(Press-News.org) Basking too long in a sauna may put bathers at risk of heat stroke, particularly if they haven’t drunk enough water beforehand, warn doctors in the journal BMJ Case Reports, after treating a woman whose condition required admission to hospital.
Although relatively rare, heat stroke can be life threatening, even in the absence of various underlying risk factors, such as heart, lung, or neurological disease, and heavy drinking or taking a cocktail of prescription meds, they point out.
Heat stroke is defined as a sharp increase in core body temperature above 40°C that is associated with acutely impaired brain function, and ‘non-exertional’ heat stroke results from prolonged exposure to high environmental temperatures, explain the authors.
They treated a woman in her early 70s who had been found unconscious in her local gym’s sauna, where she had been doing stretching exercises for around 45 minutes.
Her core body temperature was 42°C—normal temperature is 36.4°C—her blood pressure was extremely low, and her heart rate was extremely high. She had a seizure after her arrival in emergency care.
She had previously been diagnosed with type 1 diabetes and an underactive thyroid, but she wasn’t a smoker or heavy drinker, and was a regular gym goer, so had few risk factors, point out the authors.
She was rapidly cooled with wet towels and a fan and given intravenous fluids and blood products to stabilise her.
Blood tests revealed malfunctioning kidneys and liver, evidence of a minor heart attack, and muscle tissue breakdown (rhabdomyolysis).
She regained consciousness within 2 hours of reaching normal core temperature but was confused and drowsy for 2 days. By day 3 this had resolved and she had no further seizures during her inpatient stay, which lasted 12 days.
After 26 days she had more or less fully recovered, except for some mild fatigue and mild liver function disturbance.
This is just one case report after prolonged sauna use, and as far as the authors are aware, only 9 other similar cases have been reported. But 3 of those people died as a result.
“The prognosis of heat stroke varies according to patient factors, particularly extremes of age,” explain the authors. “Classical heat stroke in elderly people carries a mortality rate of [more than] 50%, and this increases further with each additional organ dysfunction.
“Heat-related deaths spike during heat waves, as has been observed in multiple large international datasets. Deaths from heat stroke are expected to rise as global temperatures continue to increase," they add.
“Once heat stroke has occurred, the key determinate of outcome is how rapidly a patient is cooled, as the time spent with elevated core body temperature is correlated to the degree of cellular damage,” they emphasise.
The woman in question comments: “My experience has emphasised the dangers of saunas and how important it is to be fully hydrated on entering a sauna, and for them to be regularly checked by staff. As a regular sauna user, I never suffered any issues and, on reflection, I believe I had not drunk enough water.”
END
Basking too long in a sauna without adequate hydration may risk heat stroke, doctors warn
Although rare, condition can be life threatening, even in absence of various risk factors
2025-01-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
DNA adds new chapter to Indonesia’s layered human history
2025-01-08
A new study from the University of Adelaide and The Australian National University (ANU) has outlined the first genomic evidence of early migration from New Guinea into the Wallacea, an archipelago containing Timor-Leste and hundreds of inhabited eastern Indonesian islands.
The study, published in PNAS, addresses major gaps in the human genetic history of the Wallacean Archipelago and West Papuan regions of Indonesia – a region with abundant genetic and linguistic diversity that is comparable to the Eurasian ...
Many children and young people with diagnosable mental health disorders are not receiving timely help, says new research
2025-01-08
Children and young people with high levels of mental health needs are struggling to receive the help they need, or to have their difficulties recognised, according to a new study.
The STADIA trial, which is published in the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, was led by experts from the School of Medicine at the University of Nottingham, and was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR).
The large study, which spans different parts of England, involved 1,225 children and young people with emotional difficulties who had been referred to Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services (CAMHS) for help, and followed them up over 18 months to see ...
Dinosaurs roamed the northern hemisphere millions of years earlier than previously thought, according to new analysis of the oldest North American fossils
2025-01-08
MADISON — How and when did dinosaurs first emerge and spread across the planet more than 200 million years ago? That question has for decades been a source of debate among paleontologists faced with fragmented fossil records. The mainstream view has held that the reptiles emerged on the southern portion of the ancient supercontinent Pangea called Gondwana millions of years before spreading to the northern half named Laurasia.
