(Press-News.org) SAN DIEGO, California (Nov. 13, 2024) — Beer drinkers have lower-quality diets, are less active, and are more likely to smoke cigarettes than people who drink wine, liquor, or a combination, according to a study scheduled for presentation at The Liver Meeting, held by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
“Alcohol overuse is the leading cause of cirrhosis in the U.S., and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is rapidly increasing,” said Madeline Novack, chief resident at Tulane School of Medicine’s internal medicine residency program and lead author of the study. “Both types of liver disease often coexist, and lifestyle changes are key to managing and preventing these conditions, starting with understanding the link between alcohol use and poor nutrition.”
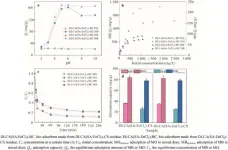
Using a survey of a nationally representative sample of more than 1,900 U.S. adults who reported current alcohol use, researchers compared the diet quality among people who consume beer only (38.9%), wine only (21.8%), liquor only (18.2%), or a combination of alcohol types (21%), measuring self-reported eating habits against the Healthy Eating Index, a validated standardized tool based on dietary guidelines.
None of the alcohol-using groups came close to achieving the 80-point score that is considered an adequate diet on the 100-point Healthy Eating Index, Novack said, but the beer drinkers scored lowest at 49. Wine drinkers scored 55, and both liquor-only drinkers and combination drinkers scored nearly 53.
Beer-only drinkers, who were more likely to be male, younger, smokers, and low income, also reported the highest total daily caloric intake, adjusting for body weight, and the lowest level of physical activity. Previous studies have found that dietary quality declines with increasing alcohol consumption of any type, but little has been reported on the influence of specific alcoholic beverage type.
Novack said the differences in diet quality among drinkers could be attributed to the context in which food and alcohol consumed together. In the U.S., beer is often chosen in settings where the available foods tend to be low in fiber and high in carbohydrates and processed meats. On the other hand, wine — particularly red wine — is often paired with meals complete with meat, vegetables and dairy.
Another possibility is the inverse, where dietary choices influence the choice of alcohol consumed, Novack said. For example, fried or salty foods create thirst that may also lead to beer-only consumption.
For prevention of liver disease and other health issues, physicians should ask about the type of alcohol consumed to guide discussion of healthy behaviors, Novack said. For example, findings of this study can be applied to patients who identify as beer-only drinkers and physicians could suggest increasing fruit and vegetable intake, as well as physical activity.
Madeline Novack, MD, will present the study, “Beer Consumption is Associated with Low Dietary Quality Among Alcohol Users,” abstract 3019, on Sunday, Nov. 17, at 1 p.m. PST. The study is simultaneously being published in the journal Nutrients.
###
About The Liver Meeting ®
The Liver Meeting® brings together clinicians, associates and scientists from around the world to exchange information on the latest research, discuss new developments in liver treatment and transplantation, and network with leading experts in the field of hepatology.
About AASLD
AASLD is the leading organization of scientists and health care professionals committed to preventing and curing liver disease. We foster research that leads to improved treatment options for millions of liver disease patients. We advance the science and practice of hepatology through educational conferences, training programs, professional publications and partnerships with government agencies and sister societies.
END
As global demand for sustainable energy solutions increases, bioethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass is gaining traction. However, traditional methods face limitations due to high processing costs and waste issues. A recent study led by Xinchuan Yuan, published in the Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts, presents an innovative biomass pretreatment method that not only improves bioethanol production efficiency but also utilizes biomass residues as bio-adsorbents for wastewater treatment, potentially transforming the industry.
Producing ...
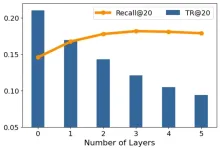
Graph convolutional networks (GCNs) have become prevalent in recommender system (RS) due to their superiority in modeling collaborative patterns. Although improving the overall accuracy, GCNs unfortunately amplify popularity bias --- tail items are less likely to be recommended. This effect prevents the GCN-based RS from making precise and fair recommendations, decreasing the effectiveness of recommender systems in the long run.
