Diabetes drug shows promise in protecting kidneys
SGLT2 inhibitor canagliflozin helps oxygenate kidneys while causing glucose removal through urine
2024-11-18
(Press-News.org)
Type 2 diabetes can lead to diabetic kidney disease, but a class of drugs that cause the kidneys to remove glucose through urine has been gaining attention. An Osaka Metropolitan University-led research group has investigated how such drugs maintain kidney health.
Known as SGLT2 (sodium-glucose cotransporter-2) inhibitors, the drugs are used to treat type 2 diabetes along with an exercise and diet regimen. The group led by Graduate School of Medicine Associate Professor Katsuhito Mori focused on the SGLT2 inhibitor canagliflozin and its effects on the kidney.
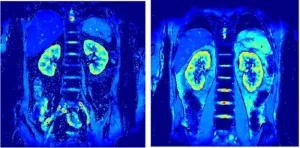
Using BOLD (blood oxygenation level-dependent) MRI, a method used to see changes in blood oxygen flow in the brain to monitor activity, the group found that patients on canagliflozin for five days showed more oxygen in their kidneys the first day after administration of the drug. The researchers believe this indicates that SGLT2 inhibitors might improve the oxygenation of the kidneys, thereby protecting the organs.
“In animal experiments, the amount of oxygen in the kidneys can be measured by inserting a microelectrode, but this is not possible in humans,” Professor Mori explained. “BOLD MRI can measure kidney oxygenation non-invasively, and this is expected to become an important technology for elucidating the mechanisms of kidney disease for the development of therapeutic drugs.”
The findings were published in Frontiers in Endocrinology.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-18
SAN DIEGO, California (Nov. 18, 2024) — Since the adoption of a new model for assessing the severity of liver disease, women are more likely to be added to the waitlist for a liver transplant, more likely to receive a transplant, and less likely to drop off the waitlist — closing the gap between men and women candidates, according to a study scheduled for presentation today at The Liver Meeting held by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
In July 2023, the federal Organ Procurement and Transplant Network (OPTN) updated its Model for End-Stage Liver Disease to a new version, known as MELD 3.0, to better account for differences between ...
2024-11-18
People who take an anticoagulant medicine double their risk of an internal bleed if they take a type of painkiller called a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as ibuprofen, diclofenac or naproxen, according to research published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Monday).
Anticoagulants are usually prescribed to people who develop a blood clot in the legs or lungs, known as a venous thromboembolism, which affects about one in 12 people. NSAIDs are a popular type of painkiller used to manage issues like headaches, period pain, back pain and arthritis.
The new study is the largest of its kind and shows that ...
2024-11-18
Researchers have developed a mindfulness therapy tailored specifically to appeal to teenagers to help them cope with increasing levels of depression and mental health problems.
The approach teaches participants to tune into and manage negative thought patterns that can trigger or maintain depression, and allow them instead to focus on the present moment.
Developed by teams at the University of Cambridge and King’s College London, the ATTEND programme – Adolescents and carers using mindfulness Therapy To END depression – also includes sessions for parents and guardians, ensuring a family-centred approach ...
2024-11-17
Using an innovative risk score assessment score, heart researchers at Intermountain Health in Salt Lake City say they can accurately predict whether patients being assessed for kidney transplant will likely have a future major cardiac event, like a heart attack or stroke, according to a new study.
Intermountain Health clinicians regularly review patient data through their electronic health system to determine who may have heart disease without knowing it. Now, in a major new study, Intermountain heart researchers found that using their Intermountain ...
2024-11-17
About The Study: In this retrospective cohort study, decline in kidney function was frequent in patients with transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM) and was consistently associated with an increased risk of mortality, even after adjusting for established markers of worsening ATTR-CM. eGFR decline represents an independent marker of ATTR-CM disease progression that could guide treatment optimization in clinical practice.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Marianna Fontana, MD, PhD, email m.fontana@ucl.ac.uk.
To access the embargoed study: ...
2024-11-17
About The Study: This randomized clinical trial found that partial cardiac denervation was an effective procedure to reduce the occurrence of postoperative atrial fibrillation (POAF) after isolated coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) without additional postoperative complications. These results suggest that partial cardiac denervation may be a good option for cardiac surgeons to consider for preventing POAF after CABG.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Wei Feng, MD, PhD (fengwei@fuwai.com) and Wei Zhao, MD, PhD (zhaowei_fw@163.com).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at ...
2024-11-17
About The Study: In the Finerenone Trial to Investigate Efficacy and Safety Superior to Placebo in Patients with Heart Failure (FINEARTS-HF), finerenone reduced the risk of the primary end point similarly in women and men with heart failure with mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction. Finerenone, a nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, had similar tolerability in women and men.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, John J. V. McMurray, MD, email john.mcmurray@glasgow.ac.uk.
To ...
2024-11-17
About The Study: In patients with heart failure with mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction, finerenone, a nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, resulted in more frequent hyperkalemia and less frequent hypokalemia. However, with protocol-directed surveillance and dose adjustment, clinical benefit associated with finerenone relative to placebo was maintained even in those whose potassium level increased to greater than 5.5 mmol/L.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Scott D. Solomon, MD, email ssolomon@rics.bwh.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our ...
2024-11-17
Skeletal size may be altered by gender-affirming hormone therapy only if puberty has also been suppressed during adolescence, according to research presented at the 62nd Annual European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology Meeting in Liverpool. The findings from this research, carried out by Amsterdam UMC, not only help researchers further understand the roles sex hormones play on the skeleton but may also improve counselling on gender-affirming treatment in transgender individuals.
Skeletons of men and women vary in size and proportion. For instance, men typically have broader shoulders while women have a wider pelvis. Gender-affirming hormones ...
2024-11-16
About The Study: Coronary heart disease polygenic risk scores that performed similarly at the population level demonstrated highly variable individual-level estimates of risk. Recognizing that coronary heart disease polygenic risk scores may generate incongruent individual-level risk estimates, effective clinical implementation will require refined statistical methods to quantify uncertainty and new strategies to communicate this uncertainty to patients and clinicians.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Scott M. Damrauer, MD, email Scott.Damrauer@pennmedicine.upenn.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Diabetes drug shows promise in protecting kidneys
SGLT2 inhibitor canagliflozin helps oxygenate kidneys while causing glucose removal through urine

