Case Western Reserve University awarded $1.5 million to study vaginal bacterial linked to serious health risks
2024-11-25
(Press-News.org) CLEVELAND—Bacterial vaginosis (BV), the most prevalent condition affecting the female reproductive system in women aged 15 to 44, is linked to such serious health risks as preterm birth, gynecological malignancies and sexually transmitted diseases.
But effective long-term treatments for BV are limited: More than half experience a recurrence within six months, according to several studies.
With a $1.5 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), researchers at the Case Western Reserve School of Medicine will study the dynamics of BV in hopes of identifying a more effective approach.
“We hope to gain insights into promoting health within the human microbiome and to find better ways to prevent and treat infections that involve multiple types of bacteria,” said Gina Lewin, assistant professor in the Department of Pathology at the School of Medicine. “This research is a promising step toward better treatments for BV and highlights Case Western Reserve’s commitment to advancing women’s health.”
BV, which causes pain, odor and discharge—in addition to possible serious health risks—occurs from an imbalance in vaginal bacteria.
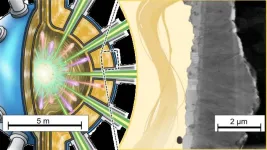
Lewin and her team of microbial ecologists—also part of Case Western Reserve’s Center for Global Health and Diseases—will investigate the diversity of bacteria in the vaginal microbiome at a single-cell level. They will focus on the different strains of bacteria present and their individual behaviors.
Lewin’s approach will examine the genetic variations within thousands of bacterial cells from vaginal microbiome, which could lead to understanding how BV develops and why some women respond better to treatment than others. This aspect of the study will work with established patient groups in collaboration with researchers at the University of Manitoba, Canada.
In addition, researchers will examine how individual bacterial cells behave and interact with a host environment, using advanced sequencing technology.
###
At Case Western Reserve, one of the nation's leading research universities, we're driven to seek knowledge and find solutions to some of the world's most pressing problems. Nearly 6,200 undergraduate and 6,100 graduate students from across 96 countries study in our more than 250 degree programs across arts, dental medicine, engineering, law, management, medicine, nursing, science and social work. Our location in Cleveland, Ohio—a hub of cultural, business and healthcare activity—gives students unparalleled access to engaging academic, research, clinical, entrepreneurial and volunteer opportunities and prepares them to join our network of 125,000+ alumni making an impact worldwide. Visit case.edu to learn more.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-25
In a sense, each of us begins life ready for action. Many animals perform amazing feats soon after they’re born. Spiders spin webs. Whales swim. But where do these innate abilities come from? Obviously, the brain plays a key role as it contains the trillions of neural connections needed to control complex behaviors. However, the genome has space for only a small fraction of that information. This paradox has stumped scientists for decades. Now, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professors Anthony Zador and Alexei Koulakov have devised a potential solution using artificial intelligence.
When Zador first encounters this problem, he puts a ...
2024-11-25
Not all plastics are equal — some types and colors are easier to recycle than others. For instance, black foam and black coffee lids, which are often made of polystyrene, usually end up in landfills because color additives lead to ineffective sorting. Now, researchers report in ACS Central Science the ability to leverage one additive in black plastics, with the help of sunlight or white LEDs, to convert black and colored polystyrene waste into reusable starting materials.
“Simple, visible light irradiation holds the potential to ...
2024-11-25
Researchers explored protective coatings on advanced to resist corrosion in fusion reactors. They tested α-Al2O3 oxide layers on ODS alloys in a high-temperature, flowing lithium-lead environment. Even bare ODS alloys formed a durable γ-LiAlO2 layer in situ, which suppressed further corrosion. The layers exhibited strong adhesion under mechanical stress, making these findings crucial for improving material durability in fusion reactors and high-temperature energy systems.
Fusion reactors, a promising source of sustainable energy, require advanced materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments ...
