(Press-News.org) Expectant mothers who maintain a diet that meets USDA dietary guidelines during pregnancy may be more likely to have infants with healthy birthweights, steadier growth patterns, and potentially a reduced risk of obesity later in childhood, according to a new study funded by the Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO) Program at the National Institutes of Health.
The research, involving more than 2,800 mother-child pairs across eight ECHO Cohort Study Sites, suggests that following a healthy prenatal diet in line with the USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans could have long-term positive effects on infant growth up to 24 months.
This study found that eating a healthy diet during pregnancy was linked with a lower chance of extremely rapid infant growth,” said Assiamira Ferrara, MD, PhD, of Kaiser Permanente Northern California Division of Research. Dr. Ferrara noted that rapid growth from birth to 24 months is a strong predictor of obesity later in life.
The study used two dietary measures—the Healthy Eating Index (HEI) and the Empirical Dietary Inflammatory Pattern (EDIP)—to look at maternal eating patterns. The HEI measures overall diet quality. The EDIP score measures how likely a diet is to cause inflammation in the body. Diets with high EDIP scores have been linked to increased levels of inflammation.
Key findings from the research showed that:
Higher HEI scores, reflecting healthier diets, were associated with a 12% reduced chance of infants being born large for gestational age (LGA), alongside lower rates of rapid growth up to 6 and 24 months.
Lower EDIP scores, indicating diets with reduced inflammatory potential, were associated with a 24% higher chance of LGA and had mixed effects on growth: slower from birth to 6 months but faster growth between birth and 12 months. This association was less clear and warrants further study.
To assess rapid growth, the study relied on a measurement called the weight-for-length z-score (WLZ) a tool used to track an infant's growth. It compares a baby’s weight to its length and tells you how far a baby's weight is from the average weight of babies of the same length. Rapid growth was defined as a significant increase in WLZ scores from birth to 6, 12, or 24 months. Babies whose WLZ scores jumped more than expected moved to a higher percentile on the growth chart, meaning they weighed more relative to their peers of the same length.
“The findings support a role for a balanced prenatal diet that aligns with the USDA Dietary Guidelines in promoting healthy birthweights and balanced growth through early childhood,” said Monique Hedderson, PhD, of Kaiser Permanente Northern California Division of Research. “This suggests the need for programs to help improve pregnant people’s access to healthy food and interventions to support healthy eating during pregnancy.”
Researchers said that the findings represent an opportunity for an early obesity prevention strategy. More research is needed to learn how low-inflammatory diets during pregnancy might benefit fetal and infant growth.
About the Study
The study analyzed data collected between 2007 and 2021 from the ECHO Program about 2,854 mother-child pairs. Among the children studied, 48.7% were girls. Children came from diverse racial and ethnic backgrounds: 23.3% White, 22.4% Black, 35.8% Hispanic, 7.8% Asian, and 7.8% other racial backgrounds. Researchers collected information on diet, birth size, and infant growth at 6, 12, and 24 months through medical records and other measurement tools.
This collaborative research was published in JAMA Network Open.
Ferrara, A. & Hedderson, M. (2024) Prenatal Diet and Infant Growth from Birth to Age 24 months. JAMA Network Open. DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.45771
###
About ECHO: Launched in 2016, the Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO) Program is a research program in the Office of the Director at the NIH with the mission to enhance the health of children for generations to come. ECHO investigators study the effects of a broad range of early environmental influences on child health and development. For more information, visit echochildren.org.
About the NIH: NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information, visit www.nih.gov.
END
Dynamic, reversible modifications of DNA and RNA regulate how genes are expressed and transcribed, which can influence cellular processes, disease development, and overall organismal health. Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are a common but overlooked group of guide RNA molecules that steer chemical modifications to cellular ribosomal RNA (rRNA) targets, like an usher showing someone to their seat in a theater.
Researchers from the University of Chicago recently developed a new approach for identifying new cellular RNA targets of snoRNAs. ...
