Dose-dependent relationship between alcohol consumption and the risks of hepatitis b virus-associated cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis and systematic review
2025-01-16
(Press-News.org) Background and Aims
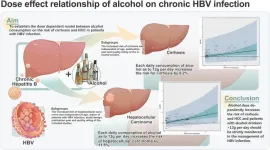
The quantitative effects of alcohol consumption on cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection are unknown. This study aimed to establish a dose-dependent model of alcohol consumption on the risks of cirrhosis and HCC.
Methods
PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and four Chinese databases were searched for studies published from their inception to 15 May 2024. A random-effects model was used to pool the data on the incidence of cirrhosis and HCC, and a dose-dependent model of alcohol’s effect on cirrhosis and HCC was established.
Results
A total of 33,272 HBV patients from 45 studies were included. Compared with non-drinkers, the overall pooled odds ratio (OR) for cirrhosis was 2.61 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.46–4.66; I2 = 94%, p < 0.001), and the OR for HCC was 2.27 (95% CI: 1.50–3.43; I2 = 90%, p < 0.001) among drinkers. Compared with low-level drinkers, the estimated pooled OR for cirrhosis was 2.34 (95% CI: 1.59–3.44; I2 = 87%, p < 0.001), and the OR for HCC was 2.42 (95% CI: 1.90–3.09; I2 = 80%, p < 0.001) among high-level drinkers. Furthermore, a linear dose-dependent analysis showed that each daily consumption of 12 g of alcohol increased the risk of cirrhosis by 6.2% and the risk of HCC by 11.5%.
Conclusions
Alcohol dose-dependently increases the risks of cirrhosis and HCC in patients with HBV infection, and patients with daily alcohol consumption of more than 12 g should be strictly monitored.
Full text
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2310-8819/JCTH-2024-00379
The study was recently published in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology.
The Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology (JCTH) is owned by the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University and published by XIA & HE Publishing Inc. JCTH publishes high quality, peer reviewed studies in the translational and clinical human health sciences of liver diseases. JCTH has established high standards for publication of original research, which are characterized by a study’s novelty, quality, and ethical conduct in the scientific process as well as in the communication of the research findings. Each issue includes articles by leading authorities on topics in hepatology that are germane to the most current challenges in the field. Special features include reports on the latest advances in drug development and technology that are relevant to liver diseases. Regular features of JCTH also include editorials, correspondences and invited commentaries on rapidly progressing areas in hepatology. All articles published by JCTH, both solicited and unsolicited, must pass our rigorous peer review process.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-01-16
January 16, 2025 – New York, NY – The International Alliance for Primary Immunodeficiency Societies (IAPIDS) and Rockefeller University Press (RUP) have entered a partnership to launch Journal of Human Immunity (JHI), the official open access journal of IAPIDS. This collaboration will ensure that JHI emerges as the destination for exciting research into human immunity, with a particular focus on inborn errors of immunity.
“The Journal of Human Immunity represents a bold step forward in advancing ...
2025-01-16
Digital Science is pleased to announce that Dr Raym Crow, a leading figure in mission-driven, sustainable open publishing models, has won the 2025 APE Award for Innovation in Scholarly Communication.
The award – a joint initiative between Digital Science and the Berlin Institute for Scholarly Publishing (BISP) – has been announced at the 20th Academic Publishing in Europe (APE) Conference in Berlin, Germany.
The APE award is presented to an individual who has brought innovation in scholarly communication to the community, through infrastructure, technology, business models, output on the topic, theory, or practice.
With more than ...
2025-01-16
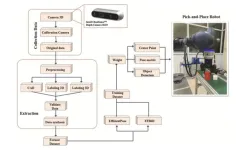
Accurate object pose estimation refers to the ability of a robot to determine both the position and orientation of an object. It is essential for robotics, especially in pick-and-place tasks, which are crucial in industries such as manufacturing and logistics. As robots are increasingly tasked with complex operations, their ability to precisely determine the six degrees of freedom (6D pose) of objects, position, and orientation, becomes critical. This ability ensures that robots can interact with objects in a reliable and safe manner. However, despite advancements in deep learning, the performance of 6D pose estimation algorithms largely depends ...
