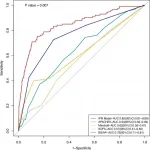
(Press-News.org) About The Study: This study found that early adoption and implementation of Tobacco 21 (T21) policies (minimum age of 21 for legal access to tobacco products) maximizes potential premature mortality reductions. However, the strength of T21 policies and enforcement varies widely across states. Enforcement of the federal T21 law is critical in the 8 states without state-level T21 cigarette policies of their own.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jamie Tam, PhD, email jamie.tam@yale.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.4445)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama-health-forum/fullarticle/10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.4445?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=122024
About JAMA Health Forum: JAMA Health Forum is an international, peer-reviewed, online, open access journal that addresses health policy and strategies affecting medicine, health and health care. The journal publishes original research, evidence-based reports and opinion about national and global health policy; innovative approaches to health care delivery; and health care economics, access, quality, safety, equity and reform. Its distribution will be solely digital and all content will be freely available for anyone to read.
END
US tobacco 21 policies and potential mortality reductions by state
JAMA Health Forum
2024-12-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI-driven approach reveals hidden hazards of chemical mixtures in rivers
2024-12-20
Artificial intelligence can provide critical insights into how complex mixtures of chemicals in rivers affect aquatic life – paving the way for better environmental protection.
A new approach, developed by researchers at the University of Birmingham, demonstrates how advanced artificial intelligence (AI) methods can help identify potentially harmful chemical substances in rivers by monitoring their effects on tiny water fleas (Daphnia).
The team worked with scientists at the Research Centre for Eco-Environmental Sciences (RCEES), in China, and the Hemholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ), in Germany, to analyse ...
Older age linked to increased complications after breast reconstruction
2024-12-20
December 20, 2024 — For women undergoing breast reconstruction after mastectomy, older age is associated with small but significant increases in certain complications, reports a study in the January issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Older women may be less satisfied with the appearance of the reconstructed breasts, ...
ESA and NASA satellites deliver first joint picture of Greenland Ice Sheet melting
2024-12-20
Academics from Northumbria University are part of an international research team which has used data from satellites to track changes in the thickness of the Greenland Ice Sheet.
Global warming is causing the Ice Sheet to melt and flow more rapidly, raising sea levels and disturbing weather patterns across our planet.
Because of this, precise measurements of its changing shape are of critical importance for tracking and adapting to the effects of climate warming.
Scientists have now delivered the first measurements of Greenland Ice Sheet thickness change using CryoSat-2 and ICESat-2 – the ESA and ...
Early detection model for pancreatic necrosis improves patient outcomes
2024-12-20
A new prediction model for infected pancreatic necrosis (IPN) in patients with acute pancreatitis (AP) offers a groundbreaking approach to improving patient outcomes. Developed by a team of researchers across eight Chinese hospitals, the model harnesses five early clinical indicators—respiratory rate, temperature, serum glucose, calcium, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN)—to identify high-risk patients within 24 hours of hospital admission.
The study, recently published in eGastroenterology, analyzed data from over 3,000 patients diagnosed with AP between 2017 and 2023. Researchers employed advanced statistical methods, including LASSO regression and multivariate analysis, to develop ...
Poor vascular health accelerates brain ageing
2024-12-20
Using an AI tool, researchers at Karolinska Institutet have analysed brain images from 70-year-olds and estimated their brains’ biological age. They found that factors detrimental to vascular health, such as inflammation and high glucose levels, are associated with an older-looking brain, while healthy lifestyles were linked to brains with a younger appearance. The results are presented in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association.
Every year, over 20,000 people in Sweden develop some form of dementia, with Alzheimer’s disease accounting for approximately two-thirds of cases. However, the speed at which ...
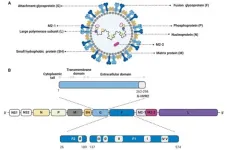
Chinese Medical Journal review provides insights into respiratory syncytial virus
2024-12-20
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a major cause of respiratory infections, particularly in infants, children under 5 years, and older adults. Its rapid spread makes RSV a serious public health concern. Currently, there are no effective medications for RSV, and current treatment focuses on providing supportive care and preventing its spread.
In a recent study, authors from the Chinese Academy of Medical Science and Peking Union Medical College, Nanjing Medical University, Children's Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention of the Chinese Center ...
Growing safer spuds: removing toxins from potatoes
2024-12-20
Scientists have discovered a way to remove toxic compounds from potatoes, making them safer to eat and easier to store. The breakthrough could cut food waste and enhance crop farming in space and other extreme environments.
