(Press-News.org) The scientific debate around the installation of a massive underwater curtain to protect Antarctic ice sheets from melting lacks its vital political perspective. A Kobe University research team argues that the serious questions around authority, sovereignty and security should be addressed proactively by the scientific community to avoid the protected seventh continent becoming the scene or object of international discord.
A January 2024 article in Nature put the spotlight on a bold idea originally proposed by Finnish researchers to save the West Antarctic Ice Sheet from melting, which is estimated to potentially raise global sea levels by up to 5 meters. The idea of installing an underground curtain 80 kilometers long and 100 meters high to prevent warm underground water from reaching the glaciers made an international splash, and “What had been a technical discussion among some scientists quickly became a social debate involving the general public,” says Kobe University international law researcher SHIBATA Akiho. In the scientific debate, however, the political aspect has either been completely ignored or dangerously downplayed, which runs the risk of kindling conflict around a project that is meant to protect humanity, in a setting that has been a model for peaceful international collaboration for over 60 years.
As experts on the international law that governs the Antarctic’s peaceful existence dedicated to scientific investigation, Shibata and a visiting scholar from the Peace Research Institute Frankfurt, Patrick FLAMM, scrambled to put together a careful analysis of the political repercussions of the global superproject. Shibata says, “We believe that it was important to publish a paper within one year of the original proposal, before the social debate takes on a life of its own.”
In a policy paper now published in the journal International Affairs, the Kobe University researcher points out consequences along three main themes: authority, sovereignty and security. Concerns about authority ask who is in a position to decide on the realization of such a project and what this means for the power balance in the body governing access to the Antarctic. Sovereignty concerns are centered around the implications for extant and dormant territorial claims. And questions around security consider how to practically safeguard a structure that would certainly be seen as planetary critical infrastructure. Shibata sums up, saying: “This paper sheds light on the political and legal ‘shadows’ hidden behind the exciting surface of science and technology. However, we believe that it is necessary for the members of society to make decisions on the development of these technologies based on a thorough understanding of such negative aspects.”
While the researchers write that “In the current climate, with growing international rivalry and great power strategic competition, it would be an extremely unlikely diplomatic achievement to secure the level of international cooperation … required for the proposed glacial geoengineering infrastructures,” they also point out a way forward by looking back. In the early 1980s, a smoldering conflict around guidelines for Antarctic mineral extraction got resolved by the 1991 “Protocol on Environmental Protection to the Antarctic Treaty,” which proactively prohibited mining in the Antarctic indefinitely. This solution set a precedent for the treaty parties to seek solutions that avoid international discord over the Antarctic.
The Kobe University law expert is careful to point out that prohibition is not the default solution, however. He explains: “Recently, momentum has gathered among natural scientists to examine such technologies more multilaterally from the viewpoint of whether they are appropriate in the first place. If in such a deeper scientific and technical discussion the argument is that there are social benefits that outweigh the governance risks we have presented, then again, we international political scientists and international legal scholars need to be involved in this discussion. Perhaps then the discussion will no longer be about protecting the key principles of the current Antarctic Treaty System while considering this technology but about modifying those key principles themselves.”
This research was funded by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (grant 21K18124) and the Kobe University Strategic International Collaborative Research Grant Type C. It was conducted in collaboration with a researcher from the Peace Research Institute Frankfurt.
Kobe University is a national university with roots dating back to the Kobe Commercial School founded in 1902. It is now one of Japan’s leading comprehensive research universities with nearly 16,000 students and nearly 1,700 faculty in 10 faculties and schools and 15 graduate schools. Combining the social and natural sciences to cultivate leaders with an interdisciplinary perspective, Kobe University creates knowledge and fosters innovation to address society’s challenges.
END
Political shadows cast by the Antarctic curtain
2024-11-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists lead study on ‘spray on, wash off’ bandages for painful EB condition
2024-11-18
Research into new bandaging aims to ease the agony experienced by those living with genetic skin condition Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB), commonly referred to as 'butterfly skin'.
Scientists at Maynooth University in Ireland are leading research into whether ‘spray on, wash off’ bandages will be a viable alternative to those currently used, which can cause severe pain when applied and removed.
EB, which affects over 500,000 children and adults worldwide including 5,000 in the UK and 300 ...
A new discovery about pain signalling may contribute to better treatment of chronic pain
2024-11-18
When pain signals are passed along the nervous system, proteins called calcium channels play a key role. Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have now pinpointed the exact location of a specific calcium channel fine-tuning the strength of pain signals. This knowledge can be used to develop drugs for chronic pain that are more effective and have fewer side effects.
Pain sensations and other information are mainly conducted through our nervous system as electrical signals. Yet at decisive moments, this information is converted to biochemical signals, in the form of specific molecules. To develop future drugs ...