About The Study: In this cohort study, racial and ethnic disparities in early-onset (before 50 years of age) colorectal cancer mortality were evident, with the highest burden among Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander and non-Hispanic Black individuals. These results provide evidence of the role of social determinants of health in explaining these differences.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Maria Elena Martinez, PhD, email e8martinez@health.ucsd.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.46820)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
About The Study: This serial cross-sectional study observed a significant decrease in positive reviews for health care facilities post-COVID. These findings underscore a disparity in patient experience, particularly in rural areas and areas with the highest proportions of Black and white residents.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Neil K. R. Sehgal, ME, email neilsehgal99@gmail.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.46890)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for ...
Tsukuba, Japan—Physical inactivity is the fourth leading mortality risk factor, following hypertension, smoking, and hyperglycemia. Therefore, acquiring an exercise habit is crucial to maintain and improve health. In Japan, Specific Health Guidance is provided to support the improvement of lifestyle habits, including exercise habits. To develop more efficient health guidance, it is important to identify factors that influence its effectiveness (e.g., characteristics and lifestyle of the target ...
Hydrogen is becoming an increasingly popular choice as we shift towards cleaner energy. It can be burned like traditional fuels, producing only water as a byproduct, and can generate electricity when used in fuel cells. However, as hydrogen production, use, and transportation increase, so do safety concerns. Hydrogen is highly flammable at concentrations as low as 4% and is odorless and colorless, making leaks challenging to detect.
To address these concerns, researchers led by Professor Yutaka Majima from Institute of Science Tokyo (Science Tokyo) have developed a sensor that detects hydrogen at ultra-low concentrations ...
Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-Suk) developed a smart monitoring system that applies digital sensing technology to maintain and manage small- and medium-sized aging bridges. This study was conducted as an international matching joint research funded by KICT, and established a foundation for technology diffusion to ASEAN countries through joint research with University of Transport and Communications (UTC) in Vietnam.
In general, bridge maintenance monitoring technology is applied to long-span bridges such as cable-stayed bridges and suspension bridges. This monitoring system consumes a lot of resources for design and installation, ...
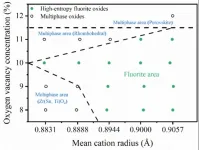
Current researches show that the standard deviation of the cationic radii, configuration entropy, or maintenance of Ce4+ have a certain impact on the formation of single-phase HEFOs, but the discovered rules are only applicable to partially synthesized material systems and have significant limitations. Furthermore, the range of elements used in the synthesized materials is relatively narrow, which restricts the potential to fully exploit the advantages of high-entropy materials and their vast compositional space.
“Inspired by the synthesized HEFOs and the stabilization mechanism ...
A research team at the University of Vienna, led by medicinal chemist Markus Muttenthaler, has developed a new class of oral peptide therapeutic leads for treating chronic abdominal pain. This groundbreaking innovation offers a safe, non-opioid-based solution for conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), which affect millions of people worldwide. The research results were recently published in the international edition of the renowned journal Angewandte Chemie.
An Innovative Approach to Pain Management
Current medications used to treat chronic abdominal pain often rely on opioids. ...
The ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) announces new appointments of cancer researchers to lead committees in its expansive scientific program. ECOG-ACRIN is at the forefront of research spanning the cancer care spectrum, from early detection to management of advanced disease. These impactful appointments, which are effective immediately, underscore the group’s commitment to wide-ranging cancer research excellence and premier professional opportunities for researchers.
Angela M. DeMichele, MD, MSCE, is chair of the Breast Cancer Committee, succeeding ...
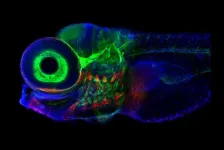
Working with week-old zebrafish larva, researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and colleagues decoded how the connections formed by a network of neurons in the brainstem guide the fishes’ gaze. The study, published Nov. 22 in Nature Neuroscience, found that a simplified artificial circuit, based on the architecture of this neuronal system, can predict activity in the network. In addition to shedding light on how the brain handles short-term memory, the findings could lead to novel approaches for ...