(Press-News.org) Scientists have called for the designation of a new United Nations Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) with the aim to conserve and sustainably use Earth's orbit, and prevent the accumulation of space junk.
There are currently 17 SDGs, adopted by UN members in 2015 as a universal call to action to end poverty, protect the planet for future generations, and ensure all people enjoy peace and prosperity.
But with growing numbers of satellites and other objects now orbiting our planet, there is growing concern that without some form of global consensus another of Earth’s once pristine environments is at risk of being irrevocably changed.
Writing in the journal One Earth, an international collaboration of experts – in fields including satellite technology and ocean plastic pollution – have proposed an 18th SDG dedicated to the protection of Earth’s orbit.
The study highlights that there are now around 100 nations involved in varying levels of space activity, and that since the 1950s, almost 20,000 satellites have been launched into Earth’s orbit.
These satellites bring immense benefits to society, from monitoring ecosystems and supporting global communications, to facilitating services used by billions of people across the planet such as satellite television and contactless bank card payments.
However, once they reach the end of their useful life, the experts say abandoned satellites, launch stages, and fragments resulting from explosions or collisions can accumulate as orbital debris. This raises the chance of collisions with active satellites, which would not only impact their ability to function but would also result in further increases in debris.
While a number of organisations have begun to recognise the need for action to address this, the authors say an additional SDG could deliver the global consensus and mechanisms for effective enforcement required to address the issue.
They believe a new SDG18 could draw direct inspiration from one of the existing goals – SDG14: Life Below Water – with lessons learned in marine debris management being used to prevent another planetary crisis before it is too late.
They also highlight that it would complement the existing SDGs, which include references to space technology for its ability to support improved understanding of global issues but not its potential to represent a future issue itself.
The article was co-authored by researchers from the University of Plymouth, PBL Works, Arribada Initiative, University of Auckland, The University of Texas at Austin, Anturus Ltd, University of Maine, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Spaceport Cornwall, Slingshot Aerospace Ltd, and ZSL (Zoological Society of London).
It builds on an article published in Science in March 2023, in which a number of the same scientists called for a legally-binding treaty to ensure that Earth’s orbit isn’t irreparably harmed by the future expansion of the global space industry.
Dr Imogen Napper, Research Fellow at the University of Plymouth, led the new study with funding from the National Geographical Society. She said: “The need to protect and connect our natural environments, from the ocean to Earth’s orbit, has never been more urgent. Both are vital to the health of our planet, yet increasingly under threat from the pressures we place on them. There is growing recognition that marine litter knows no international boundaries, and the same applies to space debris. A UN-backed agreement would be a crucial step in safeguarding Earth’s orbit for the future.”
Professor Heather Koldewey, ZSL’s Head of Ocean and FAIRER Conservation, said: “Just like plastic pollution and climate change, space junk is an issue that transcends borders. Our ongoing efforts to protect the ocean highlight just how important UN-backed agreements are for managing this crisis. It's key we learn from the challenges and solutions in tackling marine debris and act now to protect our planet’s orbit.”
Dr Thomas Dowling, Lecturer in Remote Sensing & Geospatial Science at The University of Auckland, said: “Not so long ago, our oceans were regarded as infinite resources to plunder and infinite sinks for our waste. We now know that view was grossly mistaken – many marine environments are now barren wastelands and more than eight million tonnes of plastic debris is estimated to enter the ocean every year. Earth’s orbit is a similar finite environment to the ocean, and mindlessly exploiting the orbital environment is repeating the mistakes of the past. It’s time to create policies to regulate what we’re putting in space, and we need to ensure objects entering orbit are safe, sustainable, and serving essential – or at least important – purposes for significant numbers of people around the world.”
Melissa Quinn, General Manager of the International Business Unit at Slingshot Aerospace, added: "The proposed 18th Sustainable Development Goal is a crucial step toward protecting Earth’s orbit for future generations. Space is essential to our daily lives, from global communications to understanding climate change, yet the rapid rise in satellite deployments – 2,877 in 2023 alone (~15% increase from 2022), with even more in 2024 – has led to an increasing risk of collisions and debris. In 2024, we saw a 17% year-over-year spike in the average number of close approaches in low earth orbit per satellite on Slingshot Beacon, Slingshot’s space traffic coordination application. With over 12,500 spacecraft now orbiting our planet, including more than 3,300 inactive satellites, we need urgent, coordinated global action to ensure space is safe, sustainable, and secure. This SDG offers a powerful opportunity to safeguard the benefits of space for all humanity."
END
A Sustainable Development Goal for space?
2025-01-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The Balbiani body: Cracking the secret of embryonic beginnings
2025-01-09
Researchers have uncovered how egg cells prepare for the creation of life. Their work reveals the secrets of the Balbiani body, a remarkable structure that organizes essential molecules to guide early embryonic development. Using zebrafish models and cutting-edge imaging, the team discovered how this structure transforms from liquid droplets into a stable core, laying the groundwork for life itself. This discovery sheds light on the extraordinary precision of nature’s reproductive process.
