(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON -- If you’ve ever wondered whether your parents secretly had a favorite child, they might have. Parents may be more inclined to confer the “favorite child award” to daughters and children who are agreeable and conscientious, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“For decades, researchers have known that differential treatment from parents can have lasting consequences for children,” said lead author Alexander Jensen, PhD, an associate professor at Brigham Young University. “This study helps us understand which children are more likely to be on the receiving end of favoritism, which can be both positive and negative.”
The research was published in the journal Psychological Bulletin.
The study examined the link between children's characteristics and differences in how their parents treat them, while considering potential moderators such as child age, parent gender and measurement methods.
The researchers conducted a meta-analysis of 30 peer-reviewed journal articles and dissertations/theses, along with 14 databases, encompassing a total of 19,469 participants. They examined how birth order, gender, temperament and personality traits (extraversion, agreeableness, openness, conscientiousness and neuroticism) were linked to parental favoritism.
Parents can show favoritism in numerous ways, including how they interact with their children, how much money they spend on them and how much control they exert over them, the researchers said. Altogether, they looked at five domains: overall treatment, positive interactions, negative interactions, resource allocation and control.
The researchers initially thought that mothers would tend to favor daughters and fathers would favor sons. However, the study found that both mothers and fathers were more likely to favor daughters.
Of the personality traits evaluated, children who were conscientious -- meaning they were responsible and organized -- also appeared to receive more favorable treatment. This suggests that parents may find these children easier to manage and may respond more positively. Jensen said he was surprised that extraversion was not associated with favoritism.
“Americans seem to particularly value extraverted people, but within families it may matter less,” he said.
When it came to birth order, parents were more likely to give older siblings greater autonomy, possibly because they were more mature, according to Jensen.
The researchers also examined whether parent-child relationships were influenced by other factors, such as the child's age, the parent's gender, or how favoritism was measured. They found that these factors might play a role, but if they did it was minimal, highlighting the complexity of parental favoritism.
Siblings who receive less favored treatment tend to have poorer mental health and more strained family relationships, according to Jensen.
“Understanding these nuances can help parents and clinicians recognize potentially damaging family patterns,” he said. “It is crucial to ensure all children feel loved and supported.”
The researchers said they hope their findings will encourage parents to be more aware of their biases and strive to treat all their children fairly.
“It is important to note that this research is correlational, so it doesn't tell us why parents favor certain children,” Jensen said. “However, it does highlight potential areas where parents may need to be more mindful of their interactions with their children.”
“So, the next time you're left wondering whether your sibling is the golden child, remember there is likely more going on behind the scenes than just a preference for the eldest or youngest. It might be about responsibility, temperament or just how easy or hard you are to deal with,” he said.
Article: “Parents Favor Daughters: A Meta-Analysis of Gender and Other Predictors of Parental Differential Treatment,” by Alexander Jensen, PhD, Brigham Young University and McKell Jorgensen-Wells, MS, Western University. Psychological Bulletin, published online Jan. 16, 2025.
Contact: Alexander Jensen, PhD, may be contacted via email at alexjensen@byu.edu.
END
Parental favoritism isn't a myth
Daughters, responsible kids more likely to be favored, study finds
2025-01-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
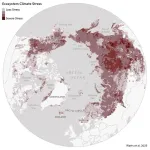
Arctic hotspots study reveals areas of climate stress in Northern Alaska, Siberia
2025-01-16
Ecological warning lights have blinked on across the Arctic over the last 40 years, according to new research, and many of the fastest-changing areas are clustered in Siberia, the Canadian Northwest Territories, and Alaska. The analysis of the rapidly warming Arctic-boreal region, published in Geophysical Research Letters this week, provides a zoomed-in picture of ecosystems experiencing some of the fastest and most extreme climate changes on Earth.
Many of the most climate-stressed areas featured permafrost, or ground that stays frozen year-round, and experienced both severe warming and drying ...
Mount Sinai study finds wearable devices can detect and predict inflammatory bowel disease flare-ups
2025-01-16
Wearable devices can identify, differentiate, and predict flare-ups, or the worsening of symptoms and inflammation, in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), Mount Sinai researchers have shown in a first-of-its-kind study.
The findings, published in the journal Gastroenterology on January 16, suggest that wearable technology can predict the subsequent development of flares in IBD, enabling continuous disease monitoring through widely available commercial devices.
“Current disease-monitoring methods rely on patients directly interacting with ...
Peripheral blood CD4+/CD8+ t cell ratio predicts HBsAg clearance in inactive HBsAg carriers treated with peginterferon alpha
2025-01-16
Background and Aims
T lymphocytes play a pivotal role in resolving hepatitis B virus infection. This study aimed to investigate the dynamics of peripheral blood T lymphocyte subsets during peginterferon alpha (peg-IFN-α) therapy and their association with hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) clearance in inactive HBsAg carriers (IHCs).
Methods
This prospective observational study enrolled 197 IHCs treated with peg-IFNα-2a/2b for 48 weeks and followed for 24 weeks (treatment group), and 221 IHCs who were regularly monitored for 72 weeks without treatment (IHC control group). ...
MIT Press’s Direct to Open reaches annual funding goal for 2025, opens access to 80 new monographs
2025-01-16
January 16, 2024 - The MIT Press is pleased to announce that Direct to Open (D2O) has reached its full funding goal for 2025 and will open access to 80 new monographs and edited book collections in the spring and fall publishing seasons.
“It has been one of the greatest privileges of my career to contribute to this program and demonstrate that our academic community can unite to publish high-quality open access monographs at scale,” said Amy Harris, Senior Manager of Library Relations ...
