(Press-News.org) Severe droughts are becoming hotter, longer, and increasingly devastating to ecosystems as climate change accelerates, according to a new study, which reports that temperate grasslands, including in parts of the United States, are facing the worst effects. The findings provide a global quantitative understanding of multiyear droughts (MYDs) – prolonged events lasting years or decades – and offer a benchmark for understanding their global trends and impacts. As droughts become more frequent worldwide, the likelihood of MYDs rises, posing severe threats to both natural ecosystems and human systems. These events deplete soil moisture and reduce streamflow, potentially causing irreversible damage, with consequences that include widespread crop failures, increased tree mortality, diminished ecosystem productivity, and reduced water supplies. Recent MYDs, like the Western U.S. drought (2000–2018) and Chile's ongoing drought (since 2010), have drawn significant concern due to their devastating impacts. However, less prominent MYDs, with fewer perceived consequences, may have gone unnoticed, highlighting the need for comprehensive knowledge of their occurrence and effects. To address this need, Liangzhi Chen and colleagues mapped the global distribution of 13,176 MYDs from 1980 to 2018 using the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index (SPEI), which measures drought severity based on the balance between precipitation and potential evaporative demand. Chen et al. also assessed these events’ impacts on vegetation through remotely sensed greenness data. The findings show that over the last 40 years, MYDs have occurred on nearly every continent and have become increasingly widespread, hotter, and drier, with global land affected by these events increasing by 49,279 ±14,771 square kilometers annually. What’s more, the authors report that the ecosystem impacts of MYDs varied significantly, with temperate grasslands exhibiting greater declines in greenness compared to subtropical and tropical forests. While grasslands demonstrated low resistance to drought, they often displayed rapid recovery following drought events, highlighting their unique resilience dynamics. In a related Perspective, David Hoover and William Smith discuss the study and its findings in greater detail.
END
Multiyear “megadroughts” becoming longer and more severe under climate change
Summary author: Walter Beckwith
2025-01-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Australopithecines at South African cave site were not eating substantial amounts of meat
2025-01-16
Seven Australopithecus specimens uncovered at the Sterkfontein fossil site in South Africa were herbivorous hominins who did not eat substantial amounts of meat, according to a new study by Tina Lüdecke and colleagues. Lüdecke et al. analyzed organic nitrogen and carbonate carbon isotopes extracted from tooth enamel in the fossil specimens to determine the hominin diets. Some researchers have hypothesized that the incorporation of animal-based foods in early hominin diets led to increased brain size, smaller gut size ...
An AI model developed to design proteins simulates 500 million years of protein evolution in developing new fluorescent protein
2025-01-16
Guided by a multimodal generative language model called ESM3, Thomas Hayes and colleagues generated and synthesized a previously unknown bright fluorescent protein, with a genetic sequence so different from known fluorescent proteins that the researchers say its creation is equivalent to ESM3 simulating 500 million years of biological evolution. The model could provide a new way to “search” the space of protein possibilities with an eye to better understanding how naturally evolved proteins work, as well as developing novel proteins for uses in medicine, environmental remediation, and a host of other applications. ESM3 can reason over protein ...
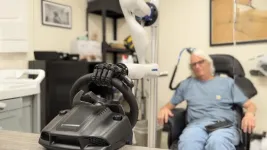
Fine-tuned brain-computer interface makes prosthetic limbs feel more real
2025-01-16
You can probably complete an amazing number of tasks with your hands without looking at them. But if you put on gloves that muffle your sense of touch, many of those simple tasks become frustrating. Take away proprioception — your ability to sense your body’s relative position and movement — and you might even end up breaking an object or injuring yourself.
“Most people don’t realize how often they rely on touch instead of vision — typing, walking, picking up a flimsy cup of water,” said Charles Greenspon, PhD, a neuroscientist at the University of Chicago. “If you can’t feel, you have ...
