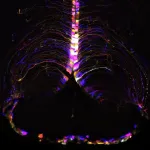
(Press-News.org) SEATTLE, WASH.—January 1, 2025—Scientists at the Allen Institute have identified specific cell types in the brain of mice that undergo major changes as they age, along with a specific hot spot where many of those changes occur. The discoveries, published in the journal Nature, could pave the way for future therapies to slow or manage the aging process in the brain.
Key findings
Sensitive cells: Scientists discovered dozens of specific cell types, mostly glial cells, known as brain support cells, that underwent significant gene expression changes with age. Those strongly affected included microglia and border-associated macrophages, oligodendrocytes, tanycytes, and ependymal cells.
Inflammation and neuron protection: In aging brains, genes associated with inflammation increased in activity while those related to neuronal structure and function decreased.
Aging hot spot: Scientists discovered a specific hot spot combining both the decrease in neuronal function and the increase in inflammation in the hypothalamus. The most significant gene expression changes were found in cell types near the third ventricle of the hypothalamus, including tanycytes, ependymal cells, and neurons known for their role in food intake, energy homeostasis, metabolism, and how our bodies use nutrients. This points to a possible connection between diet, lifestyle factors, brain aging, and changes that can influence our susceptibility to age-related brain disorders.
“Our hypothesis is that those cell types are getting less efficient at integrating signals from our environment or from things that we're consuming,” said Kelly Jin, Ph.D., a scientist at the Allen Institute for Brain Science and lead author of the study. “And that loss of efficiency somehow contributes to what we know as aging in the rest of our body. I think that's pretty amazing, and I think it’s remarkable that we're able to find those very specific changes with the methods that we're using.”
To conduct the study, funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), researchers used cutting-edge single-cell RNA sequencing and advanced brain-mapping tools developed through NIH’s The BRAIN Initiative® to map over 1.2 million brain cells from young (two months old) and aged (18 months old) mice across 16 broad brain regions. The aged mice are what scientists consider to be the equivalent of a late middle-aged human. Mouse brains share many similarities with human brains in terms of structure, function, genes, and cell types.
“Aging is the most important risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease and many other devastating brain disorders. These results provide a highly detailed map for which brain cells may be most affected by aging,” said Richard J. Hodes, M.D., director of NIH’s National Institute on Aging. “This new map may fundamentally alter the way scientists think about how aging affects the brain and also provides a guide for developing new treatments for aging-related brain diseases.”
A path toward new therapies
Understanding this hot spot in the hypothalamus makes it a focal point for future study. Along with knowing which cells to specifically target, this could lead to the development of age-related therapeutics, helping to preserve function and prevent neurodegenerative disease.
“We want to develop tools that can target those cell types,” said Hongkui Zeng, Ph.D., executive vice president and director of the Allen Institute for Brain Science. “If we improve the function of those cells, will we be able to delay the aging process?”
The latest findings also align with past studies that link aging to metabolic changes as well as research suggesting that intermittent fasting, balanced diet, or calorie restriction can influence or perhaps increase life span.
“It’s not something we directly tested in this study,” said Jin. “But to me, it points to the potential players involved in the process, which I think is a huge deal because this is a very specific, rare population of neurons that express very specific genes that people can develop tools for to target and further study.”
Future brain aging research
This study lays the groundwork for new strategies in diet and therapeutic approaches aimed at maintaining brain health into old age, along with more research on the complexities of advanced aging in the brain. As scientists further explore these connections, research may unlock more specific dietary or drug interventions to combat or slow aging on a cellular level.
“The important thing about our study is that we found the key players—the real key players—and the biological substrates for this process,” said Zeng. “Putting the pieces of this puzzle together, you have to find the right players. It’s a beautiful example of why you need to study the brain and the body at this kind of cell type-specific level. Otherwise, changes happening in specific cell types could be averaged out and undetected if you mix different types of cells together.”
This study was funded by NIH grants R01AG066027 and U19MH114830. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
About the Allen Institute
The Allen Institute is an independent, 501(c)(3) nonprofit research organization founded by philanthropist and visionary, the late Paul G. Allen. The Allen Institute is dedicated to answering some of the biggest questions in bioscience and accelerating research worldwide. The Institute is a recognized leader in large-scale research with a commitment to an open science model. Its research institutes and programs include the Allen Institute for Brain Science, the Allen Institute for Cell Science, the Allen Institute for Immunology, and the Allen Institute for Neural Dynamics. In 2016, the Allen Institute expanded its reach with the launch of The Paul G. Allen Frontiers Group, which identifies pioneers with new ideas to expand the boundaries of knowledge and make the world better. For more information, visit alleninstitute.org.
