(Press-News.org) About The Article: This article outlines the ways in which the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has worked to use electronic health record data to improve patient health, public health, and health care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Robert M. Califf, MD, email commissioner@fda.hhs.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2025.0068)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2025.0068?guestAccessKey=21162b05-bd2d-48f1-9482-4291e6c037b5&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=011825
END
A unified approach to health data exchange
JAMA
2025-01-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
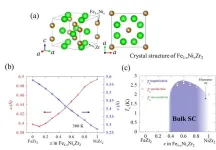
New superconductor with hallmark of unconventional superconductivity discovered
2025-01-18
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have discovered a new superconducting material. They combined iron, nickel, and zirconium, to create a new transition metal zirconide with different ratios of iron to nickel. While both iron zirconide and nickel zirconide are not superconducting, the newly prepared mixtures are, exhibiting a “dome-shaped” phase diagram typical of so-called “unconventional superconductors,” a promising avenue for developing high temperature superconducting materials which can be more widely deployed in society.
Superconductors already play ...
Global HIV study finds that cardiovascular risk models underestimate for key populations
2025-01-18
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality globally, posing a particularly significant threat to people with HIV (PWH). To address this, CVD prevention plans rely on prediction models like atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk scores to estimate the risk of heart disease.
However, previous studies have called into question whether these commonly used prediction models perform well among people with HIV, and there remains a gap in understanding of what these scores mean for PWH in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
Researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham ...
New study offers insights into how populations conform or go against the crowd
2025-01-17
Cultural traits — the information, beliefs, behaviors, customs, and practices that shape the character of a population — are influenced by conformity, the tendency to align with others, or anti-conformity, the choice to deliberately diverge. A new way to model this dynamic interplay could ultimately help explain societal phenomena like political polarization, cultural trends, and the spread of misinformation.
A study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences outlines this novel approach. Presenting a mathematical model, SFI Complexity Postdoctoral Fellow Kaleda Denton with colleagues ...
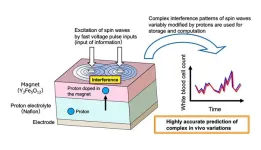
Development of a high-performance AI device utilizing ion-controlled spin wave interference in magnetic materials
2025-01-17
A research team from NIMS and the Japan Fine Ceramics Center (JFCC) has developed a next-generation AI device—a hardware component for AI systems—that incorporates an iono-magnonic reservoir. This reservoir controls spin waves (collective excitations of electron spins in magnetic materials), ion dynamics and their interactions. The technology demonstrated significantly higher information processing performance than conventional physical reservoir computing devices, underscoring its potential to transform AI technologies.
As AI devices become increasingly sophisticated, ...
WashU researchers map individual brain dynamics
2025-01-17
By Shawn Ballard
The complexity of the human brain – 86 billion neurons strong with more than 100 trillion connections – enables abstract thinking, language acquisition, advanced reasoning and problem-solving, and the capacity for creativity and social interaction. Understanding how differences in brain signaling and dynamics produce unique cognition and behavior in individuals has long been a goal of neuroscience research, yet many phenomena remain unexplained.
A study from neuroscientists and ...
Technology for oxidizing atmospheric methane won’t help the climate
2025-01-17
As the atmosphere continues to fill with greenhouse gases from human activities, many proposals have surfaced to “geoengineer” climate-saving solutions, that is, alter the atmosphere at a global scale to either reduce the concentrations of carbon or mute its warming effect.
One recent proposal seeks to infuse the atmosphere with hydrogen peroxide, insisting that it would both oxidize methane (CH4), an extremely potent greenhouse gas while improving air quality.
Too good to be true?
University of Utah atmospheric scientists Alfred Mayhew and Jessica Haskins were skeptical, so they set out to test the claims behind this proposal. Their results, published on ...
US Department of Energy announces Early Career Research Program for FY 2025
2025-01-17
WASHINGTON, D.C. – Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced it is accepting applications for the 2025 DOE Office of Science Early Career Research Program to support the research of outstanding scientists early in their careers. The program will support over 80 early career researchers for five years at U.S. academic institutions, DOE national laboratories, and Office of Science user facilities.
“The vision, creativity, and effort of early career faculty drive innovation in the basic science enterprise. The Department of Energy’s Office of Science is dedicated to ...
PECASE winners: 3 UVA engineering professors receive presidential early career awards
2025-01-17
University of Virginia School of Engineering and Applied Science faculty members James T. Burns, Coleen Carrigan and Liheng Cai received the Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers (PECASE) on Tuesday, as did two UVA Engineering alumni, Ashutosh Giri and Ryan Johnson.
PECASE is the highest honor bestowed by the U.S. government on outstanding scientists and engineers early in their careers. According to the release from the White House, this award recognizes “innovative and far-reaching developments in science and technology.”
“This award year has been extraordinary not ...
‘Turn on the lights’: DAVD display helps navy divers navigate undersea conditions
2025-01-17
ARLINGTON, Va.—A favorite childhood memory for Dr. Sandra Chapman was visiting the USS Arizona Memorial in Pearl Harbor with her father. They hung out at the memorial so often that they memorized lines to the movie playing prior to the boat ride to the memorial.
So it’s appropriate that Chapman — a program officer in the Office of Naval Research’s (ONR) Warfighter Performance Department — is passionate about her involvement in the development of an innovative technology recently applied to efforts to preserve the area around the USS Arizona ...
MSU researcher’s breakthrough model sheds light on solar storms and space weather
2025-01-17
Images
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Our sun is essentially a searing hot sphere of gas. Its mix of primarily hydrogen and helium can reach temperatures between 10,000 and 3.6 million degrees Fahrenheit on its surface and its atmosphere’s outermost layer. Because of that heat, the blazing orb constantly oozes a stream of plasma, made up of charged subatomic particles — mainly protons and electrons. The sun’s gravity can’t contain them because they hold so much energy as heat, so they drift away into space as solar wind. Understanding how charged particles ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
Improving data science education using interest‑matched examples and hands‑on data exercises
Sparkling water helps keep minds sharp during long esports sessions
Drone LiDAR surveys of abandoned roads reveal long-term debris supply driving debris-flow hazards
UGA Bioinformatics doctoral student selected for AIBS and SURA public policy fellowship
Gut microbiome connected with heart disease precursor
Nitrous oxide, a product of fertilizer use, may harm some soil bacteria
FAU lands $4.5M US Air Force T-1A Jayhawk flight simulator
SimTac: A physics-based simulator for vision-based tactile sensing with biomorphic structures
Preparing students to deal with ‘reality shock’ in the workplace
Researchers develop beating, 3D-printed heart model for surgical practice
Black soldier fly larvae show promise for safe organic waste removal
People with COPD commonly misuse medications
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
Team led by UC San Diego researchers selected for prestigious global cancer prize
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
[Press-News.org] A unified approach to health data exchangeJAMA