But now, a newly described dinosaur whose fossils were uncovered by University of Wisconsin–Madison paleontologists is challenging ...
Breakthrough Durham University research offers new insights into quenching electrical waves in the heart
2025-01-08
-With images-
Scientists at Durham University have developed a theoretical framework to predict the efficacy of quenching of electrical pulses in excitable media, such as those found in the human heart.
This breakthrough could significantly accelerate the development of more efficient defibrillation techniques for treating cardiac arrhythmias.
The study, published in Physical Review E, addresses a longstanding challenge in understanding how stable excitation waves in systems like cardiac tissue can be effectively neutralised through small changes.
These electrical waves, when irregular, are thought to underly serious conditions such as fibrillation, ...
SLAC will play a key role in DOE’s new research centers for advancing next-generation microelectronics
2025-01-07
Around the globe day and night, the microelectronics behind much of modern technology help run computers, medical devices and state-of-the-art instruments that power scientific discoveries. But all of that technology consumes energy, and adding artificial intelligence to the mix increases our energy needs dramatically. Some experts caution that this pace of energy usage is unsustainable.
To tackle this challenge, the Department of Energy (DOE) has announced funding $179 million for three Microelectronics ...
Market researchers and online advertisers, are A-B tests leading you astray? A new study says they could be
2025-01-07
Researchers from Southern Methodist University and University of Michigan published a new Journal of Marketing study that examines platforms’ A-B testing of online ads and uncovers significant limitations that can create misleading conclusions about ad performance.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Where A-B Testing Goes Wrong: How Divergent Delivery Affects What Online Experiments Cannot (and Can) Tell You About How Customers Respond to Advertising” and is authored by Michael Braun and Eric M. Schwartz.
Consider a landscaping company whose designs focus ...
Research alert: Ketamine use on the rise in U.S. adults; new trends emerge
2025-01-07
A recent study analyzing data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) found that past-year recreational ketamine use among adults has increased dramatically since 2015, including significant shifts in associations with depression and sociodemographic characteristics such as race, age and education status. Ketamine use has shown promise in clinical trials therapy for several mental illnesses, including treatment-resistant depression, and the new research suggests that ongoing monitoring of recreational use trends is crucial to balancing these ...
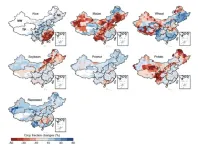
Crop switching for climate change in China
2025-01-07
A study of Chinese agriculture recommends planting areas currently growing maize and rapeseed with alternative crops to reduce environmental costs while maximizing food production as the climate changes.
Chinese food production has nearly doubled since the 1980s, mainly thanks to intensified nutrient usage and irrigation. Given that China’s demand for food is forecast to increase further, Qi Guan and colleagues modeled the country’s agricultural system under varying climate change scenarios in the 21st century, using a dynamic global vegetation model. The authors created scenarios ...
Cell-based therapy improves outcomes in a pig model of heart attacks
2025-01-07
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – In a large-animal model study, researchers have found that heart attack recovery is aided by injection of heart muscle cell spheroids derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells, or hiPSCs, that overexpress cyclin D2 and are knocked out for human leukocyte antigen classes I and II. This research, published in the journal Circulation Research, used a pig model of heart attacks. Pig hearts more closely resemble the human heart in size and physiology, and thus have a higher clinical relevance to human disease, compared to studies in mice.
University of Alabama at Birmingham researchers, led by Jianyi “Jay” ...
Researchers have a better understanding of how our cells dispose of waste while developing ways to control it
2025-01-07
Recycling takes place in our cells at all times: in a process called autophagy, cell components that are no longer needed are enclosed by membranes and broken down into their basic building blocks. This vital process prevents the formation of harmful aggregates and makes nutrients available again. A research team co-led by Prof. Dr. Claudine Kraft from the CIBSS Cluster of Excellence at the University of Freiburg and Dr. Florian Wilfling from the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt has now discovered the conditions necessary for autophagy to start. They were also able ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Basking too long in a sauna without adequate hydration may risk heat stroke, doctors warnAlthough rare, condition can be life threatening, even in absence of various risk factors