(Press-News.org) In small preliminary study, fearful pet dogs exhibited significantly different microbiomes and metabolic molecules to non-fearful dogs, suggesting the gut-brain axis might be involved in fear behaviors
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0315374
Article title: Altered microbiome and metabolome profiling in fearful companion dogs: An exploratory study
Author countries: Italy
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
END
In small preliminary study, fearful pet dogs exhibited significantly different microbiomes and metabolic molecules to non-fearful dogs, suggesting the gut-brain axis might be involved in fear behavior
2025-01-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Examination of Large Language Model "red-teaming" defines it as a non-malicious team-effort activity to seek LLMs' limits and identifies 35 different techniques used to test them
2025-01-15
Examination of Large Language Model "red-teaming" defines it as a non-malicious team-effort activity to seek LLMs' limits and identifies 35 different techniques used to test them
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0314658
Article title: Summon a demon and bind it: A grounded theory of LLM red teaming
Author countries: US, Denmark
Funding: VILLUM Foundation, grant No. 37176: ATTiKA: Adaptive Tools for Technical Knowledge Acquisition. The funders had no role in study design, data collection ...
Most microplastics in French bottled and tap water are smaller than 20 µm - fine enough to pass into blood and organs, but below the EU-recommended detection limit
2025-01-15
Most microplastics in French bottled and tap water are smaller than 20 µm - fine enough to pass into blood and organs, but below the EU-recommended detection limit for water quality assessments.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/water/article?id=10.1371/journal.pwat.0000250
Article Title: Majority of potable water microplastics are smaller than the 20 μm EU methodology limit for consumable water quality
Author Countries: Denmark, France
Funding: This work and the PhD fellowship of O.H. is funded by an 80Prime CNRS grant «4DμPlast» (G.L.R, J.E.S.). This publication was supported by ANR-20-CE34-0014 ATMO-PLASTIC (G.L.R, J.E.S.) and the Plasticopyr ...
A tangled web: Fossil fuel energy, plastics, and agrichemicals discourse on X/Twitter
2025-01-15
An analysis of the nine top players in the U.S. fossil fuel-derived hydrocarbon industries (oil/gas, plastics, and agrichemicals) shows tight linkages across the three different sectors, with news media, other petrochemical industry players, and politicians also frequently tagged, according to a study published January 15, 2025 in the open-access journal PLOS Climate by Alaina Kinol from Northeastern University, United States, and colleagues.
Previous research on connections between the fossil fuel and plastics sectors and ...
This fast and agile robotic insect could someday aid in mechanical pollination
2025-01-15
CAMBRIDGE, MA — With a more efficient method for artificial pollination, farmers in the future could grow fruits and vegetables inside multilevel warehouses, boosting yields while mitigating some of agriculture’s harmful impacts on the environment.
To help make this idea a reality, MIT researchers are developing robotic insects that could someday swarm out of mechanical hives to rapidly perform precise pollination. However, even the best bug-sized robots are no match for natural pollinators like bees when it comes to endurance, speed, and maneuverability.
Now, inspired by the anatomy of these natural pollinators, the researchers ...
Researchers identify novel immune cells that may worsen asthma
2025-01-15
Hamilton, ON (January 15, 2025) – Researchers at McMaster University have made an important discovery in the field of asthma research, identifying a new population of immune cells that may play a crucial role in the severity of asthma symptoms.
The study, published in Science Translational Medicine on Jan. 15, 2025, sheds light on the complex mechanisms behind severe asthma and opens new avenues for potential treatments.
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to difficulty breathing. Severe ...
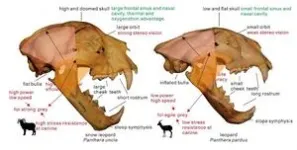
Conquest of Asia and Europe by snow leopards during the last Ice Ages uncovered
2025-01-15
The study, published in Science Advances, was led by researchers Qigao Jiangzuo, from Peking University, and Joan Madurell Malapeira, from the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB).
Snow leopards (Panthera uncia) are in serious danger of extinction, with only about 4,000 specimens remaining. They are medium to large felids that live at high altitudes, over 2,000 meters above sea level, mainly in the Himalayas. Although their distinctive traits have long been recognized, the correlation between these ...
Researchers make comfortable materials that generate power when worn
2025-01-15
Researchers have demonstrated new wearable technologies that both generate electricity from human movement and improve the comfort of the technology for the people wearing them. The work stems from an advanced understanding of materials that increase comfort in textiles and produce electricity when they rub against another surface.
At issue are molecules called amphiphiles, which are often used in consumer products to reduce friction against human skin. For example, amphiphiles are often incorporated into diapers to prevent chafing.
“We set out to develop a model that would give us ...
Study finding Xenon gas could protect against Alzheimer’s disease leads to start of clinical trial
2025-01-15
Most treatments being pursued today to protect against Alzheimer’s disease focus on amyloid plaques and tau tangles that accumulate in the brain, but new research from Mass General Brigham and Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis points to a novel—and noble—approach: using Xenon gas. The study found that Xenon gas inhalation suppressed neuroinflammation, reduced brain atrophy, and increased protective neuronal states in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Results are published in Science Translational Medicine, and a phase 1 clinical trial of the treatment in healthy volunteers will begin in early 2025.
“It ...
Protein protects biological nitrogen fixation from oxidative stress
2025-01-15
A small helper for big tasks: an oxygen sensor protein protects the enzymatic machinery of biological nitrogen fixation from serious damage. Its use in biotechnology could help to reduce the use of synthetic fertiliser in agriculture in the future. A research team led by biochemist Prof. Dr Oliver Einsle from the Faculty of Chemistry and Pharmacy and the Centre for Biological Signalling Studies (BIOSS) at the University of Freiburg has discovered exactly how the so-called Shethna protein II works. The scientists used the newly established cryo-electron microscopy in Freiburg. ...
Three-quarters of medical facilities in Mariupol sustained damage during Russia’s siege of 2022
2025-01-15
Three-quarters of medical facilities in Mariupol sustained damage during Russia’s siege of 2022, with some evidence that the attacks may have been intentionally targeted, per study using satellite imagery.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0003950
Article Title: The effect of conflict on damage to medical facilities in Mariupol, Ukraine: a quasi-experimental study
Author Countries: Germany, United States
Funding: This work was supported ...