(Press-News.org) A new study from UCLA Health adds to the growing body of evidence on the cognitive benefits of speaking multiple languages, finding that multilingualism not only enhances general cognitive abilities but also may help reduce certain symptoms and bolster control of daily thoughts and actions in children with and without autism.
The study, published in the journal Autism Research, found parents of autistic and non-autistic children in multilingual households reported their children had stronger overall executive function, including the ability to focus, understand other people’s perspectives, communication and reduced levels of repetitive behaviors, compared to children in mono-lingual households.
“It turns out that speaking multiple languages, whether or not you have a diagnosis of autism, is associated with better inhibition, better shifting or flexibility, and also better perspective taking ability,” said study lead author Dr. Lucina Uddin, a UCLA Health Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences Professor and Director of the UCLA Brain Connectivity and Cognition Laboratory.
Conducted initially at the University of Miami, the study recruited more than 100 autistic and non-autistic children ages 7 to 12 from both monolingual and multilingual households. Most of the multilingual households spoke Spanish and English at home. Parents were asked to score their child’s executive function skills, which are often affected by autism spectrum disorder. Skills assessed included:
Inhibition: the ability to suppress doing something irrelevant or get distracted.
Working memory: the ability to keep something in mind, such as remembering a phone number.
Shifting: the ability to switch between two or more different tasks, such as playing with toys and cleaning up after.
Parents were also asked to score some of the core abilities affected by autism such as the ability to understand different perspectives, social communication and repetitive behaviors.
Results from the survey found multilingualism is associated with better inhibition, shifting and perspective taking skills in children both with and without autism.
“If you have to juggle two languages, you have to suppress one in order to use the other. That's the idea, that inhibition might be bolstered by knowing two languages,” Uddin said.
Speaking multiple languages also positively affected some of the core symptoms of autism, resulting in improved communication, reduced repetitive behaviors and improved perspective taking skills, Uddin said.
Uddin said there can be a concern among parents of autistic children that speaking multiple languages could contribute to delays in their child’s development relating to language learning. However, she said the evidence so far has suggested no negative impacts and possible long-term benefits.
“The big takeaway is we don’t see any negative effects of speaking multiple languages in the home,” Uddin said. “It's actually beneficial to celebrate all the languages associated with your culture.”
From these findings, Uddin is expanding the study and addressing limitations. The new study will recruit about 150 children with autism and will include more executive function and language tests as well as brain imaging.
For information about the study and to participate, visit https://www.semel.ucla.edu/bccl
END
Multilingualism improves crucial cognitive functions in autistic children
Researchers say improvements extend to non-autistic children in multilingual households
2025-01-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The carbon in our bodies probably left the galaxy and came back on cosmic ‘conveyer belt’
2025-01-03
Link to full release:
https://www.washington.edu/news/2025/01/03/galaxy-carbon-conveyer-belt/
FROM: James Urton
University of Washington
206-543-2580
jurton@uw.edu
(Note: researcher contact information at the end)
For immediate release
Friday, Jan. 3, 2025
The carbon in our bodies probably left the galaxy and came back on cosmic ‘conveyer belt’
Life on Earth could not exist without carbon. But carbon itself could not exist without stars. Nearly all elements except hydrogen and ...
Scientists unveil surprising human vs mouse differences in a major cancer immunotherapy target
2025-01-03
Since its discovery in the 1990s, “programmed cell death protein 1,” or PD-1, has been regarded as a leading target in cancer treatments. A “checkpoint” receptor that often resides on the surface of immune system cells, the PD-1 molecule works as a type of off switch that keeps immune cells from attacking other cells.
After its discovery, which revolutionized oncology and earned a 2018 Nobel Prize, researchers developed new drugs to block PD-1 and unleash the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Yet treatments leveraging PD-1 are only effective in a small fraction of cancer patients, highlighting ...
NASA’s LEXI will provide X-ray vision of Earth’s magnetosphere
2025-01-03
A NASA X-ray imager is heading to the Moon as part of NASA's Artemis campaign, where it will capture the first global images of the magnetic field that shields Earth from solar radiation.
