(Press-News.org) A wearable electrical nerve stimulation device can provide relief to people experiencing the persistent pain and fatigue linked to long COVID, a study co-led by UCLA and Baylor College of Medicine researchers suggests.
Long-COVID, a complex and lingering condition following COVID-19 recovery, affects approximately 1 in 13 adults in the U.S. Symptoms such as widespread pain, fatigue, and muscle weakness often continue to disrupt daily activities, including walking and basic tasks.
The study, published in the peer-reviewed Nature Scientific Reports, focused on a wearable Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) device, which uses low-voltage electrical currents to reduce pain, fatigue, and mobility issues associated with long-COVID.
The project was co-led by Dr. Bijan Najafi, research director of the Center for Advanced Surgical & Interventional Technology at UCLA Health and co-director of NSF IUCRC Center to Stream HealthCare in Place (C2SHIP), who said the device could have wider applications.
“While this study focused on managing pain and fatigue caused by long COVID, it may also have potential applications for addressing similar symptoms in individuals with other respiratory diseases, those who have experienced extended ICU stays and developed post-hospitalization weaknesses, and conditions involving chronic fatigue and pain, such as fibromyalgia or chemotherapy-related side effects,” Najafi said. “But further studies are needed to confirm these potential uses.”
In the study, 25 participants with chronic musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and gait difficulties were assigned either a high-dose (active) TENS device or a low-dose (placebo) device. Both groups used the TENS device for three to five hours daily over a four-week period.
Researchers measured participants’ pain levels, fatigue, and walking performance before and after the therapy period. Findings indicated that the high-dose TENS group experienced notable improvements in pain relief (26.1% more relief compared to placebo) and walking ability (8% during fast walking), suggesting that wearable TENS therapy may help reduce long-COVID’s impact on daily life.
The high-dose TENS group also reported a slightly higher perceived benefit (71.2%) compared to the low-dose group (61.4%), underscoring the potential of wearable TENS technology to support long-COVID recovery.
One factor in the study’s success was likely the high rate of daily device usage, Najafi said. The wearable nature of the TENS device allowed participants to use it seamlessly throughout the day, without disrupting their routines.
“This wearable TENS system offered immediate, on-demand relief from pain and fatigue, making it easy to integrate into daily activities,” Najafi said.
He also cautioned that more research is needed. This study provides some hope for finding an effective, non-invasive solution for managing lingering COVID-19 symptoms that continue to affect millions,” he said. “But our sample size was limited, so further research is needed to confirm these findings.”
Study co-authors are Alejandro Zulbaran-Rojas, Rasha Bara, Myeounggon Lee, Miguel Bargas-Ochoa, Tina Phan, Manuel Pacheco, Areli Flores Camargo, Syed Murtaza Kazmi, Mohammad Dehghan Rouzi, Dipaben Modi, and Fidaa Shaib of Baylor College of Medicine.
This study was funded by the National Science Foundation’s Industry-University Cooperative Research Centers (IUCRC), specifically from the Center to Stream HealthCare in Place (C2SHIP), with award numbers NSF 2052514 and C2SHIP Y01-BCM-008. There was also in-kind support provided by Neurometrix Inc., which manufactured the Quell® TENS device.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-78651-5
END
Electrical nerve stimulation eases long COVID pain and fatigue
Wearable TENS system “offered immediate, on-demand relief,” say researchers
2024-11-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ASTRO issues update to clinical guideline on radiation therapy for rectal cancer
2024-11-25
ARLINGTON, Va., November 25, 2024 — The American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) issued today an updated clinical guideline for physicians who use radiation therapy to treat patients with locally advanced rectal cancer. This update incorporates new data on patient selection and best practices from several practice-changing clinical trials published since the prior guideline was issued in 2020. The updated ASTRO guideline is published in Practical Radiation Oncology.
Colorectal cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths for Americans aged 20 to 49 and the second most common cause of cancer-related death overall. In the U.S., the incidence of early ...
Mount Sinai opens the Hamilton and Amabel James Center for Artificial Intelligence and Human Health to transform health care by spearheading the AI revolution
2024-11-25
See accompanying video here: https://youtu.be/o-opCV6oe3o
New York, NY [November 25, 2024]—Today, the Mount Sinai Health System, one of New York City’s largest academic medical systems, announced the opening of the Hamilton and Amabel James Center for Artificial Intelligence and Human Health, which is dedicated to enhancing health care delivery through the research, development, and application of innovative artificial intelligence (AI) tools and technologies.
The state-of-the-art research center solidifies ...
