(Press-News.org) The air around us contains a powerful solution for making agriculture more sustainable. Researchers at Stanford University and King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals in Saudi Arabia have developed a prototype device that can produce ammonia – a key fertilizer ingredient – using wind energy to draw air through a mesh. The approach they developed, if perfected, might eliminate the need for a century-old method that produces ammonia by combining nitrogen and hydrogen at high pressures and temperatures. The older method consumes 2% of global energy and contributes 1% of annual carbon dioxide emissions from its reliance on natural gas.
The study, published Dec. 13 in Science Advances, involved the first on-site – rather than in a lab – demonstration of the technology. The researchers envision someday integrating the device into irrigation systems, enabling farmers to generate fertilizer directly from the air.
“This breakthrough allows us to harness the nitrogen in our air and produce ammonia sustainably,” said study senior author Richard Zare, the Marguerite Blake Wilbur Professor in Natural Science in the Stanford School of Humanities and Sciences. “It’s a significant step toward a decentralized and eco-friendly approach to agriculture.”
A cleaner alternative
In preparation for designing their device, the researchers studied how different environmental factors – like humidity, wind speed, salt levels, and acidity – affect ammonia production. They also looked at how the size of water droplets, the concentration of the solution, and the contact of water with materials that do not dissolve in water impact the process. Lastly, they tested the best mix of iron oxide and an acid polymer with fluorine and sulfur to determine the ideal conditions for producing ammonia and understand how these catalyst materials interact with water droplets.
The Stanford team’s process makes ammonia cleanly and inexpensively and utilizes the surrounding air to get nitrogen and hydrogen from water vapor. By passing air through a mesh coated with catalysts to facilitate the necessary reaction, the researchers produced enough ammonia with a sufficiently high concentration to serve as a hydroponic fertilizer in greenhouse settings. Unlike traditional methods, the new technique operates at room temperature and standard atmospheric pressure, requiring no external voltage source to be attached to the mesh. Farmers could run the portable device onsite, eliminating the need to purchase and ship fertilizer from a manufacturer.
“This approach significantly reduces the carbon footprint of ammonia production,” said study lead author Xiaowei Song, a chemistry research scientist at Stanford.
In laboratory experiments, the team demonstrated further potential by recycling water through a spraying system, achieving ammonia concentrations sufficient to fertilize plants grown in a greenhouse after just two hours. By incorporating a filter made from a microporous stone material, this approach could produce enough ammonia to support broader agricultural applications.
A future without fossil fuels
The device is two to three years away from being market-ready, according to study co-author Chanbasha Basheer of King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals. In the meantime, the researchers plan to use increasingly large mesh systems to produce more ammonia. “There is a lot of room to develop this,” Basheer said.
Ammonia’s importance extends beyond fertilizers. As a clean energy carrier, it can store and transport renewable energy more efficiently than hydrogen gas due to its higher energy density. The innovation positions ammonia as a linchpin in decarbonizing industries like shipping and power generation.
“Green ammonia represents a new frontier in sustainability,” Zare said. “This method, if it can be scaled up economically, could drastically reduce our reliance on fossil fuels across multiple sectors.”
Co-authors of the study also include Jinheng Xu, a PhD student in chemistry in the Stanford School of Humanities and Sciences.
Zare is also a professor, by courtesy, of physics in the Stanford School of Humanities and Sciences and an affiliate of the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment.
The study was funded by the U.S. Air Force Office of Scientific Research and King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals.
END
New device produces critical fertilizer ingredient from thin air, cutting carbon emissions
2024-12-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Buried landforms reveal North Sea’s ancient glacial past
2024-12-13
An international team of researchers, including a glaciologist at Newcastle University, UK, has discovered remarkably well-preserved glacial landforms buried almost 1 km beneath the North Sea.
The team used sound wave, known as seismic, data to reveal Ice Age landforms buried beneath almost 1 km of mud in the North Sea. The results, reported in the journal Science Advances, suggest that the landforms were produced about 1 million years ago, when an ice sheet centred over Norway extended towards the British Isles.
This is important because the timing of this ice advance corresponds to a period of global cooling called the Mid-Pleistocene Transition.
Glacial ...
