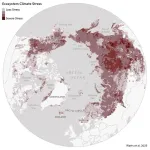
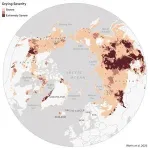
(Press-News.org) Ecological warning lights have blinked on across the Arctic over the last 40 years, according to new research, and many of the fastest-changing areas are clustered in Siberia, the Canadian Northwest Territories, and Alaska. The analysis of the rapidly warming Arctic-boreal region, published in Geophysical Research Letters this week, provides a zoomed-in picture of ecosystems experiencing some of the fastest and most extreme climate changes on Earth.
Many of the most climate-stressed areas featured permafrost, or ground that stays frozen year-round, and experienced both severe warming and drying in recent decades.
To identify these “hotspots,” a team of researchers from Woodwell Climate Research Center, the University of Oslo, the University of Montana, the Environmental Systems Research Institute (Esri), and the University of Lleida used more than 30 years of geospatial data and long-term temperature records to assess indicators of ecosystem vulnerability in three categories: temperature, moisture, and vegetation.
Building on assessments like the NOAA Arctic Report Card, the research team went beyond evaluating isolated metrics of change and looked at multiple variables at once to create a more complete, integrated picture of climate and ecosystem changes in the region.
“Climate warming has put a great deal of stress on ecosystems in the high latitudes, but the stress looks very different from place to place and we wanted to quantify those differences,” said Dr. Jennifer Watts, Arctic program director at Woodwell Climate and lead author of the study. “Detecting hotspots at the local and regional level helps us not only to build a more precise picture of how Arctic warming is affecting ecosystems, but to identify places where we really need to focus future monitoring efforts and management resources.”
The team used spatial statistics to detect “neighborhoods,” or regions of particularly high levels of change during the past decade.
“This study is exactly why we have developed these kinds of spatial statistic tools in our technology. We are so proud to be working closely with Woodwell Climate on identifying and publishing these kinds of vulnerability hotspots that require effective and immediate climate adaptation action and long-term policy,” said Dr. Dawn Wright, chief scientist at Esri. “This is essentially what we mean by the ‘Science of Where.’”
The findings paint a complex and concerning picture.
The most substantial land warming between 1997-2020 occurred in the far eastern Siberian tundra and throughout central Siberia. Approximately 99% of the Eurasian tundra region experienced significant warming, compared to 72% of Eurasian boreal forests. While some hotspots in Siberia and the Northwest Territories of Canada grew drier, the researchers detected increased surface water and flooding in parts of North America, including Alaska’s Yukon-Kuskokwim Delta and central Canada. These increases in water on the landscape over time are likely a sign of thawing permafrost.
Among the 20 most vulnerable places the researchers identified, all contained permafrost.
“The Arctic and boreal regions are made up of diverse ecosystems, and this study reveals some of the complex ways they are responding to climate warming,” said Dr. Sue Natali, lead of the Permafrost Pathways project at Woodwell Climate and co-author of the study. “However, permafrost was a common denominator—the most climate-stressed regions all contained permafrost, which is vulnerable to thaw as temperatures rise. That’s a really concerning signal.”
For land managers and other decisionmakers, local and regional hotspot mapping like this can serve as a more useful monitoring tool than region-wide averages. Take, for instance, the example of Covid-19 tracking data: maps of county-by-county wastewater data tend to be more helpful tools to guide decision making than national averages, since rates of disease prevalence and transmission can vary widely among communities at a given moment in time. So, too, with climate trends: local data and trend detection can support management and adaptation approaches that account for unique and shifting conditions on the ground.
The significant changes the team detected in the Siberian boreal forest region should serve as a wakeup call, said Watts. “These forested regions, which have been helping take up and store carbon dioxide, are now showing major climate stresses and increasing risk of fire. We need to work as a global community to protect these important and vulnerable boreal ecosystems, while also reining in fossil fuel emissions.”
***
This project was supported by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation and through the TED Audacious Project for Permafrost Pathways: Connecting Science, People, and Policy for Arctic Justice and Global Climate.
END
Arctic hotspots study reveals areas of climate stress in Northern Alaska, Siberia
2025-01-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mount Sinai study finds wearable devices can detect and predict inflammatory bowel disease flare-ups
2025-01-16
Wearable devices can identify, differentiate, and predict flare-ups, or the worsening of symptoms and inflammation, in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), Mount Sinai researchers have shown in a first-of-its-kind study.
The findings, published in the journal Gastroenterology on January 16, suggest that wearable technology can predict the subsequent development of flares in IBD, enabling continuous disease monitoring through widely available commercial devices.
“Current disease-monitoring methods rely on patients directly interacting with ...
Peripheral blood CD4+/CD8+ t cell ratio predicts HBsAg clearance in inactive HBsAg carriers treated with peginterferon alpha
2025-01-16
Background and Aims
T lymphocytes play a pivotal role in resolving hepatitis B virus infection. This study aimed to investigate the dynamics of peripheral blood T lymphocyte subsets during peginterferon alpha (peg-IFN-α) therapy and their association with hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) clearance in inactive HBsAg carriers (IHCs).