2025-01-16
Background and Aims
The performance of neurodegenerative biomarkers—neurofilament light chain (NfL), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), tau, and ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCHL1)—in diagnosing minimal hepatic encephalopathy (MHE) has not been systematically evaluated, simultaneously, nor have their associations with the development of overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE). This study aimed to evaluate the performance of plasma NfL, GFAP, tau, and UCHL1 in diagnosing MHE and predicting the development of OHE in Chinese patients with hepatic cirrhosis.
Methods
In this prospective study, 124 patients ...
2025-01-16
The remains of nearly 200 animals found in Mexico’s Teotihuacán are helping reconstruct history.
The unearthing and significance of these remains, found in four chambers within the Moon Pyramid — dating back nearly 2,000 years — are central in Nawa Sugiyama’s new book, “Animal Matter: Ritual, Place, and Sovereignty at the Moon Pyramid of Teotihuacan,” published by Oxford University Press.
Teotihuacán, one of the first megacities of the Western Hemisphere and now a UNESCO World Heritage site, is situated ...
2025-01-16
New research forthcoming in Social Psychological and Personality Science illuminates why liberals and conservatives often support different types of leaders. The study shows that these preferences stem from differences in moral priorities rather than mere partisan bias.
"This research helps explain why people across the political spectrum often support such different types of leaders," explains lead researcher Harrison Miller, of Florida State University. "Rather than simply attributing these differences to political bias, ...
2025-01-16
WASHINGTON -- If you’ve ever wondered whether your parents secretly had a favorite child, they might have. Parents may be more inclined to confer the “favorite child award” to daughters and children who are agreeable and conscientious, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“For decades, researchers have known that differential treatment from parents can have lasting consequences for children,” said lead author Alexander Jensen, PhD, an associate professor at Brigham Young University. “This study helps us understand which children are more likely to be on the receiving end of favoritism, which can ...
2025-01-16
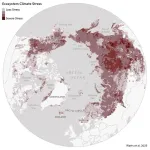
Ecological warning lights have blinked on across the Arctic over the last 40 years, according to new research, and many of the fastest-changing areas are clustered in Siberia, the Canadian Northwest Territories, and Alaska. The analysis of the rapidly warming Arctic-boreal region, published in Geophysical Research Letters this week, provides a zoomed-in picture of ecosystems experiencing some of the fastest and most extreme climate changes on Earth.
Many of the most climate-stressed areas featured permafrost, or ground that stays frozen year-round, and experienced both severe warming and drying ...
2025-01-16
Wearable devices can identify, differentiate, and predict flare-ups, or the worsening of symptoms and inflammation, in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), Mount Sinai researchers have shown in a first-of-its-kind study.
The findings, published in the journal Gastroenterology on January 16, suggest that wearable technology can predict the subsequent development of flares in IBD, enabling continuous disease monitoring through widely available commercial devices.
“Current disease-monitoring methods rely on patients directly interacting with ...
2025-01-16
Background and Aims
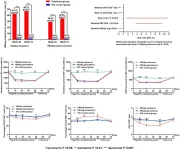
T lymphocytes play a pivotal role in resolving hepatitis B virus infection. This study aimed to investigate the dynamics of peripheral blood T lymphocyte subsets during peginterferon alpha (peg-IFN-α) therapy and their association with hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) clearance in inactive HBsAg carriers (IHCs).
Methods
This prospective observational study enrolled 197 IHCs treated with peg-IFNα-2a/2b for 48 weeks and followed for 24 weeks (treatment group), and 221 IHCs who were regularly monitored for 72 weeks without treatment (IHC control group). ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Dose-dependent relationship between alcohol consumption and the risks of hepatitis b virus-associated cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis and systematic review