Migrating birds have stowaway passengers: invasive ticks could spread novel diseases around the world
2024-11-18
Ticks travel light, but they carry pathogens with them. When they parasitize migrating birds, these journeys can take them thousands of miles away from their usual geographic range. Historically, they haven’t been able to establish themselves, due to unsuitable climate conditions at the other end of their long journeys. But now, thanks to the climate crisis, it’s getting easier for ticks to survive and spread, potentially bringing novel tick-borne pathogens with them.
“If conditions become more hospitable for tropical tick species to establish themselves in areas where they would previously have been unsuccessful, then there is a chance they could bring new diseases ...
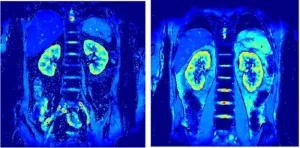
Diabetes drug shows promise in protecting kidneys
2024-11-18
Type 2 diabetes can lead to diabetic kidney disease, but a class of drugs that cause the kidneys to remove glucose through urine has been gaining attention. An Osaka Metropolitan University-led research group has investigated how such drugs maintain kidney health.
Known as SGLT2 (sodium-glucose cotransporter-2) inhibitors, the drugs are used to treat type 2 diabetes along with an exercise and diet regimen. The group led by Graduate School of Medicine Associate Professor Katsuhito Mori focused on the SGLT2 inhibitor canagliflozin and its effects on the kidney.
Using BOLD ...
Updated model reduces liver transplant disparities for women
2024-11-18
SAN DIEGO, California (Nov. 18, 2024) — Since the adoption of a new model for assessing the severity of liver disease, women are more likely to be added to the waitlist for a liver transplant, more likely to receive a transplant, and less likely to drop off the waitlist — closing the gap between men and women candidates, according to a study scheduled for presentation today at The Liver Meeting held by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
In July 2023, the federal Organ Procurement and Transplant Network (OPTN) updated its Model for End-Stage Liver Disease to a new version, known as MELD 3.0, to better account for differences between ...
Risk of internal bleeding doubles when people on anticoagulants take NSAID painkiller
2024-11-18
People who take an anticoagulant medicine double their risk of an internal bleed if they take a type of painkiller called a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as ibuprofen, diclofenac or naproxen, according to research published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Monday).
Anticoagulants are usually prescribed to people who develop a blood clot in the legs or lungs, known as a venous thromboembolism, which affects about one in 12 people. NSAIDs are a popular type of painkiller used to manage issues like headaches, period pain, back pain and arthritis.
The new study is the largest of its kind and shows that ...
‘Teen-friendly’ mindfulness therapy aims to help combat depression among teenagers
2024-11-18
Researchers have developed a mindfulness therapy tailored specifically to appeal to teenagers to help them cope with increasing levels of depression and mental health problems.
The approach teaches participants to tune into and manage negative thought patterns that can trigger or maintain depression, and allow them instead to focus on the present moment.
Developed by teams at the University of Cambridge and King’s College London, the ATTEND programme – Adolescents and carers using mindfulness Therapy To END depression – also includes sessions for parents and guardians, ensuring a family-centred approach ...
Innovative risk score accurately calculates which kidney transplant candidates are also at risk for heart attack or stroke, new study finds
2024-11-17
Using an innovative risk score assessment score, heart researchers at Intermountain Health in Salt Lake City say they can accurately predict whether patients being assessed for kidney transplant will likely have a future major cardiac event, like a heart attack or stroke, according to a new study.
Intermountain Health clinicians regularly review patient data through their electronic health system to determine who may have heart disease without knowing it. Now, in a major new study, Intermountain heart researchers found that using their Intermountain ...
Kidney outcomes in transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy
2024-11-17
About The Study: In this retrospective cohort study, decline in kidney function was frequent in patients with transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM) and was consistently associated with an increased risk of mortality, even after adjusting for established markers of worsening ATTR-CM. eGFR decline represents an independent marker of ATTR-CM disease progression that could guide treatment optimization in clinical practice.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Marianna Fontana, MD, PhD, email m.fontana@ucl.ac.uk.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Partial cardiac denervation to prevent postoperative atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass grafting
2024-11-17
About The Study: This randomized clinical trial found that partial cardiac denervation was an effective procedure to reduce the occurrence of postoperative atrial fibrillation (POAF) after isolated coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) without additional postoperative complications. These results suggest that partial cardiac denervation may be a good option for cardiac surgeons to consider for preventing POAF after CABG.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Wei Feng, MD, PhD (fengwei@fuwai.com) and Wei Zhao, MD, PhD (zhaowei_fw@163.com).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at ...