The Lunar Environment Heliospheric X-ray Imager, or LEXI, instrument is one of 10 payloads aboard the next lunar delivery through NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, set to launch from the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida no earlier than mid-January, with Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Lander. The instrument will support ...
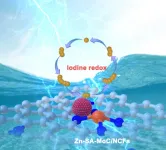
A successful catalyst design for advanced zinc-iodine batteries
2025-01-03
Aqueous zinc-ion batteries (ZIBs) have attracted extensive attention due to their high safety, abundant reserves, and environmental friendliness. Iodine with high abundance in seawater (55 μg L−1) is highly promising to fabricate zinc-iodine batteries due to high theoretical capacity (211 mAh g−1) and appropriate redox potential (0.54 V). However, the low electrical conductivity of iodine hinders the redox conversion for the efficient energy storage process with zinc. Additionally, the formed soluble polyiodides are prone to migirate to Zn anode, leading to capacity degration and ...
AMS Science Preview: Tall hurricanes, snow and wildfire
2025-01-03
The American Meteorological Society continuously publishes research on climate, weather, and water in its 12 journals. Many of these articles are available for early online access–they are peer-reviewed, but not yet in their final published form.
Below is a selection of articles published early online recently. Some articles are open-access; to view others, members of the media can contact kpflaumer@ametsoc.org for press login credentials.
JOURNAL ARTICLES
The Impact of Snowoff Timing and Associated Atmospheric Drivers on the Alaska Wildfire Season
Earth Interactions
Earlier ...
Study finds 25% of youth experienced homelessness in Denver in 2021, significantly higher than known counts
2025-01-03
AURORA, Colo. (Jan. 3, 2025) – A first of its kind study, published today in Pediatrics, has provided full-picture assessment of youth homelessness in Denver, Colorado. The findings reveal that nearly 25% of youth in Denver experienced homelessness or housing insecurity in 2021, with rates increasing almost every year since 2017.
Researchers across Colorado, led by Josh Barocas, MD and resident Matthew Westfall, MD of the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, combined multiple data sources for youth aged 14 to 17 in the City of Denver, to estimate the total number ...
Integrated spin-wave quantum memory
2025-01-03
The synchronization function of quantum memories can be employed to connect multiple short-distance entanglement into long-distance entanglement, so that to effectively overcome the transmission loss of photons and enable the construction of large-scale quantum networks. The rare-earth ions doped crystals is a candidate system for implementation of quantum memories with excellent performances, and integrated solid-state quantum memories have been successfully demonstrated with various micro- and nano- fabrication techniques.
All previous demonstrations of integrated quantum memories for light are limited to the storage ...
Brain study challenges long-held views about Parkinson's movement disorders
2025-01-03
University of Arizona researchers have revealed new insights into one of the most common complications faced by Parkinson's disease patients: uncontrollable movements that develop after years of treatment.
Parkinson's disease – a neurological disorder of the brain that affects a person's movement – develops when the level of dopamine, a chemical in the brain that's responsible for bodily movements, begins to dwindle. To counter the loss of dopamine, a drug called levodopa is administered and later gets converted into dopamine in the brain. However, long-term treatment with levodopa induces ...
Mental disorders among offspring prenatally exposed to systemic glucocorticoids
2025-01-03
About The Study: In this cohort study, prenatal exposure to glucocorticoids was associated with higher risk of some mental disorders. These data support continued caution in the use of glucocorticoids in pregnant people.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kristina Laugesen, PhD, email kristina.laugesen@clin.au.dk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.53245)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Trends in screening for social risk in physician practices
2025-01-03
About The Study: In this survey-based cross-sectional study of U.S. physician practices, social risk screening increased substantially from 2017 to 2022, although still less than one-third of practices systematically screened for a set of 5 common social risks (food, housing, utilities, interpersonal violence, and transportation). What remains to be seen is whether practices use these data to help improve patient health by adjusting health care or referring patients for assistance with social needs. As policies and incentives increasingly emphasize social risk screening, it will be important to assess the association of screening and referrals with patient ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] Multilingualism improves crucial cognitive functions in autistic childrenResearchers say improvements extend to non-autistic children in multilingual households