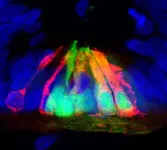
(Press-News.org) Two conflicting memories can both be activated in a worm’s brain, even if only one memory actively drives the animal’s behaviour, finds a new study by UCL researchers.
In the paper published in Current Biology, the researchers showed how an animal’s sex drive can at times outweigh the need to eat when determining behaviour, as they investigated what happens when a worm smells an odour that has been linked to both good experiences (mating) and bad experiences (starvation).
The scientists were seeking to understand how an animal’s brain decides if something it encounters is good or bad, and how this determines the animal’s response.
They found that by conditioning male worms to have both positive and negative associations with an odour, both memories will be activated when the worm smells the odour, but only one will impact the animal’s behaviour.
The researchers say their findings can be further investigated to gain insight into health conditions where this process goes wrong, such as in post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), where memories that should remain latent (dormant) are still problematically influencing behaviours and emotions.
Lead author Dr Arantza Barrios (UCL Cell & Developmental Biology) said: “For our study, we were looking into the brain of the male worm, in order to understand the cellular or molecular mechanisms that determine if a particular memory impacts behaviour. An important part of how we learn is that our brains are able to adapt to new information and override previous associations.”
Co-first author Dr Susana Colinas Fischer (UCL Cell & Developmental Biology) added: “By understanding what a very small worm is thinking, we are able to learn more about the processes underlying our own more complex thinking patterns.”
The study was undertaken with male C. elegans roundworms, a species of worm 1mm in length that is very commonly used as a model organism in scientific research. The worms were presented with an odour that is innately attractive to them, which the researchers say is akin to a person smelling a delicious dinner.
In a series of experiments, the researchers modified the worms’ preference for the odour and monitored their behaviour and brain activity.
The worms’ instinct to approach the odour was overridden with aversive conditioning, in which the worms experienced the odour together with a punishment of starvation. The researchers then sought to override this learned avoidance with further conditioning, whereby the odour was presented alongside a female mate and some sexual experience, so that the male worms developed a new positive association with the odour.
The analysis identified a circuit of brain cells that represents both positive and negative associations with things the animal has encountered previously, centred on a particular neuropeptide (a chemical messenger in the brain) that stores the memories of both the starvation and mating associations with the odour.
The researchers found that in worms that had been conditioned to associate the odour with starvation and mating, both memories were activated in the brain. But only one of them – the mating association – still caused the worm to approach the odour.
The researchers say this indicates that the prospect of a mating reward overrode the prospect of a starvation punishment, even though both memories remained intact – while the worm no longer avoided the odour, the negative memory of starvation was still represented in the brain activity.
Co-first author Dr Laura Molina-García (UCL Cell & Developmental Biology) said: “We found that even in an animal with a very small brain like that of a roundworm, two conflicting memories can both be activated at the same time, with one memory impacting behaviour and one memory remaining latent.
“The way an animal’s brain can flexibly represent something that is partly good and partly bad helps it to learn and adapt to new information. By understanding how some memories can override other conflicting memories, we hope to inform research into treating the maladaptation of this process such as in PTSD.”
The research was supported by the Royal Society, Wellcome and Leverhulme Trust.
END
How conflicting memories of sex and starvation compete to drive behavior
2024-11-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists discover ‘entirely unanticipated’ role of protein netrin1 in spinal cord development
2024-11-14
Scientists at the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA have uncovered an unexpected role for the molecule netrin1 in organizing the developing spinal cord.
The researchers discovered that netrin1, which is known primarily as a guidance cue that directs growing nerve fibers, also limits bone morphogenetic protein, or BMP, signaling to specific regions of the spinal cord. This boundary-setting function is critical because this signaling activity must be precisely confined to the dorsal region for sensory neurons to develop properly.
Their findings, published in Cell ...
Novel SOURCE study examining development of early COPD in ages 30 to 55
2024-11-14
Miami (November 14, 2024) – Researchers are exploring how small airway abnormalities in younger smokers could help identify who is at risk of developing COPD and establish how the chronic lung disease progresses, according to a new article. The article is published in the September 2024 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is an inflammatory lung disease, comprising several conditions, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, and can be caused ...
