(Press-News.org) About The Study: This study found that patient care experience worsened after private equity acquisition of hospitals. These findings raise concern about the implications of private equity acquisitions on patient care experience at U.S. hospitals.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Rishi K. Wadhera, MD, MPP, MPhil, email rwadhera@bidmc.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.23450)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2024.23450?guestAccessKey=13ff133a-e843-4e58-814e-6b3c16a7b66c&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=010925
END
Changes in patient care experience after private equity acquisition of US hospitals
JAMA
2025-01-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among Black women in the US
2025-01-09
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that addressing COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among Black women requires a multifaceted approach that acknowledges historical traumas, provides clear and transparent safety information, and avoids coercive vaccine promotion strategies. These findings emphasize the need for health care practitioners and public health officials to prioritize trust-building, engage community leaders, and tailor interventions to address the unique concerns of Black women to improve vaccine confidence and uptake.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Brittany C. Slatton, PhD, email brittany.slatton@tsu.edu.
To access the ...
An earful of gill: USC Stem Cell study points to the evolutionary origin of the mammalian outer ear
2025-01-09
The outer ear is unique to mammals, but its evolutionary origin has remained a mystery. According to a new study published in Nature from the USC Stem Cell lab of Gage Crump, this intricate coil of cartilage has a surprisingly ancient origin in the gills of fishes and marine invertebrates.
“When we started the project, the evolutionary origin of the outer ear was a complete black box,” said corresponding author Crump, professor of stem cell biology and regenerative medicine at the Keck School of Medicine of USC. “We had been studying the development and regeneration of the jawbones of fishes, and an inspiration for us was Stephen ...
A Sustainable Development Goal for space?
2025-01-09
Scientists have called for the designation of a new United Nations Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) with the aim to conserve and sustainably use Earth's orbit, and prevent the accumulation of space junk.
There are currently 17 SDGs, adopted by UN members in 2015 as a universal call to action to end poverty, protect the planet for future generations, and ensure all people enjoy peace and prosperity.
But with growing numbers of satellites and other objects now orbiting our planet, there is growing concern that without some form of global consensus ...
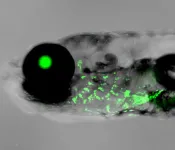
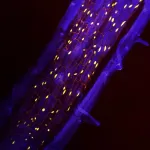
The Balbiani body: Cracking the secret of embryonic beginnings
2025-01-09
Researchers have uncovered how egg cells prepare for the creation of life. Their work reveals the secrets of the Balbiani body, a remarkable structure that organizes essential molecules to guide early embryonic development. Using zebrafish models and cutting-edge imaging, the team discovered how this structure transforms from liquid droplets into a stable core, laying the groundwork for life itself. This discovery sheds light on the extraordinary precision of nature’s reproductive process.
A new study led by Prof. Yaniv Elkouby and his team, including first co-authors Swastik Kar and Rachael Deis, from the Faculty of Medicine at the Hebrew University ...
Science behind genetic testing for identifying risk of opioid misuse remains unproven
2025-01-09
PHILADELPHIA—Opioid misuse and specifically opioid use disorder (OUD), continues to represent a significant U.S. public health threat, with more than 6 million Americans aged 12 and older meeting the criteria for OUD in 2022. Efforts to ease the crisis have included the development of genetic testing to identify individuals most at risk for OUD. New research, out today in JAMA Network Open, questions the usefulness of 15 genetic variants from an algorithm meant to predict OUD risk that was recently granted pre-marketing approval by the Food and Drug Administration. It found that the testing could lead to both false positive and false negative results.
The study was led by Christal ...
Two-in-one root armor protects plants from environmental stressors and fights climate change
2025-01-09
LA JOLLA (January 9, 2025)—Plants may burrow into the ground and stretch toward the sun, but they’re ultimately stuck where they sprout—at the mercy of environmental threats like temperature, drought, and microbial infection. To compensate for their inability to up and move when danger strikes, many plants have evolved ways to protect themselves by altering their physiology, such as building armor around parts of their body and roots called the periderm. However, since many plant biologists who study tissue development ...
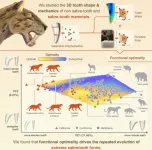
The extreme teeth of sabre-toothed predators were ‘optimal’ for biting into prey, new study reveals
2025-01-09
Sabre-toothed predators – best know from the infamous Smilodon – evolved multiple times across different mammal groups. A new study, published today in Current Biology reveals why: these teeth were ‘functionally optimal’ and highly effective at puncturing prey.
The study, led by scientists at the University of Bristol in collaboration with Monash University shows that long, sharp blade-like teeth gave sabre-tooth’s a real advantage as ...
Research spotlight: Factors contributing to treatment resistance in CAR T therapies for solid tumors
2025-01-09
Russell W. Jenkins, MD, PhD, a physician investigator in the Krantz Family Center for Cancer Research at the Mass General Cancer Center and an assistant professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School, is senior author of a new study in Cancer Immunology Research, “TBK1 is Identified as a Therapeutic Strategy to Enhance CAR T-Cell Efficacy Using Patient-Derived Organotypic Tumor Spheroids”.
The study was a collaboration with the late Soldano Ferrone, MD, PhD, and was carried across the finish line by his daughter Cristina Ferrone, MD, Moshe Sade-Feldman, PhD, and several other collaborators ...
New findings could lead to better treatment for blood cancer
2025-01-09
Which medicine is best when you are affected by cancer? This can vary from person to person. A new method can help people with a specific type of blood cancer get the best medicine for them.
“The new method can help those affected by chronic myelogenous leukemia,” says Jennifer Sheehan, a PhD research fellow from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Production at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU). Sheehan was first author of a new publication in PLOS Computational Biology that describes ...
Expanded research on COPD and metabolic syndrome would advance patient-centered care
2025-01-09
Miami (January 9, 2025) – Additional research addressing the connection between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and metabolic syndrome is needed to improve holistic patient care, according to a new editorial. The editorial is published in the November 2024 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
COPD is an inflammatory lung disease, comprising several conditions, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, and can be caused by genetics and irritants like smoke ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Changes in patient care experience after private equity acquisition of US hospitalsJAMA