(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, December 13, 2024 – Researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and Stanford University have revealed the molecular structure of TRACeR-I, a protein platform for reprogramming immune responses. A better understanding of its structure may help optimize designs for the platform, which can be used to develop cancer treatments by either directly modifying immune cells or by creating proteins that help immune cells locate cancer cells. The findings were published today by the journal Nature Biotechnology.
Immunotherapy presents a promising strategy for treating cancer, autoimmune diseases and viral infections, but its effectiveness depends on its ability to specifically target diseases cells. Monoclonal antibodies are widely used because they can target antigens – proteins generated by cancer cells that trigger an immune response – on the surface of diseased cells, but uniquely expressed antigens found on the surface are sparse.
Another potentially powerful target involves fragments of these proteins may be presented on the tumor cell surface through the presentation of peptides on the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), which displays pieces of suspicious material like parts of a virus or cancer cells on the surface of our cells. There are more than 30,000 different versions of MHC-I proteins in humans, which makes it incredibly challenging to develop treatments that can recognize these peptides across large groups of patients and treat a variety of diseases.
Researchers at Stanford make a breakthrough with the development of TRACeRs, platforms that recognizes many different versions of these MHC proteins. TRACeRs act as “master keys” that can open a variety of “locks” posed by these MHC proteins and then treat the appropriate diseased cells while sparing healthy cells.
“Our TRACeR-I and TRACeR-II platforms unlock the potential for targeting disease-associated class I and class II MHC antigens through novel binding mechanisms that overcomes many of the hurdles that have historically limited the broader development of MHC-targeting molecules,” said senior author Possu Huang, PhD, an assistant professor in the Department of Bioengineering at Stanford University. “Our platforms have high peptide-focused specificity, broad compatibility with a variety of antigens and simpler development that significantly expand the accessibility of targetable MHC biomarkers.”
To better understand the potential of the TRACeR-I platform, researchers from CHOP used x-ray crystallography to show exactly how the platform attaches to parts of the MHC-I complex that stay the same across different versions while continuing to recognize the peptides that indicate cancer cells or other dangerous material being displayed on the surface.
“We revealed TRACeR-I’s novel binding mechanism and how the structure of this platform is able to help it recognize surface proteins that indicate cancer cells,” said Nikolaos Sgourakis, PhD, Associate Professor in the Center for Computational and Genomic Medicine at CHOP. “With this collaborative work, we were able to take the Huang lab’s designs and help realizing their exciting therapeutic potential.”
This study was supported by a Stanford Bio-X Graduate Fellowship, a Stanford Graduate Fellowship Award, the NIH Biotechnology Training Program, the NIH Biophysics Training Program, The Mark Foundation for Cancer Research, the Postdoc Mobility fellowship from the Swiss National Science Foundation, the American Cancer Society grant ACS134055- 441 IRG-218, Stanford School of Medicine, Discovery Innovation Fund, NIH grants 442 R01 AI143997, R35 GM125034, U01 DK112217, the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Cell and Gene Therapy Collaborative, and the Asplundh foundation.
Du et al, “Targeting peptide antigens using a mutiallelic MHCI-binding system.” Nat Biotechnol. Online December 13, 2024. DOI: 10.1038/s41587-024-02505-8.
Du et al, “A general system for targeting MHC class II-antigen complex via a single adaptable loop.” Nat Biotechnol. Online December 13, 2024. DOI: 10.1038/s41587-024-02466-y.
About Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia:
A non-profit, charitable organization, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia was founded in 1855 as the nation’s first pediatric hospital. Through its long-standing commitment to providing exceptional patient care, training new generations of pediatric healthcare professionals, and pioneering major research initiatives, the hospital has fostered many discoveries that have benefited children worldwide. Its pediatric research program is among the largest in the country. The institution has a well-established history of providing advanced pediatric care close to home through its CHOP Care Network, which includes more than 50 primary care practices, specialty care and surgical centers, urgent care centers, and community hospital alliances throughout Pennsylvania and New Jersey, as well as the Middleman Family Pavilion and its dedicated pediatric emergency department in King of Prussia. In addition, its unique family-centered care and public service programs have brought Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia recognition as a leading advocate for children and adolescents. For more information, visit https://www.chop.edu.
END
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Stanford Researchers reveal and refine new immunotherapy platform with increased potential to target cancer cells
TRACeR-I more accurately recognizes a wide variety of surface proteins expressed by cancer cells that make them easier to target with the body’s own immune system
2024-12-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
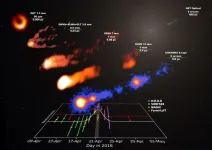
M87's powerful jet unleashes rare gamma-ray outburst
2024-12-13
Also known as Virgo A or NGC 4486, M87 is the brightest object in the Virgo cluster of galaxies, the largest gravitationally bound type of structure in the universe. It came to fame in April 2019 after scientists from EHT released the first image of a black hole in its center. Led by the EHT multi wavelength working group, a study published in Astronomy and Astrophysics Journal presents the data from the second EHT observational campaign conducted in April 2018, involving over 25 terrestrial and orbital telescopes. The authors report the first observation of a high-energy gamma-ray flare in over a decade from the supermassive black hole M87, based on nearly ...
Hippos 'vulnerable' as gaps in data hinder conservation efforts
2024-12-13
A new database of African hippo populations has revealed huge gaps in our knowledge of where the megaherbivores live and thrive, with populations fragmented and reliant on protected areas.
