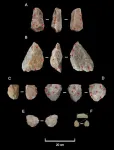
(Press-News.org) An early human ancestor of our species successfully navigated harsher and more arid terrains for longer in Eastern Africa than previously thought, according to a new study published in Nature Communications Earth & Environment.
Homo erectus, the first of our relatives to have human-like proportions and the first known early human to migrate out of Africa, was the focus of the new study led by the international research team.
The researchers analysed evidence from Engaji Nanyori in Tanzania’s Oldupai Gorge, revealing Homo erectus thrived in hyper-arid landscapes one million years ago – well before our species, Homo sapiens, emerged.
“Now extinct, Homo erectus existed more than an estimated 1.5 million years, marking them as a species survival success in the human evolution story when compared with our own estimated existence of around 300,000 years to date,” Professor Michael Petraglia said, Director of the Australian Research Centre for Human Evolution, Griffith University.
“That success came down to their ability to survive over a long period marked by many changes to the environment and climate,” noted the lead author, Professor Julio Mercader of the University of Calgary.
Using biogeochemical analyses, chronometric dating, palaeoclimate simulations, biome modelling, fire history reconstructions, palaeobotanical studies, faunal assemblages, and archaeological evidence, the research team reconstructed an environment dominated by semidesert shrubland.
Despite the challenges of these conditions, Homo erectus repeatedly occupied landscapes created by rivers and streams, leveraging water sources and ecological focal points to mitigate risk.
These findings suggest archaic humans possessed an ecological flexibility previously attributed only to later hominins.
“Debate has long centred on when the genus Homo acquired the adaptability to thrive in extreme environments such as deserts and rainforests,” said Dr Abel Shikoni of the University of Dodoma, Tanzania.
“Traditionally, only Homo sapiens was thought capable of sustained occupation in such ecosystems, with archaic hominins seen as restricted to narrower ranges”.
“However, the biogeochemical, palaeoenvironmental, and archaeological evidence we analysed suggests early Homo had the ability to adapt to diverse and unstable environments from the East African Rift floor and Afromontane areas as early as two million years ago,” Professor Petraglia said.
“This adaptive profile, marked by resilience in arid zones, challenges assumptions about early hominin dispersal limits and positions Homo erectus as a versatile generalist and the first hominin to transcend environmental boundaries on a global scale.”
“This adaptability likely facilitated the expansion of Homo erectus into the arid regions of Africa and Eurasia, redefining their role as ecological generalists thriving in some of the most challenging landscapes of the Middle Pleistocene,” said Professor Paul Durkin of the University of Manitoba.
The study ‘Homo erectus adapted to steppe-desert climate extremes one million years ago’ has been published in Nature Communications Earth & Environment.
END
Human ancestor thrived longer in harsher conditions than previous estimates
2025-01-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Evolution: Early humans adapted to extreme desert conditions over one million years ago
2025-01-16
Homo erectus was able to adapt to and survive in desert-like environments at least 1.2 million years ago, according to a paper published in Communications Earth & Environment. The findings suggest that behavioural adaptations included returning repeatedly over thousands of years to specific rivers and ponds for fresh water, and the development of specialised tools. The authors propose that this capability to adapt may have led to the expansion of H. erectus’ geographic range.
There has been significant debate over ...
Race and ethnicity and diffusion of telemedicine in Medicaid for schizophrenia care after onset of the COVID-19 pandemic
2025-01-16
About The Study: In this cohort study of Medicaid beneficiaries with schizophrenia, telemental health care diffused rapidly after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly in state-operated agencies. Together, agency-level and beneficiary-level race and ethnicity findings suggest within-agency racial and ethnic differences in diffusion of telemental health care. States should monitor the diffusion of innovations across vulnerable populations.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sharon-Lise Normand, PhD, email sharon@hcp.med.harvard.edu.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This ...
Changes in support for advance provision and over-the-counter access to medication abortion
2025-01-16
About The Study: In this serial cross-sectional analysis of people ages 15 to 49 before Dobbs and 1 year after Dobbs, findings suggested that national support for expanded access to medication abortion has grown. Alternative models of care, such as advance provision and over-the-counter, have the potential to offer a promising approach to abortion care, particularly for people living in abortion-restricted states.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, M. Antonia Biggs, PhD, email antonia.biggs@ucsf.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Protein level predicts immunotherapy response in bowel cancer
2025-01-16
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs GMT Thursday 16 January 2025
Peer reviewed
Observational study
People and cells
Protein level predicts immunotherapy response in bowel cancer
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and Barts Cancer Institute, Queen Mary University of London, have shown that the amount of a protein called CD74 can indicate which people with bowel cancer may respond best to immunotherapy.
