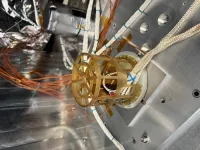
(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO — December 17, 2024 —NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) recently awarded Southwest Research Institute a $26 million contract to develop magnetometers for NOAA’s Space Weather Next (SW Next) program for two missions to be launched in 2029 and 2032. The magnetometers will measure the interplanetary magnetic field carried by the solar wind.
“The instruments provide critical data to NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center which issues forecasts, warnings and alerts that help mitigate space weather impacts,” said Dr. Roy Torbert, a program director in SwRI’s Earth, Oceans, and Space office at the University of New Hampshire (UNH) in Durham, N.H., and principal investigator of the magnetometer. “Space weather refers to the variable conditions on the Sun and in space that can influence the performance of technology we use on Earth, such as electrical power grids, and disrupt satellite-based communication and navigation systems.”
The magnetometers will be deployed on satellites that will orbit the Sun at approximately 1.5 million kilometers from the Earth at a point known as Lagrange 1, or L1. Gravitational forces from the Sun and the Earth hold objects at L1 in a stable position and offer an uninterrupted view of the Sun. The instrument will make local measurements of the magnetic field conveyed by the solar wind as it blows towards the Earth.
“The instrument, known as SW-MAG, provides key data about the solar wind as it approaches Earth,” Torbert said. “The data will be available to the science community but are targeted to the Space Weather Prediction Center.”
SwRI will work with UNH to design, develop, fabricate, integrate, calibrate and evaluate the magnetometer instrument. The team will also support launch and on-orbit check-out of the instrument, supply and maintain the instrument’s ground support equipment, and support NOAA’s mission operations center as needed. SW-MAG includes two three-axis magnetometers and associated electronics to measure the vector interplanetary magnetic field.
“The solar wind magnetic field controls the processes that transfer energy and particles into the Earth’s magnetosphere and often initiates geomagnetic storms,” Torbert said. “These disturbances can create spectacular auroras but can also shut down electrical power grids and disrupt satellite-based communication and navigation systems.”
NASA is planning to launch the SW-NEXT as a follow-up to the SWFO-L1 mission, which also will have an SwRI-developed magnetometer in its payload, in 2025 as a rideshare with the Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe (IMAP) vehicle. SwRI also plays a role in that mission, managing the payload and payload systems engineering for IMAP, which will sample, analyze and map particles streaming to Earth from the edge of interstellar space.
NASA and NOAA oversee the development, launch, testing, and operation of all the satellites in the Lagrange 1 Series project. NOAA is the program owner providing the requirements and funding along with managing the program, operations, data products, and dissemination to users. NASA and its collaborators will develop and build the instruments and spacecraft and provide launch services on behalf of NOAA. SwRI will work with NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center and Kennedy Space Center to develop the magnetometers.
For more information, visit https://www.swri.org/heliophysics.
END
SwRI awarded $26 million to develop NOAA magnetometers
SW-MAG data will help NOAA predict, mitigate the effects of space weather
2024-12-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Being digitally hyperconnected causes ‘techno-strain’ for employees
2024-12-17
A new study has shown that employees are experiencing mental and physical techno-strain due to being ‘hyperconnected’ to digital technology making it difficult for people to switch off from work.
Researchers from the University of Nottingham’s Schools of Psychology and Medicine conducted detailed interviews with employees from a range of professions and found that the cognitive and affective effort associated with constant connectivity and high work pace driven by the digital workplace is detrimental to employee wellbeing. The results have been published today in Frontiers in Organizational Psychology.
This new paper is the final part of a research ...
Missing rebound: Youth drug use defies expectations, continues historic decline
2024-12-17
Image
Adolescent drug use continued to drop in 2024, building on and extending the historically large decreases that occurred during the pandemic onset in 2020.
"I expected adolescent drug use would rebound at least partially after the large declines that took place during the pandemic onset in 2020, which were among the largest ever recorded," said Richard Miech, team lead of the Monitoring the Future study at U-M's Institute for Social Research.
"Many experts in the field had anticipated that drug use would resurge ...
Announcing the 2024 Mcknight Brain Research Foundation Innovator Awards in Cognitive Aging and Memory Loss
2024-12-17
NEW YORK CITY and ORLANDO— The American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR) and the McKnight Brain Research Foundation (MBRF) are pleased to announce the 2024 recipients of The McKnight Brain Research Foundation Innovator Awards in Cognitive Aging and Memory Loss: Janine Kwapis, PhD, of Pennsylvania State University, and Sanaz Sedaghat, PhD, of the University of Minnesota.
