differences in owl behavior and habitat use across the landscape, shedding light on how these predators navigate their environment.
A collaborative effort during challenging times
Coauthor Dr. Sabrina Taylor reflects on the collaborative nature of the project: “This study was a truly rewarding experience that brought together graduate and undergraduate students, faculty, and even community members. We wouldn’t have been able to undertake an extra research project to learn about this local species without the collaboration of many people.”
The combination of advanced technology, hands-on fieldwork, and community collaboration made this research possible, resulting in findings that could influence how urban spaces are designed in the future to better accommodate both wildlife and human residents.
Broader impacts
This research not only advances our understanding of urban ecology but also highlights the socio-economic disparities in environmental quality. As cities expand, the findings underscore the importance of designing urban landscapes that support biodiversity and offer equitable access to green spaces for all residents.
About the research:
Jirinec, V., A. M. Bresnan, M. Clément, M. R. Colón, A. M. Long, G. Rhyne, P. Rodrigues, E. Stein, A. Pérez-Umphrey, C. Varian, S. T. Williams, and S. S. Taylor (2024). Home ranges, habitat selection, and energy expenditure of Strix varia (Barred Owls): Understanding the full diel cycle matters for enhancing urban landscapes. Ornithological Applications 126:duae000. https://doi.org/10.1093/ornithapp/duae038
About the American Ornithological Society
The American Ornithological Society (AOS) is an international society dedicated to connecting ornithologists, science, and bird conservation by supporting science that advances the understanding and conservation of birds; promoting broad access to ornithological science; supporting ornithologists throughout their career paths; and fostering a welcoming, diverse, supportive, and dynamic ornithological community. The AOS publishes two top-ranked international scientific journals, Ornithology and Ornithological Applications, and hosts an annual conference that attracts ornithologists from across the globe. Its robust grants program supports student and early-career professional research initiatives. The society’s Check-list of North American Birds serves as the accepted authority for scientific nomenclature and English common names of birds in North and Middle America. The AOS is also a partner with The Cornell Lab of Ornithology in the online Birds of the World, a rich database of species accounts of the world’s birds. The AOS is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization serving about 3,000 members globally. For more information, see www.americanornithology.org.
###
END
Habitat loss and poaching have driven dramatic declines in African elephants, but it is challenging to measure their numbers and monitor changes across the entire continent. A new study has analyzed 53 years of population survey data and found large-scale declines in most populations of both species of African elephants.
From 1964-2016, forest elephant populations decreased on average by 90%, and savanna elephant populations fell on average by 70%. In combination, populations declined by 77% on average. The study compiled survey data from 475 sites in 37 countries, making it the most comprehensive assessment of African elephants to date.
Declines ...
EMBARGOED: Until 3 p.m. ET on Monday, Nov. 11, 2024
Contacts:
Laura Snider, NSF NCAR and UCAR Manager of Science Communications
lsnider@ucar.edu
303-827-1502
David Hosansky, NSF NCAR and UCAR Manager of Media Relations
hosansky@ucar.edu
720-470-2073
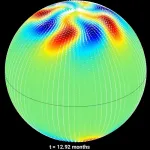
Like the Earth, the Sun likely has swirling polar vortices, according to new research led by the U.S. National Science Foundation National Center for Atmospheric Research (NSF NCAR). But unlike on Earth, the formation and evolution of these vortices ...
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- In drug discovery, targeted protein degradation is a method that selectively eliminates disease-causing proteins. A University of California, Riverside team of scientists has used a novel approach to identify protein degraders that target Pin1, a protein involved in pancreatic cancer development.
The team reports today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences that it has designed agents that not only bind tightly to Pin1 but are designed to cause its destabilization and cellular ...
Prolonged mental fatigue can wear down brain areas crucial for the individual ability to self-control, and cause people to behave more aggressively.
In a new multidisciplinary study published in the PNAS, a group of researchers from neuroscience and economics at the IMT School of Advanced Studies Lucca links the debated concept of "ego depletion", that is to say the diminution of willpower caused by previous exploitation of it, to physical changes in the areas that govern executive functions in the brain. In particular, the ...
Geologists have uncovered strong evidence from Colorado that massive glaciers covered Earth down to the equator hundreds of millions of years ago, transforming the planet into an icicle floating in space.
The study, led by the University of Colorado Boulder, is a coup for proponents of a long-standing theory known as Snowball Earth. It posits that from about 720 to 635 million years ago, and for reasons that are still unclear, a runaway chain of events radically altered the planet’s climate. Temperatures plummeted, and ice sheets that may have been several miles thick crept over every inch of Earth’s surface.
“This study presents the first physical evidence ...
Ahead of COP29, Applied Microbiology International (AMI) has partnered with leading global scientific organisations to issue a unified call to action, spotlighting microbial solutions as pivotal in combating climate change.
In a strategic publication, released in multiple high-impact scientific journals at once, the joint paper advocates for the establishment of a global science-driven climate task force. This initiative aims to expedite the deployment of microbiome technologies, providing stakeholders worldwide with access to effective and immediate solutions.
Signatories of the paper, ‘Microbial solutions must be deployed against the climate catastrophe’ ...
NEW ORLEANS – The Ochsner Transplant Institute served as one of 26 U.S. transplant centers collaborating in an HIV-to-HIV kidney transplant study published by The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM). The article, Safety of Kidney Transplantation from Donors with HIV, details findings supporting HIV-to-HIV kidney transplants as safe and just as effective as those using organs from donors without HIV.
Human immunodeficiency virus, commonly known as HIV, attacks cells in the body that fight infection and there is currently no known cure. In the U.S.,1.2 million people are living with HIV. According to the National ...
Washington, D.C. — Nov. 11, 2024 — Today, leaders from scientific societies, institutions and publishing bodies issued an urgent call for the global community and governments to take immediate and decisive emergency climate action. This appeal is made through an editorial published in mSystems, released on the opening day of the 2024 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP29). Key contributors to this initiative include Virginia Miller, past president of the American Society for Microbiology (ASM); Jack Gilbert, Editor-in-Chief of mSystems; and Jay Lennon, ...
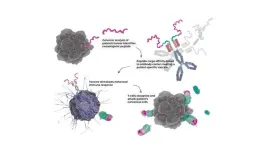
Researchers at Uppsala University and KTH Royal Institute of Technology have developed a new form of precision medicine, an antibody, with the potential to treat several types of cancer. Researchers have managed to combine three different functions in the antibody, which together strongly amplify the effect of T cells on the cancer tumour. The study has been published in Nature Communications.
Researchers have developed a unique type of antibody that both targets and delivers a drug package via the antibody itself, while simultaneously activating the immune system (“3-in-1 design”) for personalised immunotherapy treatments.
“We ...
Climate change events have, in recent years, placed increasing strain on public electrical grids in the United States. In response to this vulnerability, some consumers are turning to private alternatives to the electric utility, like generators and batteries. A new paper in the Journal of the Association of Environmental and Resource Economists studies who adopts these private alternatives and how adoption responds to grid failures. The paper also studies how public electric grid reliability may change due to this proliferation and how these changes will affect the wellbeing of all households.
In ...