Potato plants naturally produce chemicals that protect them from insects. The chemicals, called steroidal glycoalkaloids, or SGAs, are found in high quantities in the green parts of potato peels, and in the sprouting areas. They render the potatoes unsafe for insects as well as humans.
"These compounds are critical for plants to ward off insects, but they ...
Russia-Ukraine War’s unexpected casualties: Hungry people in distant nations
2024-12-20
The war in Ukraine is causing hunger thousands of miles from the battlefields, according to a study released today.
Nearly three years of war in the “breadbasket of the world” has left croplands destroyed and forced laborers who grow, harvest and process a bounty of wheat, barley and oats to flee. Combined with export bans from other countries, ripple effects resonated through global trade and upended food supply systems.
But understanding how far those disruptions reached, who suffered and who gained has been difficult. Researchers at Michigan State University’s Center for Systems Integration and Sustainability (CSIS) lead a unique effort, relying ...
York U professor’s new paper challenges tokenizing women of colour in academia
2024-12-20
TORONTO, December 20, 2024 — The unspoken rule for women of colour in academia is to be everything to everyone – mentor, diversity champion, tireless scholar, and silent workhorse, says York University equity studies Assistant Professor Yvonne Su in her recent paper published today in Nature Human Behaviour.
“We are expected to carry the banner of inclusion, but we are not truly included. Inclusion, as it’s currently defined, is about optics, not transformation,” observes Su in the Faculty of Liberal Arts and Professional Studies. “It’s about showing diversity on the surface ...
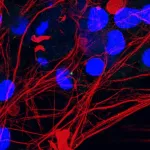
Tiny antennas on cells offer new ALS insights
2024-12-20
Leuven, 20 December 2024- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a devastating neurodegenerative disease that affects motor neurons. The average life span after diagnosis of this incurable disease is two to five years. In the relentless pursuit of understanding the cause of motor neuron death, scientists from KU Leuven and the VIB Center for Brain and Disease Research have identified an intriguing new lead: tiny, antenna-like structures 0n cells called primary cilia. Their study, published in Brain, could open a potential new avenue for therapeutic development.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Bug beats: caterpillars use complex rhythms to communicate with ants
High-risk patients account for 80% of post-surgery deaths
Celebrity dolphin of Venice doesn’t need special protection – except from humans
Tulane study reveals key differences in long-term brain effects of COVID-19 and flu
The long standing commercialization challenge of lithium batteries, often called the dream battery, has been solved.
New method to remove toxic PFAS chemicals from water
The nanozymes hypothesis of the origin of life (on Earth) proposed
Microalgae-derived biochar enables fast, low-cost detection of hydrogen peroxide
Researchers highlight promise of biochar composites for sustainable 3D printing
Machine learning helps design low-cost biochar to fight phosphorus pollution in lakes
Urine tests confirm alcohol consumption in wild African chimpanzees
Barshop Institute to receive up to $38 million from ARPA-H, anchoring UT San Antonio as a national leader in aging and healthy longevity science
Anion-cation synergistic additives solve the "performance triangle" problem in zinc-iodine batteries
Ancient diets reveal surprising survival strategies in prehistoric Poland
Pre-pregnancy parental overweight/obesity linked to next generation’s heightened fatty liver disease risk
Obstructive sleep apnoea may cost UK + US economies billions in lost productivity
Guidelines set new playbook for pediatric clinical trial reporting
Adolescent cannabis use may follow the same pattern as alcohol use
Lifespan-extending treatments increase variation in age at time of death
From ancient myths to ‘Indo-manga’: Artists in the Global South are reframing the comic
Putting some ‘muscle’ into material design
House fires release harmful compounds into the air
Novel structural insights into Phytophthora effectors challenge long-held assumptions in plant pathology
Q&A: Researchers discuss potential solutions for the feedback loop affecting scientific publishing
A new ecological model highlights how fluctuating environments push microbes to work together
Chapman University researcher warns of structural risks at Grand Renaissance Dam putting property and lives in danger
Courtship is complicated, even in fruit flies
Columbia announces ARPA-H contract to advance science of healthy aging
New NYUAD study reveals hidden stress facing coral reef fish in the Arabian Gulf
36 months later: Distance learning in the wake of COVID-19
[Press-News.org] US tobacco 21 policies and potential mortality reductions by stateJAMA Health Forum