(Press-News.org) About The Study: The results of this economic evaluation suggest that cardiovascular polypill treatment (single pill containing a statin and 3 half-standard dose antihypertensives) could be a high value intervention for a low-income, majority Black population with limited access to health care services. It could additionally reduce health disparities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ciaran N. Kohli-Lynch, PhD, email ciaran.kohli-lynch@northwestern.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2024.4812)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflicts of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamacardiology/fullarticle/10.1001/jamacardio.2024.4812?guestAccessKey=99044e91-31bb-43a6-bf32-d1e42e9b434c&utm_source=for_the_media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=010825
END
Cost-effectiveness of a polypill for cardiovascular disease prevention in an underserved population
JAMA Cardiology
2025-01-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Development and validation of a tool to predict onset of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer dementia
2025-01-08
About The Study: In this prognostic study, with the use of a statistical modeling approach, the Florey Dementia Index was developed and validated to predict the onset age of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer dementia. This tool may be useful in organizing health care for older adults with cognitive decline or dementia and in the future may help prioritize patients for the use of disease-modifying monoclonal antibody drugs.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Yijun Pan, PhD (yijun.pan@unimelb.edu.au) ...
New AI predicts inner workings of cells
2025-01-08
NEW YORK, NY (Jan. 8, 2025)--Using a new artificial intelligence method, researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons can accurately predict the activity of genes within any human cell, essentially revealing the cell’s inner mechanisms. The system, described in the current issue of Nature, could transform the way scientists work to understand everything from cancer to genetic diseases.
“Predictive generalizable computational models allow to uncover biological ...
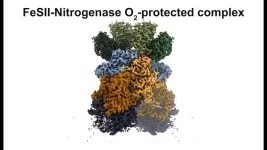
Scientists uncover key step in how diazotrophs “fix” nitrogen
2025-01-08
Nitrogen is an essential component in the production of amino acids and nucleic acids — both necessary for cell growth and function. Although the atmosphere is composed of nearly 80% nitrogen, this nitrogen is in the form of dinitrogen (N2), which cannot be processed by most organisms. Atmospheric nitrogen must first be converted, or “fixed,” into a form that can be used by plants, often as ammonia.
There are only two ways of fixing nitrogen, one industrial and one biological. To better understand a key component of the biological process, University of California San Diego Professor of Chemistry and Biochemistry Akif Tezcan and Assistant Professor of Chemistry ...
The hidden mechanics of earthquake ignition
2025-01-08
A new study has unravelled the hidden mechanics of how earthquakes ignite, shedding light on the mysterious transition from quiet, creeping motion to the violent ruptures that shake the Earth. Using cutting-edge experiments and innovative models, the research reveals that slow, silent stress release is a prelude and a necessary trigger for seismic activity. By incorporating the overlooked role of fault geometry, the study challenges long-held beliefs and offers a fresh perspective on how and when earthquakes begin. These findings not only deepen our understanding of nature’s ...
Scientists leverage artificial intelligence to fast-track methane mitigation strategies in animal agriculture
2025-01-08
BUSHLAND, Texas, Jan. 8, 2025 –A new study from USDA’s Agricultural Research Service (ARS) and Iowa State University (ISU) reveals that generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) can help expedite the search for solutions to reduce enteric methane emissions caused by cows in animal agriculture, which accounts for about 33 percent of U.S. agriculture and 3 percent of total U.S. greenhouse gas emissions.
"Developing solutions to address methane emissions from animal agriculture is a critical priority. Our scientists continue to use innovative and data-driven strategies to help ...
Researchers unravel a novel mechanism regulating gene expression in the brain that could guide solutions to circadian and other disorders
2025-01-08
A collaborative effort between Mount Sinai and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center has shed valuable light on how monoamine neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and now histamine help regulate brain physiology and behavior through chemical bonding of these monoamines to histone proteins, the core DNA-packaging proteins of our cells.
By uncovering how these histone modifications influence the brain, the team has identified a novel mechanism for controlling circadian gene expression and behavioral rhythms. ...
Discovery of 'Punk' and 'Emo' fossils challenges our understanding of ancient molluscs
2025-01-08
Researchers have unearthed two fossils, named Punk and Emo, revealing that ancient molluscs were more complex and adaptable than previously known.
Molluscs are one of life’s most diverse animal groups and analysis of the rare 430 million year old fossils is challenging long-held views on their early origins.
The fossils dating from the Silurian period were retrieved from Herefordshire and shed light on the molluscs’ complex evolutionary history and how they moved.
The discovery challenges the longstanding ...
Exposure to aircraft noise linked to worse heart function
2025-01-08
People who live close to airports and are exposed to high aircraft noise levels could be at greater risk of poor heart function, increasing the likelihood of heart attacks, life-threatening heart rhythms and strokes, according to a new study led by UCL (University College London) researchers.
The study, published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC), looked at detailed heart imaging data from 3,635 people who lived close to four major airports in England.
Within this group, the research team compared the hearts of those who lived in areas with higher aircraft noise with those who lived in lower aircraft noise areas.
They found that those who lived in ...
Deans of the University of Nottingham visited Korea University's College of Medicine
2025-01-08
Deans of the University of Nottingham Visited Korea University's College of Medicine
Korea University's College of Medicine Dean, Sung Bom Pyun, and Deans of the University of Nottingham; successfully held a researcher meeting program for 2 days from November 11th to 12th.
Fuve representative deans visited the University of Korea: Professor Claire Stewart, the Dean and Head of the School of Medicine at the University of Nottingham; Professor Nigel Mongan, Professor Alan McIntyre, Professor Srinivasan Madhusudan, and Professor Victoria James. They joined the program to conduct a tour and meeting with Korea University's researchers.
On ...
New study assesses wildfire risk from standing dead trees in Yellowstone National Park
2025-01-08
Standing dead trees in Yellowstone National Park are growing wildfire hazards, especially near park infrastructure. A new study published in Forest Ecosystems explores how these dead trees contribute to fire risk and threaten roads, buildings, and trails.
Dead trees, particularly those that remain standing, are a significant fire hazard. These trees—often caused by pests, diseases, and climate change—create a large amount of dry, combustible material. As temperatures rise and droughts intensify, the risk of wildfires increases, making it essential to understand how dead trees contribute to fire danger.
The team used a random forest classification model, a powerful ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Cost-effectiveness of a polypill for cardiovascular disease prevention in an underserved populationJAMA Cardiology