Camrelizumab vs placebo in combination with chemotherapy as neoadjuvant treatment in patients with early or locally advanced triple-negative breast cancer
2024-12-13
About The Study: Among patients with early or locally advanced triple-negative breast cancer, the addition of camrelizumab, an anti–PD-1 antibody, to neoadjuvant chemotherapy significantly improved pathological complete response.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Zhi-Ming Shao, MD (zhiminshao@fudan.edu.cn) and Lei Fan, MD (teddyfl@163.com).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.23560)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
Intermittent fasting inhibits hair regeneration in mice
2024-12-13
Intermittent fasting has proven benefits for metabolic health, but a new study shows that it could slow hair growth—at least in mice. Researchers report December 13 in the Cell Press journal Cell that mice subjected to intermittent fasting regimes showed improved metabolic health but slower hair regeneration compared to mice with 24/7 access to food. A similar process might occur in humans, based on a small clinical trial that the team also conducted, but it’s likely to be less severe since humans have a much slower metabolic rate and different hair growth patterns compared to mice.
“We don't want to scare people away ...
Changes in adult obesity trends in the US
2024-12-13
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that body mass index and obesity prevalence in the U.S. decreased in 2023 for the first time in more than a decade. The most notable decrease was in the South, which had the highest observed per capita glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) dispensing rate. However, dispensing does not necessarily mean uptake, and the South also experienced disproportionately high COVID-19 mortality among individuals with obesity.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Benjamin Rader, PhD, MPH, email benjamin.rader@childrens.harvard.edu.
To ...
Prevalence of post–COVID-19 condition and activity-limiting post–COVID-19 condition among adults
2024-12-13
About The Study: In 2023, among 29,522 respondents to the National Health Interview Survey, a nationally representative household survey, 8.4% of adults in the U.S. reported they ever had post–COVID-19 condition (PCC; also known as long COVID), 3.6% currently had PCC, and 2.3% currently had activity-limiting PCC. Significant differences across all 3 outcomes were observed by sex, sexual orientation, age, race and Hispanic origin, family income, and urbanization.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Anjel Vahratian, PhD, MPH, email avahratian@cdc.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Scientists innovate breeding strategies to create climate-smart crops
2024-12-13
A recent study has reported a novel breeding strategy to rapidly create climate-smart crops that show higher yield under normal conditions and greatly rescue yield losses under heat stress both in staple grain and vegetable crops.
The study, which was published in Cell on 13 December, was conducted by Prof. XU Cao’s team from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology (IGDB) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The year 2050 is fast approaching and farm productivity must increase by 60% in order to feed a projected global population of 10 billion. However, current crop production is insufficient and is expected to worsen due to the abiotic-stress burden ...
The genetic basis of fertility, family and longevity
2024-12-13
Led by researchers from the University of Oxford’s Leverhulme Centre for Demographic Science and the University of Iceland, the review explores how genetic variations can explain differences in reproductive health and longevity.
The study provides the most comprehensive review of male and female genetic discoveries of reproductive traits to date, and provides new insights into how our DNA affects when we have children, the timing of menopause, and even how that is connected to how long we live.
Genes at the heart of reproduction
Using the GWAS Catalog, an online database of Genome Wide Association Studies (GWAS), the researchers identified ...
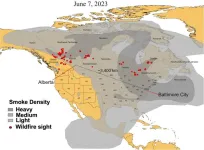
Exposure to remote wildfire smoke drifting across the US linked to increased medical visits for heart and lung problems
2024-12-13
Wildfire smoke has long been known to exacerbate health problems like heart disease, lung conditions, and asthma, but now a new study finds that smoke from these fires can lead to poor health thousands of miles away. Researchers from the University of Maryland Institute for Health Computing (UM-IHC) found that medical visits for heart and lung problems rose by nearly 20 percent during six days in June, 2023, when smoke from Western Canadian wildfires drifted across the country, leading to very poor air quality days in Baltimore and ...
Northwestern University joins Giant Magellan Telescope International Consortium
2024-12-13
PASADENA, CA – December 13, 2024 – The Giant Magellan Telescope announced today that Northwestern University has joined its international consortium to construct the $2.54 billion observatory.
Home to the world-renowned Center for Interdisciplinary Exploration and Research in Astrophysics (CIERA) and the newly founded NSF-Simons AI Institute for the Sky (SkAI), Northwestern is at the forefront of advancing astrophysical research. Northwestern researchers will develop and apply cutting-edge artificial intelligence ...
HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer patients with high risk of recurrence may benefit from addition of anthracyclines to taxane- based chemotherapy
2024-12-13
SAN ANTONIO – Patients with early-stage, node-negative, hormone receptor (HR)-positive, HER2- negative breast cancer who have a high risk of recurrence based on the OncotypeDX genomic test had better outcomes when treated with adjuvant anthracycline- plus taxane-based chemotherapy regimens compared with those receiving adjuvant taxane-based chemotherapy regimens alone, according to results presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS), held December 10-13, 2024.
“HR-positive, HER2-negative is the most common type of breast cancer in the United States and we frequently need to decide whether or not adjuvant chemotherapy ...