(Press-News.org) In 2023, the United Nations climate conference (COP28) officially recognized the importance of agriculture in influencing and mitigating climate change. In a Policy Forum, Johan Swinnen and colleagues offer an approach to overcome challenges related to improving climate-sensitive farming practices across the globe. They discuss the importance of working with Agricultural Value Chains (AVC) by incentivizing small businesses who play an important role in the support of small- and medium-sized farms. This would involve both upstream enterprises related to seeds, fertilizer, irrigation, and insurance, for example, and downstream enterprises like those related to distribution, storage, and transportation. Most agricultural production occurs within small- to medium-sized farms – a fragmented farm sector – leading to pessimism about the possibility to enact change. But the authors counter this pessimism, citing decades of evidence of AVC companies having employed their tools – such as resource provision, training, and loans – to encourage farmers to be more “climate smart.” Targeting these institutional relationships with farmers can be a positive force for needed policy transformation, say the authors.
END
The key to “climate smart” agriculture might be through its value chain
Summary author: Zachary Graber
2024-11-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
These hibernating squirrels could use a drink—but don’t feel the thirst
2024-11-28
The thirteen-lined ground squirrel doesn’t drink during its winter hibernation, even though systems throughout its body are crying out for water. Madeleine Junkins and colleagues now show that the squirrel suppresses the need to quench its thirst by reducing the activity of a set of neurons in highly vascularized brain structures called circumventricular organs, which act as a specialized connection point between brain, blood circulation and cerebrospinal fluid. The study by Junkins et al. helps explain how some hibernating animals ignore the powerful physiological drive to seek out water ...
New footprints offer evidence of co-existing hominid species 1.5 million years ago
2024-11-28
Newly discovered footprints show that at least two hominid species were walking through the muddy submerged edge of a lake in Kenya’s Turkana Basin at the same time, about 1.5 million years ago. The find from the famous hominid fossil site of Koobi Fora described by Kevin Hatala and colleagues provides physical evidence for the co-existence of multiple hominid lineages in the region—something that has only been inferred previously from overlapping dates for scattered fossils. Based on information on gait and stance gleaned from the footprints, Hatala et al. think that the two species were Homo erectus and Paranthropus ...
Moral outrage helps misinformation spread through social media
2024-11-28
Social media posts containing misinformation evoke more moral outrage than posts with trustworthy information, and that outrage facilitates the spread of misinformation, according to a new study by Killian McLoughlin and colleagues. The researchers also found that people are more likely to share outrage-evoking misinformation without reading it first. The findings suggest that attempts to mitigate the online spread of misinformation by encouraging people to check its accuracy before sharing may not be successful, the researchers ...
U-M, multinational team of scientists reveal structural link for initiation of protein synthesis in bacteria
2024-11-28
IMAGE
ANN ARBOR—Within a cell, DNA carries the genetic code for building proteins.
To build proteins, the cell makes a copy of DNA, called mRNA. Then, another molecule called a ribosome reads the mRNA, translating it into protein. But this step has been a visual mystery: scientists previously did not know how the ribosome attaches to and reads mRNA.
Now, a team of international scientists, including University of Michigan researchers, have used advanced microscopy to image how ribosomes recruit to mRNA while it's being transcribed by an enzyme called RNA polymerase, or RNAP. Their results, which examine the process in bacteria, are published in the journal ...
New paper calls for harnessing agrifood value chains to help farmers be climate-smart
2024-11-28
Washington DC, November 28, 2024: The global food system is uniquely vulnerable to climate impacts, making adaptation of paramount importance. While contributing roughly one-third of total anthropogenic emissions, food systems around the world fortunately also hold immense potential for mitigation through improved practices and land use. A new article published today in Science emphasizes the critical role of agrifood value chains (AVCs) in supporting both adaptation and mitigation at the farm level.
Authored by Johan Swinnen (International Food Policy Research Institute), Loraine Ronchi (World Bank Group), and Thomas Reardon (Michigan State University and IFPRI), the paper pushes back ...
Preschool education: A key to supporting allophone children
2024-11-28
Learning French while also developing language skills in one’s mother tongue is no easy task. As a result, allophone children often face learning and communication difficulties in kindergarten, which can negatively impact their educational journey. However, solutions are emerging.
According to a study led by Sylvana Côté, preschool education services significantly help bridge the gap between children whose mother tongue is French and those for whom French is a second or even a third language.
Professor Côté, from the School of Public Health at the Université de Montréal (ESPUM), is the director of the Observatory ...
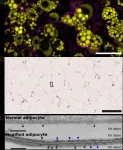
CNIC scientists discover a key mechanism in fat cells that protects the body against energetic excess
2024-11-28
A team at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC), led by Professor Miguel Ángel del Pozo Barriuso, who heads the Mechanoadaptation and Caveolae Biology group at the CNIC, has identified an essential mechanism in fat cells (adipocytes) that enables them to enlarge safely to store energy. This process avoids tissue damage and protects the body from the toxic effects of accumulating fat molecules (lipids) in inappropriate places. The results, published in Nature Communications, signify a major advance in the understanding of metabolic diseases. Moreover, this discovery ...
Chemical replacement of TNT explosive more harmful to plants, study shows
2024-11-28
The increased use of a chemical compound to replace TNT in explosive devices has a damaging and long lasting effect on plants, new research has shown.
In recent years, TNT has started to be replaced with DNAN, but until now very little was known about how this substance impacts the environment and how long it can remain in the soil.
Researchers at the University of York have been studying the environmental impact of the explosive, TNT, for more than a decade. They have shown that the chemical compound, which is used by the military around the world, remains in ...
Scientists reveal possible role of iron sulfides in creating life in terrestrial hot springs
2024-11-28
An international team of scientists recently published a study highlighting the potential role of iron sulfides in the formation of life in early Earth’s terrestrial hot springs. According to the researchers, the sulfides may have catalyzed the reduction of gaseous carbon dioxide into prebiotic organic molecules via nonenzymatic pathways.
This work, which appeared in Nature Communications, offers new insights into Earth’s early carbon cycles and prebiotic chemical reactions, underscoring the significance of iron sulfides in supporting the terrestrial hot ...
Hormone therapy affects the metabolic health of transgender individuals
2024-11-28
New research from Karolinska Institutet shows that long-term sex hormone treatment in transgender individuals can lead to significant changes in body composition and risk factors for cardiovascular disease, particularly in transgender men. The study is published in the Journal of Internal Medicine.
“We saw that transgender men treated with testosterone increased their muscle volume by an average of 21 percent over six years, but also that the amount of abdominal fat increased by 70 percent,” says Tommy Lundberg, docent at the Department of Laboratory Medicine, Karolinska Institutet. “In addition, they had more liver ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
Researchers find that landowner trust, experience influence feral hog management
Breaking down the battery problem
ACMG Foundation to present adaptive bikes to Baltimore-area children with genetic conditions at heartwarming “Day of Caring” event on March 13
Racial disparities in food insecurity for high- and low-income households
Incidence of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest on a postholiday weekday
Prior authorization bans for buprenorphine alone may not improve treatment retention
When light boosts protein evolution
New model may predict preeclampsia in late pregnancy
Lifestyle medicine experts call meaning, purpose, and spirituality foundational to evidence-based, whole-person lifestyle change
Significant acceleration of global warming since 2015
FAU awarded $2.4M NIH grant to study immune signaling and social behavior
Deep learning-enabled virtual multiplexed immunostaining of label-free tissue for vascular invasion assessment
New PET imaging study reveals how ketamine relieves treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] The key to “climate smart” agriculture might be through its value chainSummary author: Zachary Graber