(Press-News.org) Children born to mothers who take antiseizure medications to manage seizures and psychiatric conditions during pregnancy may face increased risks of neurodevelopmental conditions, according to new data from researchers at Drexel’s Dornsife School of Public Health.
The current work -- using data from more than three million children from the United Kingdom and Sweden, including 17,495 who were exposed to antiseizure medications during pregnancy -- found that children exposed to the antiseizure drug lamotrigine in utero were at no additional risk for autism or intellectual disability compared with those exposed to other antiseizure medications. However, children exposed to valproate, topiramate, and carbamazepine were linked to specific neurodevelopmental issues. The findings were published this month in the journal Nature Communications.
However, the absolute risk of neurodevelopmental outcomes in offspring is low, the researchers caution, regardless of antiseizure drug regimen. Compared to children unexposed to antiseizure medications, those exposed to the drug topiramate during pregnancy were 2.5 times more likely to be diagnosed with intellectual disability, which raises their risk to 2.1% by age 12. In comparison with other drugs available, the authors found very little data suggesting that the drug lamotrigine in pregnancy increases the risk of neurodevelopmental issues in offspring.
“Our findings suggest that while certain medications may pose some risk, lamotrigine may be a less risky option,” said co-senior author Brian K. Lee, PhD, a professor in the Dornsife School of Public Health. “Active monitoring of any antiseizure medication is critical to ensure safety and effectiveness, particularly during pregnancy.”
This study contrasts earlier studies in that it did not find a statistically significant link between topiramate or levetiracetam and ADHD in children, regardless of whether the birthing parent had an epilepsy diagnosis.
According to the researchers, the data does not argue against use of antiseizure medications in patients who benefit, but rather encourages these patients to have a conversation with their doctor to determine if their course of treatment is most appropriate for them.
“Decisions should be made that are tailored to individual patients,” said co-lead author Paul Madley-Dowd, PhD, a research fellow at the University of Bristol. “Stopping antiseizure medications can cause individual harm and harm to offspring, so these conversations always need to happen with a clinician.”
This study supports findings from previous research that link the antiseizure drugs valproate, topiramate, and carbamazepine with neurodevelopmental diagnoses in offspring, such as autism, intellectual disability and ADHD. Previous studies in smaller populations also link in utero exposure of these drugs with neurodevelopmental outcomes in offspring, such as ones linking topiramate and intellectual disability, and those associating valproate and lower IQ.
The study utilized data on drug prescriptions in the United Kingdom, and dispensation and self-reported data on drug use in Sweden, as well as electronic health records data for diagnoses. The authors conducted a sibling analysis to help minimize the influence of other factors, such as severity of diagnosis and underlying genetics, that may influence the results.
“The link between these drugs and children’s neurodevelopmental outcomes is there, even if the risk isn’t much higher than it is in the unexposed population,” said co-lead author Viktor H. Ahlqvist, a postdoctoral researcher at Karolinska Institutet. “If you’re pregnant or trying to become pregnant, and taking one of these medications, it may be worth talking with your physician to make sure you’re taking the best medicine for your needs, while minimizing risk to future children.”
Despite the study’s large sample size, the authors say patients could benefit from further research from multiple countries on safety of these drugs as the landscape of options available to patients changes.
In addition to Lee, Madley-Dowd and Ahlqvist, other authors included co-senior authors Cecilia Magnusson from the Karolinska Institutet and Dheeraj Rai from the University of Bristol, and collaborators from Drexel University, Pennylvania State University, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, University College London, University of Bristol, and the Karolinska Institutet.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health (1R01NS107607).
The paper, “Antiseizure Medication Use During Pregnancy and Children’s Neurodevelopmental Outcomes” is available here.
END
Children exposed to antiseizure meds during pregnancy face neurodevelopmental risks, Drexel study finds
2024-11-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Adding immunotherapy to neoadjuvant chemoradiation may improve outcomes in esophageal cancer
2024-11-15
Bottom Line: In patients with unresectable, locally advanced esophageal cancer, the triple combination of radiation, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy made tumors more amenable to surgery, which was associated with significantly improved outcomes.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Background: “Curative resection unequivocally serves as the cornerstone for treating resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC); ...
Scientists transform blood into regenerative materials, paving the way for personalized, blood-based, 3D-printed implants
2024-11-15
Scientists have created a new ‘biocooperative’ material based on blood, which has shown to successfully repair bones, paving the way for personalised regenerative blood products that could be used as effective therapies to treat injury and disease.
Researchers from the Schools of Pharmacy and Chemical Engineering at the University of Nottingham have used peptide molecules that can guide key processes taking place during the natural healing of tissues to create living materials that enhance tissue regeneration. The research published today in Advanced ...