Performance change of LightGCN with different graph convolution layers on Gowalla. Recall@20 and TR@20 ...
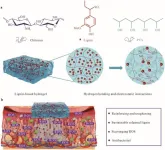
As the demand for advanced wound healing and drug delivery materials grows, scientists are turning to sustainable, bioactive materials for innovative solutions. A recent study by Bowei Wang et al., published in the Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts, presents a breakthrough in lignin-based hydrogels designed to combine mechanical strength with bioactivity. This research reveals a controlled-release polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and chitosan (CS) hydrogel, augmented with sulfonated lignin, which could revolutionize the treatment of complex wounds and enable sustained drug ...
With an increasing focus on environmental sustainability, researchers are seeking ways to improve the biodegradability and mechanical properties of bioplastics, particularly polylactic acid (PLA). A recent study by June-Ho Choi and colleagues, published in the Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts, presents a promising approach that enhances the compatibility and decomposition of PLA when combined with biomass through a process called torrefaction. This innovation offers practical improvements for sustainable material applications, positioning PLA as a viable, eco-friendly alternative in various industries.
PLA, ...
Scientists detect a heightened “threat vigilance” reaction in adolescents after a few hours of isolation, which socialising online doesn’t appear to ameliorate.
They say the findings might shed light on the link between loneliness and mental health conditions such as anxiety disorders, which are on the rise in young people.
Experiment is the first to find an increased threat response triggered by isolation in humans (previous studies have found the effect in animals such as mice).
People ...
Migratory birds are known for their ability to traverse thousands of kilometres to reach their breeding or wintering grounds. Research by Bangor University found that these birds, in this case, Eurasian reed warblers (Acrocephalus scirpaceus) are using only the Earth's magnetic inclination and declination to determine their position and direction. This challenges the long-held belief that all components of the Earth's magnetic field, especially total intensity, are essential for accurate navigation.
Scientists have long believed that these birds use a 'map-and-compass' system: they first ...
The ketogenic “keto” diet and intermittent fasting have surged in popularity, embraced by everyone from weekend warriors to endurance athletes. These trends promise to harness the power of ketosis — a metabolic state where the body burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. Advocates tout its benefits, from weight loss to neuroprotection.
A collaborative research team is now tackling the unanswered questions surrounding ketosis.
Rather than adding to the growing, and often confusing, literature on the effects of ketogenic ...
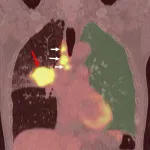
Niigata, Japan – Dr. Watanabe and his teams from Niigata University have revealed that PET/CT image analysis using artificial intelligence (AI) can predict the occurrence of interstitial lung disease, known as a serious side effect of immunotherapy in lung cancer.
Immunotherapy has dramatically improved the treatment outcomes of primary lung cancer; however, it sometimes causes a serious side effect called interstitial lung disease. Interstitial lung disease is characterized by scarring (fibrosis) of the ...
There is a large window-lined laboratory in the back of one of Clemson University’s most storied buildings, Newman Hall, filled with machines that look like they were extracted straight from Dr. Jekyll’s lab. On one wall a contraption made of pullies and wires attached to the ceiling waits to drop objects and measure the impact; in the middle of the room, a giant metal base shakes a pallet of boxes in perpetuity; on the other side of the room sits what looks like a gigantic nut cracker big enough to squish a small car – but the most Medieval-looking area is the bay on the east side of the room full of machines designed to smack heads.
This is the Clemson Headgear ...
Specific combinations of long term conditions have a major role in the additional pressures the NHS faces every winter, because they are associated with significantly higher risks of hospital admissions and death, finds research published in the open access journal BMJ Medicine.
The risk of hospital admission was 11 times higher among those with the quartet of cancer, kidney disease, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes than it was among those without any of these long term conditions, the findings show.
And ...