(Press-News.org) Washington, November 12, 2024—As student absenteeism reaches record highs in schools across the United States, new research finds that student absences are linked to lower teacher job satisfaction, raising concerns that this may exacerbate growing teacher shortages. The findings were published today in Educational Researcher, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association.
The study, by Michael Gottfried and Colby Woods at the University of Pennsylvania, and Arya Ansari at The Ohio State University, is the first to examine the connection between student absenteeism and teacher satisfaction. Using nationally representative data from the U.S. Department Education on 2,370 kindergarten teachers, the researchers found that when teachers have more absent students, they report feeling less satisfied with their jobs. This was true for new teachers as well as more experienced teachers.
“Our findings show that a lack of good student attendance has the potential to detract from the satisfaction teachers get from instructing and helping their students learn and grow,” said Gottfried, a professor at the University of Pennsylvania Graduate School of Education. “This has important implications for the current educational landscape. Addressing absenteeism is critical not only for improving student outcomes, but also for bolstering the teacher workforce, which faces a host of challenges.”
The study found that student absenteeism had no link to teachers’ feelings about other aspects of school, such as their teaching ability or school climate—just job satisfaction. There was also no indication that teachers who were less satisfied to begin with were being assigned to the students who were more likely to be absent.
“We show that student absenteeism emerges as a teacher challenge, and so there is a need for a more well-rounded approach to addressing the effects of absenteeism in the classroom,” Gottfried said. “Approaches need to go beyond only those that are focused on students. Broader efforts will have the potential to yield positive impacts across teachers, contributing to a more satisfied and engaged workforce.”
Examples of effective efforts include investing in interventions that strengthen teachers’ relationships with students and families, implementing trauma-informed teaching, and professional development to support the diverse needs of students, including those at risk of absenteeism. Absenteeism initiatives could also improve working conditions for teachers. For example, reducing administrative burdens and increasing staffing support to better address absenteeism-related challenges could bolster more regular school attendance and, in turn, improve satisfaction, according to Gottfried.
Study citation: Gottfried, M.A., Woods C. S., & Ansari, A. (2024). Do teachers with absent students feel less job satisfaction? Educational Researcher. Prepublished November 12, 2024. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X241292331
###
About AERA
The American Educational Research Association (AERA) is the largest national interdisciplinary research association devoted to the scientific study of education and learning. Founded in 1916, AERA advances knowledge about education, encourages scholarly inquiry related to education, and promotes the use of research to improve education and serve the public good. Find AERA on Facebook, X, LinkedIn, Instagram, Threads, and Bluesky.
END
Study: Student absenteeism crisis may be hurting teacher job satisfaction
Researchers warn that rising absenteeism could worsen growing teacher shortages
2024-11-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Medicaid enrollment continuity tied to lymphoma stage at diagnosis
2024-11-12
(WASHINGTON, November 12, 2024) – Continuous enrollment in Medicaid was associated with a lower rate of a late-stage lymphoma diagnosis in children and adolescents/young adults (AYAs). However, fewer than half of Medicaid-insured patients in these age ranges were continuously enrolled before diagnosis, according to a study published today in Blood Advances.
Lymphoma – which is divided into two types, Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) – is a cancer of the lymphatic system and ...
INSEAD launches free Negotiation Course for the World
2024-11-12
If knowledge is power, empowering the world with the art and science of negotiation offers even more far-reaching benefits – a more peaceful and prosperous world, according to the INSEAD Negotiation and Conflict Management Collaborative (NCMC).
The Negotiation Course for the World (NCW) is a pioneering effort by the NCMC to make quality negotiation teaching materials and expertise accessible to all, and in so doing, democratise negotiation education. “It is an integral part of the NCMC’s mandate to bring scholars and practitioners together to collaborate on research and education on negotiation and conflict management,” said Roderick Swaab, Professor ...
Wyss Institute’s iNodes team receives ARPA-H Sprint for Women’s Health award to advance the first implantable immune organs to treat ovarian cancer
2024-11-12
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — Ovarian cancer is more deadly than any other type of female reproductive organ cancer. It is estimated that in 2024, in the U.S. alone, more than 12,000 women will die from the disease because available therapies are not effective. To help overcome this striking deficit in women’s health, ARPA-H has selected a team at the Wyss Institute at Harvard University as an awardee of its Sprint for Women’s Health effort to develop “iNodes” – implantable lymphoid organs containing patients’ immune cells – as an entirely novel form of personalized immunotherapy to treat ovarian ...