Methods
This prospective observational study enrolled 197 IHCs treated with peg-IFNα-2a/2b for 48 weeks and followed for 24 weeks (treatment group), and 221 IHCs who were regularly monitored for 72 weeks without treatment (IHC control group). ...
MIT Press’s Direct to Open reaches annual funding goal for 2025, opens access to 80 new monographs
2025-01-16
January 16, 2024 - The MIT Press is pleased to announce that Direct to Open (D2O) has reached its full funding goal for 2025 and will open access to 80 new monographs and edited book collections in the spring and fall publishing seasons.
“It has been one of the greatest privileges of my career to contribute to this program and demonstrate that our academic community can unite to publish high-quality open access monographs at scale,” said Amy Harris, Senior Manager of Library Relations ...
New NCCN patient resource shares latest understanding of genetic testing to guide patient decision making
2025-01-16
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [January 16, 2025] — Today, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—published a new resource to inform people about the latest recommendations around hereditary and familial cancer risk. This essential guide is based on the latest evidence and expert consensus in the rapidly advancing field of cancer genetics. It provides guidance on how best to assess, and test for, inherited genetic mutations that can raise the ...
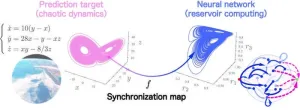
Synchronization in neural nets: Mathematical insight into neuron readout drives significant improvements in prediction accuracy
2025-01-16
Reservoir computing (RC) is a powerful machine learning module designed to handle tasks involving time-based or sequential data, like tracking patterns over time or analyzing sequences. It is widely used in areas such as finance, robotics, speech recognition, weather forecasting, natural language processing, and predicting complex nonlinear dynamical systems. What sets RC apart is its efficiency—it delivers powerful results with much lower training costs compared to other methods.
RC uses a fixed, randomly connected network layer, known as the reservoir, to turn input data into a more complex representation. ...
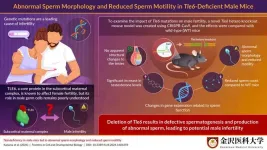
TLE6 identified as a protein associated with infertility in male mice
2025-01-16
Infertility is a major global challenge associated with physiological and psychological impact. Genetic mutations that affect early embryonic development, oocyte (egg cell) maturation, and fertilization have recently been studied as causes of infertility. One of the most well-studied causes of early embryonic infertility is mutations in the subcortical maternal complex (SCMC)-related genes.
SCMC participates in embryo development and cleavage by maintaining the structure of the egg cytoplasm and recruiting proteins that assist proper embryo formation. SCMC is composed of multiple proteins, of which the transducin-like ...
Thin lenses have a bright future
2025-01-16
Paper-thin optical lenses simple enough to mass produce like microchips could enable a new generation of compact optical devices. A team with researchers at the University of Tokyo and JSR Corp. fabricated and tested flat lenses called Fresnel zone plates (FZPs), but did so for the first time using only common semiconductor manufacturing equipment, the i-line stepper, for the first time. These flat lenses currently lack the efficiency of in-production lenses, but have the potential to reshape optics for industries ranging from astronomy to health care and consumer electronics.
Flat lenses, such as metalenses, exist, but they come with hefty price tags ...
Volcanic eruption caused Neolithic people to sacrifice unique "sun stones"
2025-01-16
Throughout history, volcanic eruptions have had serious consequences for human societies such as cold weather, lack of sun, and low crop yields. In the year 43 BC when a volcano in Alaska spewed large quantities of sulphur into the stratosphere, harvests failed the following years in the countries around the Mediterranean, causing famine and disease. This is well-documented in written sources from ancient Greece and Rome.
We do not have written sources from the Neolithic. But climate scientists from the Niels Bohr Institute at the University of Copenhagen have analysed ice cores from the Greenland ice sheet and can now document that around 2,900 ...
Drug in clinical trials for breast cancer could also treat some blood cancers
2025-01-16
Two new studies led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a possible way to block the progression of several forms of blood cancer using a drug already in clinical trials against breast cancer.
The studies — both conducted in patient samples and animal models — found that inhibiting a protein called RSK1 reduces inflammation and stops the progression of blood cancers called myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) as well as an aggressive form of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). With the RSK1 inhibitor already in clinical testing, the path to expanded use as a treatment for blood ...
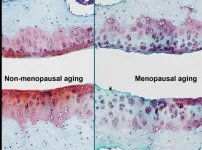
Study identifies mechanism underlying increased osteoarthritis risk in postmenopausal females
2025-01-16
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a condition that disproportionally affects postmenopausal women, and the millions affected can attest to the pain, reduced mobility and diminished quality of life that comes from this disease. While the hormonal changes associated with menopause have long been known to accelerate the development and progression of OA, a deeper understanding of the biological mechanisms that underlie this correlation is crucial for developing effective treatments.
A new study led by researchers at Spaulding Rehabilitation, a member of the Mass General Brigham ...