If integrated into the clinic, testing for this protein could potentially allow hundreds of previously ineligible patients to benefit ...
The staying power of bifocal contact lens benefits in young kids
2025-01-16
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Young nearsighted kids who wear bifocal contact lenses that slow uncoordinated eye growth do not lose the benefits of the treatment once they stop wearing the lenses, new research shows.
The study is a follow-up to a clinical trial published in 2020 showing that soft multifocal contact lenses with a heavy dose of added reading power dramatically slowed further progression of myopia in kids as young as 7 years old. Researchers wondered if discontinuing that treatment might cause a rebound of faster-than-normal eye growth that wipes out the benefit.
In the new trial, nearsighted kids wore ...
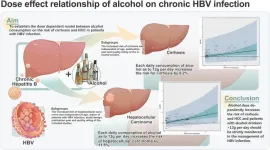
Dose-dependent relationship between alcohol consumption and the risks of hepatitis b virus-associated cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis and systematic review
2025-01-16
Background and Aims
The quantitative effects of alcohol consumption on cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection are unknown. This study aimed to establish a dose-dependent model of alcohol consumption on the risks of cirrhosis and HCC.
Methods
PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and four Chinese databases were searched for studies published from their inception to 15 May 2024. A random-effects model was used to pool the data on the incidence of cirrhosis and HCC, and a dose-dependent model of alcohol’s effect on cirrhosis and HCC was established.
Results
A total of 33,272 HBV patients ...
International Alliance for Primary Immunodeficiency Societies selects Rockefeller University Press to publish new Journal of Human Immunity
2025-01-16
January 16, 2025 – New York, NY – The International Alliance for Primary Immunodeficiency Societies (IAPIDS) and Rockefeller University Press (RUP) have entered a partnership to launch Journal of Human Immunity (JHI), the official open access journal of IAPIDS. This collaboration will ensure that JHI emerges as the destination for exciting research into human immunity, with a particular focus on inborn errors of immunity.
“The Journal of Human Immunity represents a bold step forward in advancing ...
Leader in mission-driven open publishing wins APE Award for Innovation in Scholarly Communication
2025-01-16
Digital Science is pleased to announce that Dr Raym Crow, a leading figure in mission-driven, sustainable open publishing models, has won the 2025 APE Award for Innovation in Scholarly Communication.
The award – a joint initiative between Digital Science and the Berlin Institute for Scholarly Publishing (BISP) – has been announced at the 20th Academic Publishing in Europe (APE) Conference in Berlin, Germany.
The APE award is presented to an individual who has brought innovation in scholarly communication to the community, through infrastructure, technology, business models, output on the topic, theory, or practice.
With more than ...
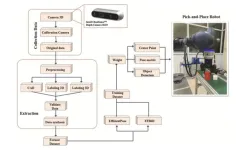
Innovative 6D pose dataset sets new standard for robotic grasping performance
2025-01-16
Accurate object pose estimation refers to the ability of a robot to determine both the position and orientation of an object. It is essential for robotics, especially in pick-and-place tasks, which are crucial in industries such as manufacturing and logistics. As robots are increasingly tasked with complex operations, their ability to precisely determine the six degrees of freedom (6D pose) of objects, position, and orientation, becomes critical. This ability ensures that robots can interact with objects in a reliable and safe manner. However, despite advancements in deep learning, the performance of 6D pose estimation algorithms largely depends ...
Evaluation of plasma neurodegenerative biomarkers for diagnosing minimal hepatic encephalopathy and predicting overt hepatic encephalopathy in Chinese patients with hepatic cirrhosis
2025-01-16
Background and Aims
The performance of neurodegenerative biomarkers—neurofilament light chain (NfL), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), tau, and ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCHL1)—in diagnosing minimal hepatic encephalopathy (MHE) has not been systematically evaluated, simultaneously, nor have their associations with the development of overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE). This study aimed to evaluate the performance of plasma NfL, GFAP, tau, and UCHL1 in diagnosing MHE and predicting the development of OHE in Chinese patients with hepatic cirrhosis.
Methods
In this prospective study, 124 patients ...