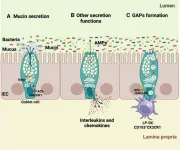
Goblet cells could be the guardians of the gut
2024-11-12
In a recent study, researchers at the University of California, San Diego, have provided new insights into the central role of goblet cells—specialized cells that line the gut—in maintaining a healthy and balanced immune environment within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Led by Dr Fernanda Raya Tonetti, with Dr. Cristina Llorente directing the project and making significant contributions, the study underscores the critical roles of these cells, which act not only as a physical barrier but also ...
Romania’s science journalists join forces on new reporting handbook
2024-11-12
The Balkan Network of Science Journalists and the European Federation for Science Journalism are launching a new science journalism guide, this time in Romanian.
From the Field: A Science Journalist's Handbook is the result of a collective effort by more than 20 Romanian journalists and content creators who dedicated their time and expertise to build a 138-page document designed to help journalists navigate the complex world of science reporting.
The guide was coordinated by science ...
SwRI-led team proposes new solar composition ratios that could reconcile longstanding questions
2024-11-12
SAN ANTONIO — November 12, 2024 — A Southwest Research Institute-led team combined compositional data of primitive bodies like Kuiper Belt objects, asteroids and comets with new solar data sets to develop a revised solar composition that potentially reconciles spectroscopy and helioseismology measurements for the first time. Helioseismology probes the Sun’s interior by analyzing the waves that travel through it, while spectroscopy reveals the surface composition based on the spectral signature produced by each chemical element.
A paper about this research, which ...
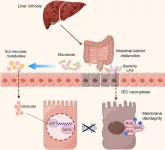
Sodium butyrate inhibits necroptosis by regulating MLKL via E2F1 in intestinal epithelial cells of liver cirrhosis
2024-11-12
Background and Aims
Necroptosis is critical for regulating intestinal epithelial cells (IECs). Butyric acid (BA), produced during intestinal microbial metabolism, protects the intestinal epithelial barrier. However, whether necroptosis occurs in IECs during liver cirrhosis and whether sodium butyrate (NaB) can regulate necroptosis have not yet been reported. In this study, we aimed to investigate whether IECs undergo necroptosis in cirrhosis and whether NaB can regulate necroptosis and the related regulatory mechanisms.
Methods
Serum levels of RIPK3, MLKL, and Zonulin, as well as fecal BA levels, were measured and correlated in 48 patients with liver cirrhosis ...
In greening Arctic, caribou and muskoxen play key role
2024-11-12
The story of Arctic greening has overlooked some main characters. At center stage are climate change and warming temperatures. Meanwhile, large grazing wildlife, such as caribou and muskoxen, also play a key role in the timing and abundance of Arctic plants, according to a study from the University of California, Davis.
The study, published today in the journal PNAS Nexus, highlights the importance of large herbivores to the Arctic ecosystem, linking grazing with plant phenology and abundance in the Arctic tundra.
Phenology is the study of the timing and cyclical patterns in nature, such as when birds migrate, or when a plant first sprouts or blooms. ...
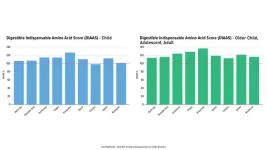
New study confirms whole pork carcass products as high-quality protein sources across diverse cultures and preparations
2024-11-12
A recent study led by researchers from the University of Illinois, including Dr. Hans Stein, confirms that a wide range of pork cuts, Italian hams, and sausages offer excellent protein quality. The study, published in JSFA Reports,1 utilized the Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score (DIAAS) method to measure protein quality, finding that all tested pork products, except one, achieved a DIAAS greater than 100, qualifying them as "excellent" protein sources for children, adolescents, and adults.
The researchers ...
Astronomers’ theory of how galaxies formed may be upended
2024-11-12
CLEVELAND—The standard model for how galaxies formed in the early universe predicted that the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) would see dim signals from small, primitive galaxies. But data are not confirming the popular hypothesis that invisible dark matter helped the earliest stars and galaxies clump together.
Instead, the oldest galaxies are large and bright, in agreement with an alternate theory of gravity, according to new research from Case Western Reserve University published Tuesday November 12 in The Astrophysical Journal. The results challenge astronomers’ understanding of the early universe.
“What the theory of dark matter predicted is not what we ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
[Press-News.org] Study: Student absenteeism crisis may be hurting teacher job satisfactionResearchers warn that rising absenteeism could worsen growing teacher shortages