Hippos are classified as “vulnerable to extinction” by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List and have been called the “neglected megafauna”, with a lack of scientific attention and much less research into their lives and habitats than other large mammals.
University of Leeds School of Biology Postgraduate Researcher Hannah Lacy ...
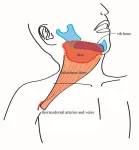
Faster, safer complex head and neck reconstruction with preserved blood supply tissue
2024-12-13
Sometimes, moving just a few inches can go a long way.
Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have developed a promising technique for head and neck reconstruction that shifts the placement of transferred tissue with blood vessels attached, offering a safer, faster option for patients with complex tissue defects, especially those at high risk.
Head and neck reconstruction plays a crucial role in the treatment of patients with head and neck cancer. The goal is to preserve functions vital for breathing, ...
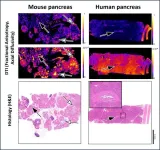
For the first time, researchers detect pre-malignant pancreatic lesions with magnetic resonance imaging
2024-12-13
Precursor lesions of pancreatic cancer are very difficult to characterise with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). But now, in a new study, researchers led by Noam Shemesh and Carlos Bilreiro – respectively head of the Preclinical MRI lab at Champalimaud Research and a doctor at the Champalimaud Clinical Centre’s Radiology Department – have shown, for the first time, that a particular form of MRI, called Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI), is capable of robustly detecting pre-malignant lesions in the pancreas. ...
Combined screening can detect liver damage in diabetes patients
2024-12-13
New research from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden highlights the possibility of screening people with type 2 diabetes for liver damage at the same time as they undergo screening for eye disease. The study is published in Lancet Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
More than half of all people with type 2 diabetes have steatotic (or fatty) liver disease, but most do not realise it since liver disease rarely causes any symptoms in the earlier stages. Over time, liver fibrosis can develop. This is a type of scarring of the liver that can lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer in some patients. International ...
Giraffes really struggle with slopes
2024-12-13
New research finds that giraffes much prefer flat terrain and do not traverse slopes of more than 20°, which severely limits the areas in, and outside, protected reserves they can access. The findings, which is are yet to be published, will be presented at the British Ecological Society’s (BES) Annual meeting in Liverpool on the 13th December.
A new study analysing the movements of 33 GPS collared giraffes in South Africa has found that they avoid steep terrain and are unable to navigate slopes with a gradient of more than 20° , most likely due to the energy required and the risk of falling.
The researchers from the University of Manchester ...
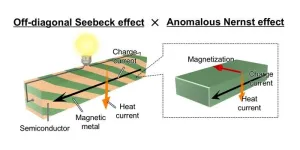
Enhancing transverse thermoelectric conversion performance in magnetic materials with tilted structural design
2024-12-13
1. A research team from NIMS and UTokyo has proposed and demonstrated that the transverse magneto-thermoelectric conversion in magnetic materials can be utilized with much higher performance than previously by developing artificial materials comprising alternately and obliquely stacked multilayers of a magnetic metal and semiconductor.
2. When a temperature gradient is applied to a magnetic conductor, a charge current is generated in a direction orthogonal to directions of both temperature gradient and magnetization of the magnetic conductor. This transverse magneto-thermoelectric phenomenon, ...
Durham University scientists unlock secrets of the longest runout sediment flows on earth using seabed seismographs
2024-12-13
-With images-
Durham University scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery in marine geoscience, revealing unprecedented insights into the dynamics of Earth’s longest runout sediment flows.
By using seabed seismographs placed safely outside the destructive paths of powerful underwater avalanches of sediment, researchers have successfully monitored turbidity currents—a natural phenomenon that shapes deep-sea landscapes, damages telecommunication cables, and transports large quantities of sediment and organic carbon to the ocean floor.
The study recorded two massive turbidity ...
Study sheds light on the origin of the genetic code
2024-12-12
Despite awe-inspiring diversity, nearly every lifeform – from bacteria to blue whales – shares the same genetic code. How and when this code came about has been the subject of much scientific controversy.
Taking a fresh approach at an old problem, Sawsan Wehbi, a doctoral student in the Genetics Graduate Interdisciplinary Program at the University of Arizona, discovered strong evidence that the textbook version of how the universal genetic code evolved needs revision. Wehbi is the first author of a study published in the journal PNAS suggesting the order with which amino acids – the code's building blocks –
were recruited is at odds with ...
Changemaker K-12: Empowering teachers and students to be innovators
2024-12-12
A program designed to prepare future teachers and K-12 students for a lifetime of innovation recently received a $572,890 boost from the National Science Foundation.
The ChangeMaker K-12 program, designed by faculty from the University of Louisiana at Lafayette’s College of Education & Human Development, received a second round of grant funding to expand the teacher prep program to other universities. The new partners are the University of Louisiana Monroe, Louisiana Tech University and the University of Hawaii at Manoa.
The project is led by Dr. Doug Williams, director of UL Lafayette’s Center for Innovative Learning and Assessment Technologies, along with Dr. Aimee Barber, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Stanford Researchers reveal and refine new immunotherapy platform with increased potential to target cancer cellsTRACeR-I more accurately recognizes a wide variety of surface proteins expressed by cancer cells that make them easier to target with the body’s own immune system