New superconductor with hallmark of unconventional superconductivity discovered
Student project uncovers superconductivity in polycrystalline iron nickel zirconide
2025-01-18
(Press-News.org)
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have discovered a new superconducting material. They combined iron, nickel, and zirconium, to create a new transition metal zirconide with different ratios of iron to nickel. While both iron zirconide and nickel zirconide are not superconducting, the newly prepared mixtures are, exhibiting a “dome-shaped” phase diagram typical of so-called “unconventional superconductors,” a promising avenue for developing high temperature superconducting materials which can be more widely deployed in society.
Superconductors already play an active role in cutting-edge technologies, from superconducting magnets in medical devices and maglev systems to superconducting cables for power transmission. However, they generally rely on cooling to temperatures of around four Kelvin, a key roadblock in wider deployment of the technology. Scientists are on the lookout for materials which can show zero resistivity at higher temperatures, particularly the 77 Kelvin threshold at which liquid nitrogen can be used to cool the materials instead of liquid helium.
The good news is that promising candidates have begun to appear, like iron-based superconductors discovered in 2008. It is becoming increasingly clear that high-temperature superconductivity might follow a different mechanism from those of “conventional superconductors” that follow well-established theoretical frameworks, notably the BCS (Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer) theory. In particular, materials with magnetic elements, or those that exhibit “magnetic ordering,” have begun to emerge as being important for the emergence of “unconventional superconductivity.”
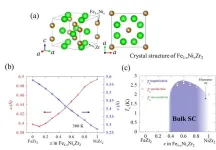
Now, a team of researchers led by Associate Professor Yoshikazu Mizuguchi from Tokyo Metropolitan University have conceived a new superconducting material containing a magnetic element. For the first time, they showed that a polycrystalline alloy of iron, nickel, and zirconium shows superconducting properties. Curiously, both iron zirconide and nickel zirconide are not superconducting in crystalline form. In experiments which began as an undergraduate student project, the team combined iron, nickel, and zirconium in different ratios using a method known as arc melting, confirming that the resulting alloy had the same crystal structure as tetragonal transition-metal zirconides, a family of promising superconducting materials. The lattice constants, or the lengths of repeating cells, were also found to change smoothly with the ratio of iron to nickel. Crucially, they found a region of compositions where the superconducting transition temperature rose, then fell again. This “dome-like” form is a promising hallmark of unconventional superconductivity.
Further experiments confirmed that the magnetization of nickel zirconide exhibits a magnetic-transition-like anomaly, suggesting a close relationship between their findings and the unconventional superconductivity arising from magnetic order suggested in other materials. They hope that their new platform for studying unconventional superconductivity might inspire new inroads into our understanding of its mechanism, as well as in the practical design of cutting-edge materials for the next generation of superconducting devices.
This work was supported by JSPS-KAKENHI Grant Number 23KK0088, a TMU Research Project for an Emergent Future Society, and a Tokyo Government-Advanced Research Grant (H31–1).
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-01-18
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality globally, posing a particularly significant threat to people with HIV (PWH). To address this, CVD prevention plans rely on prediction models like atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk scores to estimate the risk of heart disease.
However, previous studies have called into question whether these commonly used prediction models perform well among people with HIV, and there remains a gap in understanding of what these scores mean for PWH in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
Researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham ...
2025-01-17
Cultural traits — the information, beliefs, behaviors, customs, and practices that shape the character of a population — are influenced by conformity, the tendency to align with others, or anti-conformity, the choice to deliberately diverge. A new way to model this dynamic interplay could ultimately help explain societal phenomena like political polarization, cultural trends, and the spread of misinformation.
A study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences outlines this novel approach. Presenting a mathematical model, SFI Complexity Postdoctoral Fellow Kaleda Denton with colleagues ...
2025-01-17
A research team from NIMS and the Japan Fine Ceramics Center (JFCC) has developed a next-generation AI device—a hardware component for AI systems—that incorporates an iono-magnonic reservoir. This reservoir controls spin waves (collective excitations of electron spins in magnetic materials), ion dynamics and their interactions. The technology demonstrated significantly higher information processing performance than conventional physical reservoir computing devices, underscoring its potential to transform AI technologies.
As AI devices become increasingly sophisticated, ...
2025-01-17
By Shawn Ballard
The complexity of the human brain – 86 billion neurons strong with more than 100 trillion connections – enables abstract thinking, language acquisition, advanced reasoning and problem-solving, and the capacity for creativity and social interaction. Understanding how differences in brain signaling and dynamics produce unique cognition and behavior in individuals has long been a goal of neuroscience research, yet many phenomena remain unexplained.
A study from neuroscientists and ...
2025-01-17
As the atmosphere continues to fill with greenhouse gases from human activities, many proposals have surfaced to “geoengineer” climate-saving solutions, that is, alter the atmosphere at a global scale to either reduce the concentrations of carbon or mute its warming effect.
One recent proposal seeks to infuse the atmosphere with hydrogen peroxide, insisting that it would both oxidize methane (CH4), an extremely potent greenhouse gas while improving air quality.
Too good to be true?
University of Utah atmospheric scientists Alfred Mayhew and Jessica Haskins were skeptical, so they set out to test the claims behind this proposal. Their results, published on ...
2025-01-17
WASHINGTON, D.C. – Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced it is accepting applications for the 2025 DOE Office of Science Early Career Research Program to support the research of outstanding scientists early in their careers. The program will support over 80 early career researchers for five years at U.S. academic institutions, DOE national laboratories, and Office of Science user facilities.
“The vision, creativity, and effort of early career faculty drive innovation in the basic science enterprise. The Department of Energy’s Office of Science is dedicated to ...
2025-01-17
University of Virginia School of Engineering and Applied Science faculty members James T. Burns, Coleen Carrigan and Liheng Cai received the Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers (PECASE) on Tuesday, as did two UVA Engineering alumni, Ashutosh Giri and Ryan Johnson.
PECASE is the highest honor bestowed by the U.S. government on outstanding scientists and engineers early in their careers. According to the release from the White House, this award recognizes “innovative and far-reaching developments in science and technology.”
“This award year has been extraordinary not ...
2025-01-17
ARLINGTON, Va.—A favorite childhood memory for Dr. Sandra Chapman was visiting the USS Arizona Memorial in Pearl Harbor with her father. They hung out at the memorial so often that they memorized lines to the movie playing prior to the boat ride to the memorial.
So it’s appropriate that Chapman — a program officer in the Office of Naval Research’s (ONR) Warfighter Performance Department — is passionate about her involvement in the development of an innovative technology recently applied to efforts to preserve the area around the USS Arizona ...
2025-01-17
Images
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Our sun is essentially a searing hot sphere of gas. Its mix of primarily hydrogen and helium can reach temperatures between 10,000 and 3.6 million degrees Fahrenheit on its surface and its atmosphere’s outermost layer. Because of that heat, the blazing orb constantly oozes a stream of plasma, made up of charged subatomic particles — mainly protons and electrons. The sun’s gravity can’t contain them because they hold so much energy as heat, so they drift away into space as solar wind. Understanding how charged particles ...
2025-01-17
Maital Neta, professor of psychology at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln, has received the Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, the highest honor bestowed by the U.S. government on outstanding scientists and engineers early in their careers.
Neta, Carl A. Happold Professor of Psychology, directs the Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience Lab and is resident faculty of the Center for Brain, Biology and Behavior.
Neta said she was “very grateful” for the honor, announced ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New superconductor with hallmark of unconventional superconductivity discovered
Student project uncovers superconductivity in polycrystalline iron nickel zirconide