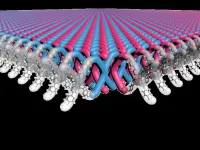
New chainmail-like material could be the future of armor
2025-01-16
EVANSTON, Il. --- In a remarkable feat of chemistry, a Northwestern University-led research team has developed the first two-dimensional (2D) mechanically interlocked material.
Resembling the interlocking links in chainmail, the nanoscale material exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength. With further work, it holds promise for use in high-performance, light-weight body armor and other uses that demand lightweight, flexible and tough materials.
Publishing on Friday (Jan. 17) in the journal ...
The megadroughts are upon us
2025-01-16
Increasingly common since 1980, persistent multi-year droughts will continue to advance with the warming climate, warns a study from the Swiss Federal Institute for Forest, Snow, and Landscape Research (WSL), with Professor Francesca Pellicciotti from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) participating. This publicly available forty-year global quantitative inventory, now published in Science, seeks to inform policy regarding the environmental impact of human-induced climate change. It also detected previously ‘overlooked’ events.
Fifteen years of a persistent, devastating megadrought—the longest lasting in a thousand years—have nearly dried out ...
Eavesdropping on organs: Immune system controls blood sugar levels
2025-01-16
When we think about the immune system, we usually associate it with fighting infections. However, a study published in Science by the Champalimaud Foundation reveals a surprising new role. During periods of low energy—such as intermittent fasting or exercise—immune cells step in to regulate blood sugar levels, acting as the “postman” in a previously unknown three-way conversation between the nervous, immune and hormonal systems. These findings open up new approaches for managing conditions like diabetes, obesity, and cancer.
Rethinking the Immune ...
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors
2025-01-16
The trick to creating a better quantum sensor? Just give it a little squeeze.
For the first time ever, scientists have used a technique called “quantum squeezing” to improve the gas sensing performance of devices known as optical frequency comb lasers. These ultra-precise sensors are like fingerprint scanners for molecules of gas. Scientists have used them to spot methane leaks in the air above oil and gas operations and signs of COVID-19 infections in breath samples from humans.
Now, in a series of lab experiments, researchers have laid out a path for making those kinds of measurements even more sensitive and faster—doubling the speed of ...
New study reveals how climate change may alter hydrology of grassland ecosystems
2025-01-16
New research co-led by the University of Maryland reveals that drought and increased temperatures in a CO2-rich climate can dramatically alter how grasslands use and move water. The study provides the first experimental demonstration of the potential impacts of climate change on water movement through grassland ecosystems, which make up nearly 40% of Earth’s land area and play a critical role in Earth’s water cycle. The study appears in the January 17, 2025, issue of the journal Science.
“If we want to predict the effects of climate change ...
Polymer research shows potential replacement for common superglues with a reusable and biodegradable alternative
2025-01-16
EMBARGO: THIST CONTENT IS UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 2 PM U.S. EASTERN STANDARD TIME ON JANUARY 16, 2025. INTERESTED MEDIA MAY RECIVE A PREVIEW COPY OF THE JOURNAL ARTICLE IN ADVANCE OF THAT DATE OR CONDUCT INTERVIEWS, BUT THE INFORMATION MAY NOT BE PUBLISHED, BROADCAST, OR POSTED ONLINE UNTIL AFTER THE RELEASE WINDOW.
Researchers at Colorado State University and their partners have developed an adhesive polymer that is stronger than current commercially available options while also being biodegradable ...
Research team receives $1.5 million to study neurological disorders linked to long COVID
2025-01-16
The National Institute of Mental Health has awarded a significant grant of $1.5 million to Jianyang Du, PhD, of the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, for a research study aimed at uncovering the cellular and molecular mechanisms that lead to neurological disorders caused by long COVID-19.
Dr. Du is an associate professor at the College of Medicine in the Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology. Colleen Jonsson, PhD, director of the UT Health Science Center Regional Biocontainment Laboratory and professor in the Department of Microbiology, is co-investigator on the grant, and Kun Li, PhD, assistant ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] Multiyear “megadroughts” becoming longer and more severe under climate changeSummary author: Walter Beckwith