Now in its fourth year, the Innovator Awards provide funding to research scientists pursuing groundbreaking studies in the field of cognitive aging.
Janine Kwapis, PhD, is an Assistant Professor and Paul Berg Early Career Professor ...
Study shows drop in use of antiviral medications in young children with influenza
2024-12-17
Despite national medical guidelines supporting the use of antiviral medications in young children diagnosed with influenza, a recent study reports an underuse of the treatment.
“Antiviral Use Among Children Hospitalized with Laboratory-Confirmed Influenza Illness: A Prospective, Multicenter Surveillance Study” was published in Clinical Infectious Diseases, the flagship journal of the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Flu illness accounts for up to 10% of all pediatric hospitalizations during ...
Generative AI against diseases: Insilico Medicine announced Pharma.AI-powered HPK1 inhibitor series in peer-reviewed publication trilogy, as potential immunotherapy options
2024-12-17
Hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 (HPK1), a member of the Ste20 serine/threonine kinases family, negatively regulates T cell function and is considered a promising target for immunotherapy. Despite the promising efficacy demonstrated in preclinical models, no HPK1 inhibitors are currently approved for clinical use, due to challenges including balance between kinase selectivity and pharmacokinetic properties.
CAMBRIDGE, Mass., Dec 17, 2024 --- Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, is proud to announce its latest AI-powered ...
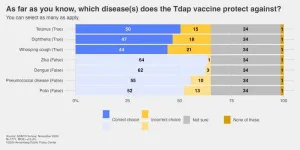
Cases of whooping cough growing, but knowledge about it is lacking
2024-12-17
PHILADELPHIA – Following a several-year lull during the pandemic, cases of whooping cough are increasing across the United States. As of Nov. 30, early U.S. data show over 28,000 cases reported this year, or six times as many as in the same period in 2023, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Whooping cough or pertussis, a highly contagious bacterial infection of the respiratory tract, was one of the most common childhood diseases in the 20th century and a major cause ...
Research alert: Neural stem cell transplantation shows promise for treating chronic spinal cord injury
2024-12-17
A Phase I clinical trial led by researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine has demonstrated the long-term safety and feasibility of neural stem cell transplantation for treating chronic spinal cord injuries. These devastating injuries often result in partial or full paralysis and are currently incurable. The study, which followed four patients with chronic spinal cord injuries for five years, found that two patients showed durable evidence of neurological improvement after treatment with neural stem cell implantation, including increased ...
Gruyère cheese, or a history of the domestication of bacteria
2024-12-17
The domestication of plants and animals has played a key role in the development of human societies. And microbes, too, have been tamed: a study by UNIL, published in the journal Nature Communications, shows that the bacteria used to produce Gruyère, Emmental and Sbrinz cheese show signs of ancient domestication.
The domestication of livestock and plants marked an important stage in the settlement of human populations in the Neolithic period, as they moved from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to a subsistence model based on animal husbandry and agriculture. Because of the microscopic size and virtual absence of fossils ...
Simulating natural selection in assisted reproduction
2024-12-17
A Perspective summarizes the risks of bypassing natural selection when using assisted reproductive technologies (ART) in humans and livestock. The authors call for dialogue between the fields of assisted reproduction and evolutionary biology.
Jonathan P. Evans and Francisco Garcia-Gonzalez detail how techniques used in ART, including in vitro fertilization, artificial insemination, and intracytoplasmic sperm injection, can stress and damage gametes and embryos and lead to deleterious epigenetic changes in offspring. Some ART techniques also bypass a system of filters in the female reproductive tract that select healthy sperm and may lead to better genetic matches with ...
Almost three quarters of adolescents experience depression or anxiety
2024-12-17
Almost three quarters of adolescents in Australia experience clinically significant depression or anxiety symptoms, with most being chronic, according to a new study. And preventive strategies outside our clinics are urgently required to address this considerable public health problem facing the nation.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) and published in The Lancet Psychiatry, found mental health problems were frequently chronic with 64 per cent reporting symptoms three or more times across their adolescent years.
MCRI Dr Ellie Robson said the rate and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
[Press-News.org] SwRI awarded $26 million to develop NOAA magnetometersSW-MAG data will help NOAA predict, mitigate the effects of space weather