New NCCN patient resource shares latest understanding of genetic testing to guide patient decision making
2025-01-16
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [January 16, 2025] — Today, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—published a new resource to inform people about the latest recommendations around hereditary and familial cancer risk. This essential guide is based on the latest evidence and expert consensus in the rapidly advancing field of cancer genetics. It provides guidance on how best to assess, and test for, inherited genetic mutations that can raise the ...
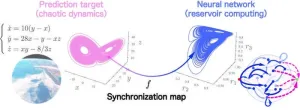
Synchronization in neural nets: Mathematical insight into neuron readout drives significant improvements in prediction accuracy
2025-01-16
Reservoir computing (RC) is a powerful machine learning module designed to handle tasks involving time-based or sequential data, like tracking patterns over time or analyzing sequences. It is widely used in areas such as finance, robotics, speech recognition, weather forecasting, natural language processing, and predicting complex nonlinear dynamical systems. What sets RC apart is its efficiency—it delivers powerful results with much lower training costs compared to other methods.
RC uses a fixed, randomly connected network layer, known as the reservoir, to turn input data into a more complex representation. ...
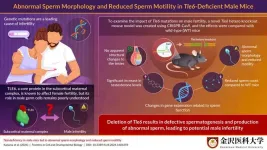
TLE6 identified as a protein associated with infertility in male mice
2025-01-16
Infertility is a major global challenge associated with physiological and psychological impact. Genetic mutations that affect early embryonic development, oocyte (egg cell) maturation, and fertilization have recently been studied as causes of infertility. One of the most well-studied causes of early embryonic infertility is mutations in the subcortical maternal complex (SCMC)-related genes.
SCMC participates in embryo development and cleavage by maintaining the structure of the egg cytoplasm and recruiting proteins that assist proper embryo formation. SCMC is composed of multiple proteins, of which the transducin-like ...
Thin lenses have a bright future
2025-01-16
Paper-thin optical lenses simple enough to mass produce like microchips could enable a new generation of compact optical devices. A team with researchers at the University of Tokyo and JSR Corp. fabricated and tested flat lenses called Fresnel zone plates (FZPs), but did so for the first time using only common semiconductor manufacturing equipment, the i-line stepper, for the first time. These flat lenses currently lack the efficiency of in-production lenses, but have the potential to reshape optics for industries ranging from astronomy to health care and consumer electronics.
Flat lenses, such as metalenses, exist, but they come with hefty price tags ...
Volcanic eruption caused Neolithic people to sacrifice unique "sun stones"
2025-01-16
Throughout history, volcanic eruptions have had serious consequences for human societies such as cold weather, lack of sun, and low crop yields. In the year 43 BC when a volcano in Alaska spewed large quantities of sulphur into the stratosphere, harvests failed the following years in the countries around the Mediterranean, causing famine and disease. This is well-documented in written sources from ancient Greece and Rome.
We do not have written sources from the Neolithic. But climate scientists from the Niels Bohr Institute at the University of Copenhagen have analysed ice cores from the Greenland ice sheet and can now document that around 2,900 ...
Drug in clinical trials for breast cancer could also treat some blood cancers
2025-01-16
Two new studies led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a possible way to block the progression of several forms of blood cancer using a drug already in clinical trials against breast cancer.
The studies — both conducted in patient samples and animal models — found that inhibiting a protein called RSK1 reduces inflammation and stops the progression of blood cancers called myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) as well as an aggressive form of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). With the RSK1 inhibitor already in clinical testing, the path to expanded use as a treatment for blood ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
Self-cleaning fuel cells? Researchers reveal steam-powered fix for ‘sulfur poisoning’
Bacteria found in mouth and gut may help protect against severe peanut allergic reactions
Ultra-processed foods in preschool years associated with behavioural difficulties in childhood
A fanged frog long thought to be one species is revealing itself to be several
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
Largest high-precision 3D facial database built in China, enabling more lifelike digital humans
SwRI upgrades facilities to expand subsurface safety valve testing to new application
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
Some young gamers may be at higher risk of mental health problems, but family and school support can help
Reduce rust by dumping your wok twice, and other kitchen tips
High-fat diet accelerates breast cancer tumor growth and invasion
Leveraging AI models, neuroscientists parse canary songs to better understand human speech
Ultraprocessed food consumption and behavioral outcomes in Canadian children
The ISSCR honors Dr. Kyle M. Loh with the 2026 Early Career Impact Award for Transformative Advances in Stem Cell Biology
The ISSCR honors Alexander Meissner with the 2026 ISSCR Momentum Award for exceptional work in developmental and stem cell epigenetics
The ISSCR honors stem cell COREdinates and CorEUstem with the 2026 ISSCR Public Service Award
Minimally invasive procedure effectively treats small kidney cancers
SwRI earns CMMC Level 2 cybersecurity certification
Doctors and nurses believe their own substance use affects patients
Life forms can planet hop on asteroid debris – and survive
Sylvia Hurtado voted AERA President-Elect; key members elected to AERA Council
Mount Sinai and King Saud University Medical City forge a three-year collaboration to advance precision medicine in familial inflammatory bowel disease
AI biases can influence people’s perception of history
Prenatal opioid exposure and well-being through adolescence
Big and small dogs both impact indoor air quality, just differently
Wearing a weighted vest to strengthen bones? Make sure you’re moving
Microbe survives the pressures of impact-induced ejection from Mars
[Press-News.org] Parental favoritism isn't a mythDaughters, responsible kids more likely to be favored, study finds