(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University researchers have created the smallest walking robot yet. Its mission: to be tiny enough to interact with waves of visible light and still move independently, so that it can maneuver to specific locations – in a tissue sample, for instance – to take images and measure forces at the scale of some of the body’s smallest structures.
The team’s paper, “Magnetically Programmed Diffractive Robotics,” published in Science.
“A walking robot that’s small enough to interact with and shape light effectively takes a microscope’s lens and puts it directly into the microworld,” said Paul McEuen, professor of physical science emeritus, who led the team. “It can perform up-close imaging in ways that a regular microscope never could.”
Cornell scientists already hold the world’s record for the world’s smallest walking robot at 40-70 microns.
The new diffractive robots are “going to blow that record out of the water,” said Itai Cohen, professor of physics and co-author of the study. “These robots are 5 microns to 2 microns. They’re tiny. And we can get them to do whatever we want by controlling the magnetic fields driving their motions.”
Diffractive robotics connects, for the first time, untethered robots with imaging techniques that depend on visible light diffraction – the bending of a light wave when it passes through an opening or around something. The imaging technique requires an opening of a size comparable to the light’s wavelength. For the optics to work, the robots must be on that scale, and for the robots to reach targets to image, they have to be able to move on their own. The Cornell team has achieved both objectives.
Controlled by magnets making a pinching motion, the robots can inch-worm forward on a solid surface. They can also “swim” through fluids using the same motion.
The combination of maneuverability, flexibility and sub-diffractive optical technology create a significant advance in the field of robotics, the researchers said.
The research was made possible by the Cornell Center for Materials Research, the National Science Foundation and the Cornell NanoScale Science and Technology Facility.
For additional information, read this Cornell Chronicle story.
Cornell University has dedicated television and audio studios available for media interviews.
-30-
END
Smallest walking robot makes microscale measurements
2024-12-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Peroxisomal protein boosts plant immunity to thrive under environmental stress
2024-12-02
Salicylic acid is vital for protecting plants from pathogens, but its synthesis remains unclear. A recent study by Shinshu University researchers has discovered that the protein HSR201 is key to its production. They found that HSR201 localizes to specific organelles called peroxisomes through a unique targeting signal. This discovery improves our understanding of how plants produce salicylic acid and could pave the way for developing engineered crops with improved disease resistance.
Plant hormones, or phytohormones, are vital for plant growth, adaptation, and defense. ...
Critical relationship between stem cells and mechanical signals unveiled
2024-12-02
A new study from The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) and Institut Curie reveals how stem cells sense and respond to their environment, with implications for inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer.
Stem cells constantly adapt to their environment to maintain organ and tissue health, informed by chemical signals and physical forces. When they do not function as intended, stem cells can result in a number of health conditions including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and colorectal (bowel) cancer, where they continue to divide until a tumour forms.
Until ...
A cause of hyperinflammatory response in lethal COVID-19 identified
2024-12-02
As part of the COVID-19 International Research Team, researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, the University of Pittsburgh and Weill Cornell Medicine discovered a novel cause of cytokine storm — the extreme inflammatory response associated with increased risk of death in COVID-19 infection.
Their findings were reported Nov. 27 in the online issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
In an intensive genomic search for causes of cytokine storm, the research team used autopsy samples obtained from 40 patients who died from COVID-19. They performed genome analysis ...
Sleep deprivation in dementia: Heart disease, diabetes, anxiety, and thyroid disorders
2024-12-02
"Sleep disturbances are a significant concern in individuals with dementia, affecting their overall health and quality of life, as well as that of their family members and caregivers.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 2, 2024 – A new review was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 21, titled, “Sleep deprivation in dementia comorbidities: focus on cardiovascular disease, diabetes, anxiety/depression and thyroid disorders.”
The review, authored by Upasana Mukherjee, Ujala Sehar, Malcolm Brownell, and ...
Temporary tattoo printed directly on the scalp offers easy, hair-friendly solution for measuring brainwaves
2024-12-02
For the first time, scientists have invented a liquid ink that doctors can print onto a patient’s scalp to measure brain activity. The technology, presented December 2 in the Cell Press journal Cell Biomaterials, offers a promising alternative to the cumbersome process currently used for monitoring brainwaves and diagnosing neurological conditions. It also has the potential to enhance non-invasive brain-computer interface applications.
“Our innovations in sensor design, biocompatible ink, and high-speed printing pave the way for future on-body manufacturing of electronic tattoo sensors, with broad applications both within and beyond ...
Ketone bodies: more than energy, they are powerful signaling metabolites that clean up damaged proteins
2024-12-02
Ketone bodies, produced by the body to provide fuel during fasting, have roles in regulating cellular processes and aging mechanisms beyond energy production. Research at the Buck Institute shows that ketone bodies can best be understood as powerful signaling metabolites affecting brain function in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. A new study demonstrates that ketone bodies and similar metabolites have profound effects on the proteome and protein quality control in the brain. Publishing in Cell Chemical Biology, Buck Institute scientists, ...
Implementation of electronic triggers to identify diagnostic errors in emergency departments
2024-12-02
About The Study: In this retrospective medical record review study, rules-based e-triggers were useful for post hoc detection of missed opportunities in diagnosis in emergency department visits. Interventions to target emergency department work system factors are urgently needed to support patient-clinician encounters and minimize harm from diagnostic errors.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hardeep Singh, MD, MPH, email hardeeps@bcm.edu.
To access the embargoed study: ...
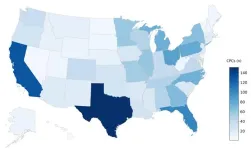
Characterizing services advertised on crisis pregnancy center websites
2024-12-02
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest the need for greater scrutiny of crisis pregnancy center practices, particularly their service provision, provider qualifications, and how these conform with regulations or best practices. A key concern is their promotion of abortion pill reversal, which lacks FDA approval or scientific support and may cause harm.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, John W. Ayers, PhD, MA, email ayers.john.w@gmail.com.
To ...
Study of crisis pregnancy centers reveals misleading and dangerous claims
2024-12-02
La Jolla, Calif. (December 2, 2024) — A new study from scientists at the University of California San Diego introduces a powerful new approach to understanding the operation of crisis pregnancy centers, non-profit organizations dedicated to an anti-abortion agenda. The study published in JAMA Internal Medicine provides the first account of the practices of crisis pregnancy centers (CPC) operating in the United States.
"While our study shows crisis pregnancy centers provide valuable community services, like parenting classes, there is a clear need for consumer safety measures to prevent the promotion and use of their ...
Researchers deal a blow to theory that Venus once had liquid water on its surface
2024-12-02
A team of astronomers has found that Venus has never been habitable, despite decades of speculation that our closest planetary neighbour was once much more like Earth than it is today.
The researchers, from the University of Cambridge, studied the chemical composition of the Venusian atmosphere and inferred that its interior is too dry today for there ever to have been enough water for oceans to exist at its surface. Instead, the planet has likely been a scorching, inhospitable world for its entire history.
The results, reported in the journal Nature Astronomy, have implications for understanding Earth’s uniqueness, and for the search for life on planets outside ...