Researchers develop tools to examine neighborhood economic effects on spinal cord injury outcomes
2024-11-25
East Hanover, NJ – November 25, 2024 – Kessler Foundation researchers have developed robust measures of neighborhood economic factors to study how social determinants influence health outcomes after spinal cord injury (SCI). The study reveals that individuals in disadvantaged neighborhoods face higher risks of poor health, emphasizing the need for public policy to address environmental inequities.
Research scientists developed and validated two composite measures – neighborhood socioeconomic ...
Case Western Reserve University awarded $1.5 million to study vaginal bacterial linked to serious health risks
2024-11-25
CLEVELAND—Bacterial vaginosis (BV), the most prevalent condition affecting the female reproductive system in women aged 15 to 44, is linked to such serious health risks as preterm birth, gynecological malignancies and sexually transmitted diseases.
But effective long-term treatments for BV are limited: More than half experience a recurrence within six months, according to several studies.
With a $1.5 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), researchers at the Case Western Reserve School of Medicine will study the dynamics of BV in hopes of identifying a more effective approach.
“We hope to gain insights into promoting ...
The next evolution of AI begins with ours
2024-11-25
In a sense, each of us begins life ready for action. Many animals perform amazing feats soon after they’re born. Spiders spin webs. Whales swim. But where do these innate abilities come from? Obviously, the brain plays a key role as it contains the trillions of neural connections needed to control complex behaviors. However, the genome has space for only a small fraction of that information. This paradox has stumped scientists for decades. Now, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professors Anthony Zador and Alexei Koulakov have devised a potential solution using artificial intelligence.
When Zador first encounters this problem, he puts a ...
Using sunlight to recycle black plastics
2024-11-25
Not all plastics are equal — some types and colors are easier to recycle than others. For instance, black foam and black coffee lids, which are often made of polystyrene, usually end up in landfills because color additives lead to ineffective sorting. Now, researchers report in ACS Central Science the ability to leverage one additive in black plastics, with the help of sunlight or white LEDs, to convert black and colored polystyrene waste into reusable starting materials.
“Simple, visible light irradiation holds the potential to ...
ODS FeCrAl alloys endure liquid metal flow at 600 °C resembling a fusion blanket environment
2024-11-25
Researchers explored protective coatings on advanced to resist corrosion in fusion reactors. They tested α-Al2O3 oxide layers on ODS alloys in a high-temperature, flowing lithium-lead environment. Even bare ODS alloys formed a durable γ-LiAlO2 layer in situ, which suppressed further corrosion. The layers exhibited strong adhesion under mechanical stress, making these findings crucial for improving material durability in fusion reactors and high-temperature energy systems.
Fusion reactors, a promising source of sustainable energy, require advanced materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments ...
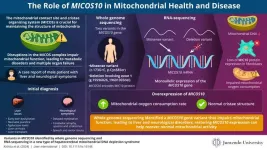
A genetic key to understanding mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome
2024-11-25
Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome (MTDPS) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by a marked decrease in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). This condition can cause symptoms including muscle weakness, fatigue, and neurological issues, particularly affecting the liver and brain in cases of hepatocerebral MTDPS. Mitochondrial diseases, which represent some of the most common types of metabolic disorders, can result in the failure of multiple organ systems. Currently, over 400 genes linked to these diseases have been identified. Notably, many of these genes are associated with the mitochondrial contact site and cristae ...
The future of edge AI: Dye-sensitized solar cell-based synaptic device
2024-11-25
Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming increasingly useful for the prediction of emergency events such as heart attacks, natural disasters, and pipeline failures. This requires state-of-the-art technologies that can rapidly process data. In this regard, reservoir computing, specially designed for time-series data processing with low power consumption, is a promising option. It can be implemented in various frameworks, among which physical reservoir computing (PRC) is the most popular. PRC with optoelectronic artificial synapses (junction structures that permit a nerve cell to transmit an electrical or chemical signal to another cell) that mimic human ...
Bats’ amazing plan B for when they can’t hear
2024-11-25
When bats can’t hear, new research finds that these hearing-dependent animals employ a remarkable compensation strategy.
They adapt immediately and robustly, suggesting for the first time that bats’ brains are hard-wired with an ability to launch a Plan B in times of diminished hearing.
The Johns Hopkins University work, newly published in Current Biology, raises questions about whether other animals and even humans might be capable of such deft accommodations.
“Bats have this amazing flexible adaptive behavior that they can employ anytime,” said senior author ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
Hotspots of accelerated bird decline linked to agricultural activity
How ancient attraction shaped the human genome
NJIT faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors
[Press-News.org] Electrical nerve stimulation eases long COVID pain and fatigueWearable TENS system “offered immediate, on-demand relief,” say researchers