2024-11-25
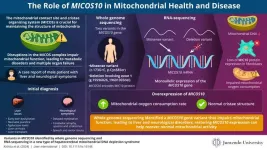
Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome (MTDPS) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by a marked decrease in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). This condition can cause symptoms including muscle weakness, fatigue, and neurological issues, particularly affecting the liver and brain in cases of hepatocerebral MTDPS. Mitochondrial diseases, which represent some of the most common types of metabolic disorders, can result in the failure of multiple organ systems. Currently, over 400 genes linked to these diseases have been identified. Notably, many of these genes are associated with the mitochondrial contact site and cristae ...
2024-11-25
Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming increasingly useful for the prediction of emergency events such as heart attacks, natural disasters, and pipeline failures. This requires state-of-the-art technologies that can rapidly process data. In this regard, reservoir computing, specially designed for time-series data processing with low power consumption, is a promising option. It can be implemented in various frameworks, among which physical reservoir computing (PRC) is the most popular. PRC with optoelectronic artificial synapses (junction structures that permit a nerve cell to transmit an electrical or chemical signal to another cell) that mimic human ...
2024-11-25
When bats can’t hear, new research finds that these hearing-dependent animals employ a remarkable compensation strategy.
They adapt immediately and robustly, suggesting for the first time that bats’ brains are hard-wired with an ability to launch a Plan B in times of diminished hearing.
The Johns Hopkins University work, newly published in Current Biology, raises questions about whether other animals and even humans might be capable of such deft accommodations.
“Bats have this amazing flexible adaptive behavior that they can employ anytime,” said senior author ...
2024-11-25
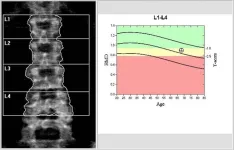
CHICAGO – Levothyroxine, the second most commonly prescribed medication among older adults in the U.S., may be associated with bone loss, according to a study being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Levothyroxine, marketed under multiple brand names including Synthroid, is a synthetic version of a hormone called thyroxine and is commonly prescribed to treat the condition hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid. In people with hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroxine on its own, often resulting in fatigue, weight gain, hair loss and other symptoms. If left untreated, hypothyroidism ...
2024-11-25
CHICAGO – Researchers have identified acute effects of cigarette and e-cigarette smoking on vascular function, even without nicotine. The results of the ongoing research are being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
E-cigarettes, also known as vapes, are battery-operated devices that heat a liquid to produce an aerosol, which is then inhaled into the lungs. Vapes contain significantly fewer chemicals and toxins than are found in tobacco smoke. As a result, e-cigarettes are believed by many to be less harmful than cigarette smoking. Vapes also come in various flavors, making them popular among young people.
“E-cigarettes ...
2024-11-25
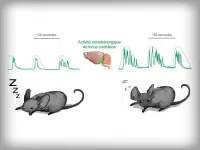
Researchers at the University of Lausanne have identified a novel role for the brain’s ‘locus coeruleus’ in sleep and its disruptions. This brain region facilitates the transition between NREM and REM sleep states while maintaining an unconscious vigilance toward the external world. Stress disrupts its functions and negatively impacts on sleep quality.
Sleep disorders affect an increasing number of people, with potentially serious consequences for their health. Mammalian sleep consists of cycles between two states: non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye ...
2024-11-25
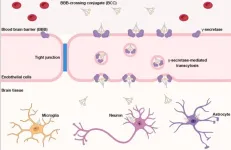
New York, NY [November 25, 2024]—Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have developed an innovative approach—demonstrated in mouse models and isolated human brain tissue—to safely and effectively deliver therapeutics into the brain, providing new possibilities for treating a wide range of neurological and psychiatric diseases.
Published in the November 25 online issue of Nature Biotechnology [https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02487-7], the study introduces a first-of-its-kind blood-brain barrier-crossing conjugate (BCC) system, designed to overcome the protective barrier that typically blocks large biomolecules from ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Case Western Reserve University awarded $1.5 million to study vaginal bacterial linked to serious health risks