Maarja Öpik to take up the position of New Phytologist Editor-in-Chief from January 2025
2024-11-15
The New Phytologist Foundation is delighted to announce that Professor Maarja Öpik will take up the position of Editor-in-Chief of New Phytologist from January 2025 for an initial term of five years.
Maarja has served as a member of New Phytologist's editorial board since 2013 and is Professor of Molecular Ecology and Director of the Institute of Ecology and Earth Sciences at the Faculty of Science and Technology at the University of Tartu, Estonia.
Maarja’s research addresses the interactions between plants and mycorrhizal fungi, with ...
Mountain lions coexist with outdoor recreationists by taking the night shift
2024-11-15
Mountain lions in greater Los Angeles are proactively shifting their activity to avoid interacting with cyclists, hikers, joggers and other recreationists, finds a study from the University of California, Davis, Cal Poly Pomona and the National Park Service.
The study, published Nov. 15 in the journal Biological Conservation, found that mountain lions living in areas with higher levels of human recreation were more nocturnal than lions in more remote regions who were more active at dawn and dusk. The authors said their findings offer a hopeful example of human-wildlife coexistence amid a large, dense human population.
“People are increasingly enjoying recreating ...
Students who use dating apps take more risks with their sexual health
2024-11-15
In May, the WHO raised the alarm over the rise in incidence of sexually transmitted illnesses (STIs) in many regions of the world, currently running at more than a million new cases per day. Among high-income countries, the US has one of the highest prevalences of STIs, and this problem is getting worse. For example, the incidence of chlamydia has more than doubled since 2000, while gonorrhea increased by 40% and syphilis by 400%. The highest prevalence is among young adults between 20 and 34 years of age.
Over ...
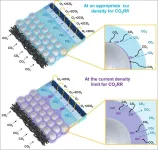
Breakthrough idea for CCU technology commercialization from 'carbon cycle of the earth'
2024-11-15
The research team led by Dr. Hyung-Suk Oh and Dr. Woong Hee Lee at the Clean Energy Research Center at Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Sang-Rok Oh) has developed a silver-silica composite catalyst capable of reversible local pH control through a silica-hydroxide cycle, inspired by Earth’s natural cycles. This research draws inspiration from the carbonate-silicate cycle, known as the Earth’s inorganic carbon cycle, where carbon dioxide (CO₂) maintains balance. CO₂ is removed from ...
Keck Hospital of USC earns an ‘A’ Hospital Safety Grade from The Leapfrog Group
2024-11-15
LOS ANGELES — Keck Hospital of USC earned an “A” Hospital Safety Grade from The Leapfrog Group, an independent national nonprofit watchdog focused on patient safety.
This is the ninth “A” grade the hospital has received since 2019.
“An ‘A’ grade once again puts Keck Hospital among the safest hospitals in the nation, and reflects the hospital’s dedication to maintaining the highest standards of quality and safety protocols,” ...
Depression research pioneer Dr. Philip Gold maps disease's full-body impact
2024-11-15
Bethesda, Maryland, USA, 14 November 2024 – A landmark paper by distinguished neuroendocrine psychiatrist Dr. Philip W. Gold, published in Brain Medicine's Seymour Reichlin Centenary Festschrift collection, presents a masterful synthesis of how depression fundamentally alters the body's stress response systems, challenging long-held views of the condition.
The Viewpoint Review, published online November 14, 2024, represents a culmination of Dr. Gold's pioneering work in neuroendocrine psychiatry and honors the centenary of Dr. Seymour Reichlin, a foundational figure in neuroendocrinology whose ...
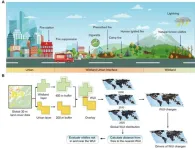
Rapid growth of global wildland-urban interface associated with wildfire risk, study shows
2024-11-15
Rapid human expansion into natural landscapes, resulting in the growth of the wildland-urban interface (WUI), has heightened risks associated with wildfires.
Prof. WANG Jianghao’s team from the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has recently mapped global WUI changes in 2000, 2010, and 2020, revealing alarming upward trends in WUI areas.
This work, published in Science Advances, provides critical insights into how urbanization can intensify potential wildfire risks faced by people worldwide.
Against ...
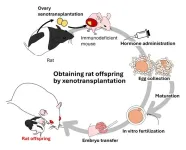
Generation of rat offspring from ovarian oocytes by Cross-species transplantation
2024-11-15
Niigata and Toyama, Japan - The idea of maturing oocytes in the ovary to produce offspring has been implemented in various ways. One such method, ovarian transplantation, is a relatively simple procedure for obtaining eggs, compared to in vitro culture of ovaries and follicles. However, it is still difficult to transplant ovaries into cellular immunodeficient mice and produce offspring from the eggs grown in the mice.
In order to produce offspring from xenotransplanted ovaries, Japanese researchers at Niigata University and University ...