NRL completes development of robotics capable of servicing satellites, enabling resilience for the U.S. space infrastructure
2024-11-14
WASHINGTON – U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) Naval Center for Space Technology (NCST) in partnership with Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) successfully completed development of a spaceflight qualified robotics suite capable of servicing satellites in orbit, Oct. 8.
Under DARPA funding, NRL developed the Robotic Servicing of Geosynchronous Satellites (RSGS) Integrated Robotic Payload (IRP). This transformative new space capability was delivered to DARPA’s commercial partner, Northrop Grumman’s SpaceLogistics, for ...
Clinical trial shows positive results for potential treatment to combat a challenging rare disease
2024-11-14
An international, phase 3 clinical trial led by investigators at Mass General Brigham could improve the treatment of a rare disease that can cause debilitating symptoms. The study, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, found that treatment with inebilizumab greatly reduced the symptoms of immunoglobulin G4–related disease (IgG4-RD), compared to placebo.
“This is a huge day in the history of this disease,” said lead author John Stone, MD, MPH, a rheumatologist in the Division of Rheumatology, Allergy, and Immunology at Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system. “We are thrilled to have ...
New research shows relationship between heart shape and risk of cardiovascular disease
2024-11-14
A new multi-national study has revealed that the shape of the heart is influenced in part by genetics and may help predict the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Researchers from Queen Mary University of London, King’s College London, University of Zaragoza and University College London, as well as Complexo Hospitalario Universitario A Coruña are first to examine the genetic basis of the heart’s left and right ventricles using advanced 3D imaging and machine learning.
Prior ...
Increase in crisis coverage, but not the number of crisis news events
2024-11-14
The world appears to be plagued by crises.
“The financial crisis, the European debt crisis, the migration crisis, the COVID-19 pandemic, the war in Ukraine, the war in Gaza… The world seems to be stumbling from one existential crisis to the next, barely recovering from one before the next one hits,” said Stefan Geiß, a professor from the Department of Sociology and Political Science at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU).
However, are there really more crises now than before?
Has it always been this way, or is something new happening? And if there are more public crises today ...
New study provides first evidence of African children with severe malaria experiencing partial resistance to world’s most powerful malaria drug
2024-11-14
NEW ORLEANS (November 14, 2024) — A new study from Uganda provides the first evidence to date that resistance to a lifesaving malaria drug may be emerging in the group of patients that accounts for most of the world’s malaria deaths: young African children suffering from serious infections. The study, presented today at the Annual Meeting of the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene and published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), documented partial resistance to the malaria drug artemisinin in 11 of 100 children, ages 6 months to 12 years, who were being treated for ...
Texting abbreviations makes senders seem insincere, study finds
2024-11-14
If you want to seem sincere and receive more responses to your texts, spell out words instead of abbreviating them, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
Researchers conducted eight experiments with a total of more than 5,300 participants using various methods. Across the experiments, individuals who used texting abbreviations were perceived as more insincere and were less likely to receive replies because they were seen as exerting less effort in text conversations. The research was published online in the Journal of Experimental Psychology: General.
“In daily interactions, ...
Living microbes discovered in Earth’s driest desert
2024-11-14
Highlights:
The Atacama Desert is one of the most extreme habitats on Earth.
Atacama surface soil samples include a mix of DNA from inside and outside living cells.
A new technique allows researchers to separate external and internal DNA to identify microbes colonizing this hostile environment.
This approach for analyzing microbial communities could potentially be applied to other hostile environments, like those on other planets.
Washington, D.C.—The Atacama Desert, which runs along the Pacific Coast in Chile, is the driest place on the planet and, largely because of that aridity, hostile to most living things. ...
Artemisinin partial resistance in Ugandan children with complicated malaria
2024-11-14
About The Study: This study found artemisinin partial resistance in Ugandan children with complicated malaria associated with the Pfkelch13 A675V variation and also found suboptimal 28-day efficacy of parenteral artesunate followed by oral artemether/lumefantrine therapy.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Chandy C. John, MD, MS, email chjohn@iu.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.22343)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...