(Press-News.org) About The Study: This study found artemisinin partial resistance in Ugandan children with complicated malaria associated with the Pfkelch13 A675V variation and also found suboptimal 28-day efficacy of parenteral artesunate followed by oral artemether/lumefantrine therapy.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Chandy C. John, MD, MS, email chjohn@iu.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.22343)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: This study is being presented at the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene Annual Meeting.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2024.22343?guestAccessKey=e1d2a9e9-6787-4bb6-8a5e-012c4e656527&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=111424
END
Artemisinin partial resistance in Ugandan children with complicated malaria
JAMA
2024-11-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
When is a hole not a hole? Researchers investigate the mystery of 'latent pores'
2024-11-14
Sometimes the holes, or pores, in the molecular structure of a chemical only appear in the presence of certain conditions or other ‘guest’ molecules. This affects the field of separation—one of the most important processes in industry—but researchers have only just begun to unravel this phenomenon
Researchers have explored how a particular chemical can selectively trap certain molecules in the cavities of its structure—even though in normal conditions it has no such cavities. This innovative material with now-you-see-them-now-you-don’t holes could lead to more efficient methods for separating ...
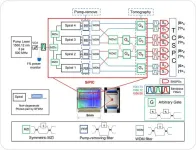
ETRI, demonstration of 8-photon qubit chip for quantum computation
2024-11-14
A group of South Korean researchers has successfully developed an integrated quantum circuit chip using photons (light particles). This achievement is expected to enhance the global competitiveness of the team in quantum computation research.
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) announced that they have developed a system capable of controlling eight photons using a photonic integrated-circuit chip. With this system, they can explore various quantum phenomena, such as multipartite entanglement resulting from the interaction of the photons.
ETRI’s extensive research on silicon-photonic quantum ...
Remote telemedicine tool found highly accurate in diagnosing melanoma
2024-11-14
Collecting images of suspicious-looking skin growths and sending them off-site for specialists to analyze is as accurate in identifying skin cancers as having a dermatologist examine them in person, a new study shows.
According to the study authors, the findings add to evidence that such technology could help to reliably address diagnostic and treatment disparities for lower-income populations with limited access to dermatologists. It may also help dermatologists quickly catch cases of melanoma, a serious form of skin cancer that kills more than 8,000 Americans a year.
Their new system, which the researchers call SpotCheck, enables skin cancer specialists ...
New roles in infectious process for molecule that inhibits flu
2024-11-14
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Researchers have identified new roles for a protein long known to protect against severe flu infection – among them, raising the minimum number of viral particles needed to cause sickness.
The protein also helps prevent unfamiliar viruses from mutating after they infect a new host, the study found – meaning its absence during an immune response could enable an animal virus spilled over to people to adapt rapidly to human hosts.
The combined findings by scientists at The Ohio State University add up to potential trouble for people deficient in the protein, called IFITM3 – especially if an avian or swine flu were to gain ...
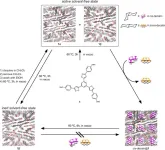
Transforming anion exchange membranes in water electrolysis for green hydrogen production
2024-11-14
Hydrogen is a promising energy source due to its high energy density and zero carbon emissions, making it a key element in the shift toward carbon neutrality. Traditional hydrogen production methods, like coal gasification and steam methane reforming, release carbon dioxide, undermining environmental goals. Electrochemical water splitting, which yields only hydrogen and oxygen, presents a cleaner alternative. While proton exchange membrane (PEM) and alkaline water electrolyzers (AWEs) are available, they face limitations in either cost or efficiency. PEM electrolyzers, for instance, rely on costly platinum group metals (PGMs) as catalysts, whereas ...
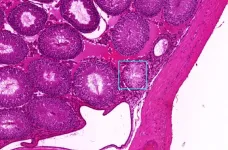
AI method can spot potential disease faster, better than humans
2024-11-14
PULLMAN, Wash. – A “deep learning” artificial intelligence model developed at Washington State University can identify pathology, or signs of disease, in images of animal and human tissue much faster, and often more accurately, than people.
The development, detailed in Scientific Reports, could dramatically speed up the pace of disease-related research. It also holds potential for improved medical diagnosis, such as detecting cancer from a biopsy image in a matter of minutes, a process that typically takes ...
A development by Graz University of Technology makes concreting more reliable, safer and more economical
2024-11-14
Concreting mistakes can be expensive. Concrete poured too quickly often leads to a lack of colour uniformity, irregularities in the structure and uneven surfaces. Particularly in the case of exposed concrete, expensive reworking using concrete cosmetics is then necessary, sometimes a wall may even have to be demolished. In addition, if the fresh concrete rises too quickly in the formwork, there is a certain risk potential for the workers, as this can cause the formwork to break. In their DigiCoPro project, Ralph Stöckl and ...
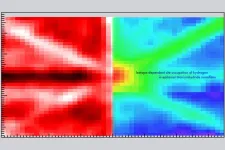
Pinpointing hydrogen isotopes in titanium hydride nanofilms
2024-11-14
Tokyo, Japan – Although it is the smallest and lightest atom, hydrogen can have a big impact by infiltrating other materials and affecting their properties, such as superconductivity and metal-insulator-transitions. Now, researchers from Japan have focused on finding an easy way to locate it in nanofilms.
In a study published recently in Nature Communications, researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo have reported a method for determining the location of hydrogen in nanofilms.
Because they are very small, hydrogen atoms can easily migrate into the framework of other materials. Titanium absorbs hydrogen to give titanium hydrides, making ...
Political abuse on X is a global, widespread, and cross-partisan phenomenon, suggests new study
2024-11-14
A new study suggests that political abuse is a key feature of political communication on social media platform, ‘X’, and whether on the political left or right, it is just as common to see politically engaged users abusing their political opponents, to a similar degree, and with little room for moderates.
While previous research into such online abuse has typically focused on the USA, the current study found that abuse followed a common ally-enemy structure across the nine countries for which there was available data: Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Poland, Spain, Turkey, ...
Reintroduction of resistant frogs facilitates landscape-scale recovery in the presence of a lethal fungal disease
2024-11-14
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — A remote lakeshore deep inside Yosemite National Park teems with life: coyotes, snakes, birds, tadpoles, frogs. The frogs are at the heart of this scene, which a decade ago was much different. It was quiet — and not in a good way. The frogs that are so central to this ecosystem were absent, extirpated by a deadly fungal disease known as amphibian chytrid fungus.
Now, thanks to the consistent and focused efforts of researchers and conservationists to save, then reintroduce, mountain yellow-legged frogs to this and numerous other lakes in Yosemite, their populations are again thriving.
A ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
[Press-News.org] Artemisinin partial resistance in Ugandan children with complicated malariaJAMA