# # #
Media Contact
Liz Dueweke, Sr. Communications and Media Relations Specialist
206-225-0596 | liz.dueweke@alleninstitute.org
END
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University researchers have found the pupil is key to understanding how, and when, the brain forms strong, long-lasting memories.
By studying mice equipped with brain electrodes and tiny eye-tracking cameras, the researchers determined that new memories are being replayed and consolidated when the pupil is contracted during a substage of non-REM sleep. When the pupil is dilated, the process repeats for older memories. The brain’s ability to separate these two substages of sleep with a previously unknown micro-structure is what ...
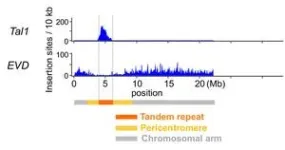
A joint research group team led by Sayuri Tsukahara and Tetsuji Kakutani of the University of Tokyo has clarified a mechanism of how retrotransposons, genetic elements that can “jump around” chromosomes and are known drivers of evolution, preferentially insert in the centromere. The findings were published in the journal Nature.
The centromere is the thinnest part of the chromosome that divides it into a long and short arm, much like how the waist separates the upper and lower body. Its role in transmitting information via cell division has been preserved ...
New York, NY—January 1, 2025—Mechanical force is an essential feature for many physical and biological processes. Remote measurement of mechanical signals with high sensitivity and spatial resolution is needed for a wide range of applications, from robotics to cellular biophysics and medicine and even to space travel. Nanoscale luminescent force sensors excel at measuring piconewton forces, while larger sensors have proven powerful in probing micronewton forces. However, large gaps remain in the force magnitudes that can be probed remotely from subsurface ...
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00 GMT Wednesday 1 January 2025
Peer reviewed
Observational study
Ancient people
Ancient DNA unlocks new understanding of migrations in the first millennium AD
Waves of human migration across Europe during the first millennium AD have been revealed using a more precise method of analysing ancestry with ancient DNA, in research led by the Francis Crick Institute.
Researchers can bring together a picture of how people moved across the world by looking at changes in their DNA, but this becomes a lot harder when historical ...
Fast radio bursts are brief and brilliant explosions of radio waves emitted by extremely compact objects such as neutron stars and possibly black holes. These fleeting fireworks last for just a thousandth of a second and can carry an enormous amount of energy — enough to briefly outshine entire galaxies.
Since the first fast radio burst (FRB) was discovered in 2007, astronomers have detected thousands of FRBs, whose locations range from within our own galaxy to as far as 8 billion light-years away. Exactly how ...
Leuven, 2 January 2024 – Researchers from the lab of Prof. Sarah-Maria Fendt (VIB-KU Leuven) and colleagues have uncovered that the availability of the amino acid aspartate is one reason why the lung is a frequent organ of metastasis. Their work appears in Nature and improves our understanding of cancer biology while providing the foundation for new therapeutic interventions in metastatic diseases.
A role for aspartate
More than half of cancer patients in whom the cancer spreads beyond the primary site have lung metastases. What makes the lungs such a ...
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE: Jan. 1, 2025, 11 a.m. ET
CONTACT:
NIAPressTeam@mail.nih.gov, 301-496-1752
Aging may change some brain cells more than others
NIH-funded mouse study provides roadmap for how aging may alter brain cell genetic activity
Based on new brain mapping research funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), scientists have discovered that not all cell types in the brain age in the same way. They found that some cells, such as a small group of hormone-controlling cells, may undergo more age-related changes in genetic activity than others. The results, published ...
WASHINGTON, D.C., Jan. 1, 2025—As the body of research grows around the potential promise of psychedelic medications in psychiatry, many questions and challenges remain. The January issue of the American Journal of Psychiatry features a series of articles, including new research, reviews and commentaries, on the use of these treatments.
The issue addresses many of the ongoing challenges and looming questions in the field of psychiatric psychedelic research and treatment. These include issues relevant to basic ...
TORONTO, Ontario, Canada, 31 December 2024 - In a comprehensive Genomic Press Interview, leading geneticist Dr. Cathy Barr unveils crucial discoveries about the complex interplay between genes and childhood psychiatric disorders. As a Senior Scientist at both the Hospital for Sick Children and Krembil Research Institute, Dr. Barr's research illuminates the genetic foundations of conditions including depression, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, reading disabilities, and Tourette syndrome.
"After decades of searching ...
AURORA, Colo. (Dec. 31, 2024) – A groundbreaking study has shed light on the complex interactions between dystrophin, a protein critical to muscle stability, and its partner protein, dystrobrevin, offering new pathways for understanding and treating Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD).
Published in the December issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry, researchers characterize the mysterious C-terminal (CT) domain of dystrophin and its role in stabilizing cellular membranes across various tissues.
DMD, a severe genetic disorder that causes muscle weakness and shortens lifespans, arises from mutations in the gene encoding ...