(Press-News.org) About The Study: This study found a steep decline in cervical cancer mortality among U.S. women younger than 25 years between 2016 and 2021. This cohort of women is the first to be widely protected against cervical cancer by human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccines. The findings from this study in the context of other published research suggest that HPV vaccination affected the sequential decline in HPV infection prevalence, cervical cancer incidence, and cervical cancer mortality.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ashish A. Deshmukh, PhD, MPH, email deshmukha@musc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.22169)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2024.22169?guestAccessKey=96c86a3c-4972-4bcc-8b6a-5957503cab01&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=112724
END
Cervical cancer mortality among US women younger than age 25
JAMA
2024-11-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fossil dung reveals clues to dinosaur success story
2024-11-27
In an international collaboration, researchers at Uppsala University have been able to identify undigested food remains, plants and prey in the fossilised faeces of dinosaurs. These analyses of hundreds of samples provide clues about the role dinosaurs played in the ecosystem around 200 million years ago. The findings have been published in the journal Nature.
“Piecing together ‘who ate whom’ in the past is true detective work,” says Martin Qvarnström, researcher at the Department of Organismal Biology and lead author of the study. “Being able to examine what animals ate and how they interacted with their environment helps us understand what enabled ...
New research points way to more reliable brain studies
2024-11-27
Brain-wide association studies, which use magnetic resonance imaging to identify relationships between brain structure or function and human behavior or health, have faced criticism for producing results that often cannot be replicated by other researchers.
A new study published in Nature demonstrates that careful attention to study design can substantially improve the reliability of this type of research. For the study, Kaidi Kang, a biostatistics PhD student, Simon Vandekar, PhD, associate professor of Biostatistics, and colleagues analyzed data from more than 77,000 brain scans across 63 studies.
The ...
‘Alzheimer’s in dish’ model shows promise for accelerating drug discovery
2024-11-27
A decade ago, researchers introduced a new model for studying Alzheimer’s disease. Known as “Alzheimer’s in a dish,” the model uses cultures of mature brain cells suspended in a gel to recapitulate what takes place in the human brain over 10 to 13 years in just six weeks. But does the model truly produce the same changes that take place in patients? In a new study, researchers from Mass General Brigham, in collaboration with colleagues at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC), created an algorithm to assess, in an unbiased manner, how well models of Alzheimer’s disease ...
Ultraprocessed food intake and psoriasis
2024-11-27
About The Study: The results of this study showed an association between high ultraprocessed food intake and active psoriasis status. After adjustments for age, body mass index (BMI), alcohol intake, and comorbidities, the results remained significant, suggesting that ultraprocessed food intake has a proinflammatory action separate from high BMI.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Emilie Sbidian, MD, PhD, email emilie.sbidian@aphp.fr.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Race and ethnicity, gender, and promotion of physicians in academic medicine
2024-11-27
About The Study: The findings of this study indicate that preferential promotion of white men within academic medicine continues to persist in the new millennium, with racially and ethnically diverse women experiencing greater underpromotion. To achieve a workforce that reflects the diversity of the U.S. population, this study suggests that academic medicine needs to transform its culture and practices surrounding faculty appointments and promotions.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lauren Clark, MS, email lclark5@kumc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Testing and masking policies and hospital-onset respiratory viral infections
2024-11-27
About The Study: In this study, stopping universal masking and SARS-CoV-2 testing was associated with a significant increase in hospital-onset respiratory viral infections relative to community infections. Restarting the masking of health care workers was associated with a significant decrease.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Theodore R. Pak, MD, PhD, email tpak@mgh.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.48063)
Editor’s ...
A matter of life and death
2024-11-27
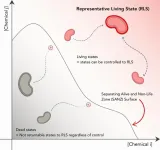
Cellular death is a fundamental concept in the biological sciences. Given its significance though, its definition depends on the context in which it takes place, and lacks a general mathematical definition. Researchers from the University of Tokyo propose a new mathematical definition of death based on whether a potentially dead cell can return to a predefined “representative state of living,” which are the states of being that we can confidently call “alive.” The researchers’ work could be useful for biological researchers and future medical research.
While it’s ...
Huge cost savings from more efficient use of CDK4/6 inhibitors in metastatic breast cancer reported in SONIA study
2024-11-27
On November 27, the prestigious journal Nature will publish the results of an innovative breast cancer research project from the Netherlands. This study, the SONIA trial, showed that delaying and shortening the duration of a specific anti-cancer therapy (CDK4/6 inhibitors) in patients with hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer leads to similar survival outcomes, while reducing toxicity and achieving substantial cost reductions: over 45 million euros per year in the Netherlands and over 5 billion dollars in the United States. This is the first time an efficiency study like this has been conducted in collaboration with Dutch health ...
What a gut fungus reveals about symbiosis and allergy
2024-11-27
A fungus discovered in the mouse stomach may hold a key to fungal evolution within the gastrointestinal tract, according to new research led by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators. The finding suggests that preclinical studies until now have overlooked a major influencer of mouse physiology.
Scientists recently have come to appreciate the importance, for human health and disease, of microbes—often called “commensals”—that naturally dwell in the gut. Bacterial commensals, for example, are known to have ...
Insilico Medicine recognized by Endeavor Venture Group & Mount Sinai Health System with Showcase AI and Biotech Innovation Award
2024-11-27
Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, is proud to be recognized for the impact on the future of drug discovery and development, as a distinguished honoree of the Showcase AI and Biotech Innovation Award on November 13, 2024, at the Fifth Endeavor Venture Group & Mount Sinai Health System Healthcare AI and Technology Investor Summit. Michelle Chen, Ph.D., Chief Business Officer of Insilico Medicine, received the award on behalf of the company.
Delivered ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
[Press-News.org] Cervical cancer mortality among US women younger than age 25JAMA