A new study led by Prof. Yaniv Elkouby and his team, including first co-authors Swastik Kar and Rachael Deis, from the Faculty of Medicine at the Hebrew University ...
Science behind genetic testing for identifying risk of opioid misuse remains unproven
2025-01-09
PHILADELPHIA—Opioid misuse and specifically opioid use disorder (OUD), continues to represent a significant U.S. public health threat, with more than 6 million Americans aged 12 and older meeting the criteria for OUD in 2022. Efforts to ease the crisis have included the development of genetic testing to identify individuals most at risk for OUD. New research, out today in JAMA Network Open, questions the usefulness of 15 genetic variants from an algorithm meant to predict OUD risk that was recently granted pre-marketing approval by the Food and Drug Administration. It found that the testing could lead to both false positive and false negative results.
The study was led by Christal ...
Two-in-one root armor protects plants from environmental stressors and fights climate change
2025-01-09
LA JOLLA (January 9, 2025)—Plants may burrow into the ground and stretch toward the sun, but they’re ultimately stuck where they sprout—at the mercy of environmental threats like temperature, drought, and microbial infection. To compensate for their inability to up and move when danger strikes, many plants have evolved ways to protect themselves by altering their physiology, such as building armor around parts of their body and roots called the periderm. However, since many plant biologists who study tissue development ...
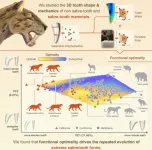
The extreme teeth of sabre-toothed predators were ‘optimal’ for biting into prey, new study reveals
2025-01-09
Sabre-toothed predators – best know from the infamous Smilodon – evolved multiple times across different mammal groups. A new study, published today in Current Biology reveals why: these teeth were ‘functionally optimal’ and highly effective at puncturing prey.
The study, led by scientists at the University of Bristol in collaboration with Monash University shows that long, sharp blade-like teeth gave sabre-tooth’s a real advantage as ...
Research spotlight: Factors contributing to treatment resistance in CAR T therapies for solid tumors
2025-01-09
Russell W. Jenkins, MD, PhD, a physician investigator in the Krantz Family Center for Cancer Research at the Mass General Cancer Center and an assistant professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School, is senior author of a new study in Cancer Immunology Research, “TBK1 is Identified as a Therapeutic Strategy to Enhance CAR T-Cell Efficacy Using Patient-Derived Organotypic Tumor Spheroids”.
The study was a collaboration with the late Soldano Ferrone, MD, PhD, and was carried across the finish line by his daughter Cristina Ferrone, MD, Moshe Sade-Feldman, PhD, and several other collaborators ...
New findings could lead to better treatment for blood cancer
2025-01-09
Which medicine is best when you are affected by cancer? This can vary from person to person. A new method can help people with a specific type of blood cancer get the best medicine for them.
“The new method can help those affected by chronic myelogenous leukemia,” says Jennifer Sheehan, a PhD research fellow from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Production at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU). Sheehan was first author of a new publication in PLOS Computational Biology that describes ...
Expanded research on COPD and metabolic syndrome would advance patient-centered care
2025-01-09
Miami (January 9, 2025) – Additional research addressing the connection between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and metabolic syndrome is needed to improve holistic patient care, according to a new editorial. The editorial is published in the November 2024 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
COPD is an inflammatory lung disease, comprising several conditions, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, and can be caused by genetics and irritants like smoke ...
Mount Sinai-led team enhances automated method to detect common sleep disorder affecting millions
2025-01-09
A Mount Sinai-led team of researchers has enhanced an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered algorithm to analyze video recordings of clinical sleep tests, ultimately improving accurate diagnosis of a common sleep disorder affecting more than 80 million people worldwide. The study findings were published in the journal Annals of Neurology on January 9.
REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) is a sleep condition that causes abnormal movements, or the physical acting out of dreams, during the rapid eye movement (REM) phase of sleep. RBD that occurs in otherwise healthy adults ...
Dr. Ruth Westheimer, Dr. Helen Fisher, and Dr. Judith Allen donate historic archives to the Kinsey Institute
2025-01-09
The Kinsey Institute at Indiana University has acquired remarkable archives from three pioneering figures in the study of human sexuality, relationships, and wellbeing: the legendary sex therapist Dr. Ruth Westheimer, renowned anthropologist Dr. Helen Fisher, and respected feminist historian Dr. Judith Allen. These invaluable collections represent decades of groundbreaking research, education, and cultural contributions that will advance future scholarship and research.
“For almost 80 ...
Bridging oceans: A US-Japan approach to flood risk and climate resilience
2025-01-09
An innovative project jointly funded by the United States National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) brings together a team of scientists from Florida Atlantic University and Lehigh University, along with a team from Japan that includes researchers from Kyoto University, University of Tokyo and Kumamoto University.
The project, titled “NSF-JST: An Inclusive Human-Centered Risk Management Modeling Framework for Flood Resilience,” is supported by a three-year, $1 million award split evenly between the U.S. and Japanese teams, with the U.S. team receiving $499,271. ...