(Press-News.org) Vadim N. Gladyshev and 80 colleagues surveyed the participants of the 2022 Systems Aging Gordon Research Conference to explore how researchers of aging perceive their subject of study. The authors found wide disagreement on fundamental questions, including “what is aging?” and “what causes aging?”. The collected responses indicated that some of the 103 professors, postdocs, graduate students, industry professionals, and other experts in the survey saw aging as a demographic increase in mortality rate, while other respondents saw aging as a loss of function over time, while still other respondents saw aging as the accumulation of damage or an overall pathological decline. Some respondents saw aging as a normal developmental stage. In terms of when aging begins, some respondents saw aging as a lifelong process that begins as early as gametogenesis—when the gametes that will form the individual are made—while others saw aging as a process specific to adults. Some disagreements indicated a difference in perspective between those who see aging as something that happens to cells and those who see aging as a process that happens to organisms. There was no consensus on whether aging is a disease or not and respondents did not even agree on the question of whether the field ought to have a single consensus definition of aging. Yet behind the wide disagreement there were some implied points of agreement: aging exists; aging is a process; and aging is inherently deleterious. According to the authors, the field could benefit from considering its foundations to better move forward.
END
Experts on aging disagree on the causes and definition of aging
2024-12-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Regional, racial, and economic disparities in cancer risk from air pollution exposure persist, but improving, new research suggests
2024-12-03
New research builds on scientific understanding of how air pollution and cancer risk are distributed throughout the U.S. Air pollution, often resulting from industrial or vehicle emissions, can travel for hundreds of miles and impact the health of communities through higher rates of asthma, respiratory infections, stroke, and lung cancer. Although previous studies have identified disparities in how public health risks vary by income and race, a new study takes a detailed look across U.S. census tracts to find patterns in who is most at risk from cancer resulting from lifetime exposure to air pollution and how ...
COVID infection and age-related blindness
2024-12-03
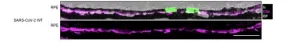
An experimental study in mice shows that SARS-CoV-2 infection can damage the retinas, with long-term implications for vision. Post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection include various neurocognitive symptoms, suggesting the virus can affect the central nervous system. The eyes are also part of the central nervous system, but little is known about the virus’s effects on these organs. David Williams and Nan Hultgren led a study in which transgenic mice that express human SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 were infected with ...
Parasite-inspired medical devices
2024-12-03
Inspired by the diverse attachment organs of parasites, researchers have designed a millimeter-scale mechanism for soft tissue anchoring. Robert J. Wood and colleagues turned to the world of parasites as inspiration for developing methods to affix small-scale medical devices to the gastrointestinal tract or other soft tissues for sensing, sample collection, and extended drug release. While evolution has produced a wide range of different biomechanical structures that can attach to soft tissues, the authors ...
Twenty-seven scientists become EMBO Young Investigators
2024-12-03
3 December 2024 – EMBO announces the selection of 27 life scientists as the newest members of the EMBO Young Investigator Programme. The programme supports young group leaders in Europe and beyond. The new young investigators will start in January, be active members of the programme for four years, and become part of an international network of nearly 800 current and former EMBO Young Investigators, Installation Grantees and Global Investigators. They carry out research across a wide range of life sciences topics from cell and computational biology to immunology and neuroscience.
"EMBO welcomes ...
The viral puzzle of why humans are susceptible to hepatitis B virus, but monkeys are not!
2024-12-03
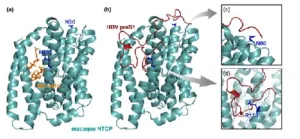
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a leading cause of chronic liver diseases, that spreads among individuals through blood or body fluids. According to the World Health Organization, globally 1.2 million new HBV infections are reported every year. Caused by the HBV, these infections are limited to a few species, including humans and chimpanzees. Despite their close evolutionary relationship with these animals, old-world monkeys are not susceptible to HBV infections. In a new study published in Nature Communications on October 25, 2024, scientists including Dr. Kaho Shionoya from the Tokyo University of Science, Dr. Jae-Hyun Park, Dr. Toru Ekimoto, Dr. Mitsunori Ikeguchi, and Dr. Sam-Yong ...
Microfiber plastics appear to tumble, roll and move slowly in the environment
2024-12-03
PULLMAN, Wash. -- The first-known direct observations of the movement of microfiber plastics through a thin layer of soil-like particles show that they tend to tumble, roll and sometimes get stuck in spaces.
The findings, reported in the journal, Water Resources Research, mean that the fibers could get easily trapped in sediment. The work helps to improve understanding of the exposure risks and possible health impacts of the pervasive pieces of plastic, which are the largest pollutant in the world by mass.
“The ...
Prestigious EU research grants awarded to two Hebrew University researchers
2024-12-03
The Hebrew University of Jerusalem proudly congratulates two of its esteemed researchers for receiving prestigious European Research Council (ERC) grants. These grants, each valued at approximately 2 million euros, are awarded to researchers leading innovative projects and join a long tradition of Hebrew University scholars who have been recognized with this honor in previous years.
The recipients from Hebrew University are:
Prof. Dina Schneidman, The Rachel and Selim Benin School of Computer Science and Engineering, for her research titled "Deep Learning for Structure-Based Discovery of Adaptive Immune Receptors." Prof. Schneidman’s research ...
Experts reveal how revolutionary technological advances could use the sun to source hydrogen fuel
2024-12-03
In the future, we could fuel the world with sunlight and water – using sunlight to derive hydrogen fuel from H2O. Currently, most hydrogen that’s used as feedstock and fuel is derived from natural gas, and therefore doesn’t help us cut out fossil fuels. But Japanese scientists are leading the way towards a future powered by hydrogen, with new, easily-manufactured photocatalytic sheets and a proof-of-concept panel reactor which shows that it is possible to refine hydrogen fuel from water at scale.
“Sunlight-driven water splitting using photocatalysts is an ideal technology for solar-to-chemical ...
Muscle loss could increase dementia risk
2024-12-03
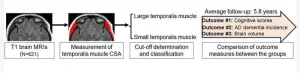
CHICAGO – Skeletal muscle loss is a risk factor for developing dementia, according to a study being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Skeletal muscles make up about one-third of a person’s total body mass. They are connected to the bones and allow for a wide range of movements. As people grow older, they begin to lose skeletal muscle mass.
Because age-related skeletal muscle loss is often seen in older adults with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) dementia, this study aimed to examine whether temporalis muscle ...
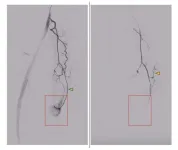
Minimally invasive procedure relieves knee arthritis
2024-12-03
CHICAGO – A minimally invasive procedure provides significant relief from knee pain and may prevent the need for knee replacement surgery in people with osteoarthritis, according to a study being presented this week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“This study addresses osteoarthritis, which is a significant public health issue and the leading cause of chronic pain and disability worldwide,” said the study’s lead author, Florian Nima Fleckenstein, M.D., interventional radiologist at Charité – University Hospital Berlin in Germany. “With millions of people affected by knee ...