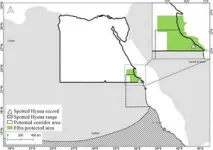
(Press-News.org) A spotted hyena (Crocuta crocuta) has been found in South Eastern Egypt: the first recorded instance of the creature in this region for thousands of years.
The lone individual was caught and killed by people around 30km from the border with Sudan, a paper in De Gruyter’s Mammalia reports.
“My first reaction was disbelief until I checked the photos and videos of the remains,” said the study’s lead author, Dr. Adbullah Nagy from Al-Azhar University, Egypt. “Seeing the evidence, I was completely taken aback. It was beyond anything we had expected to find in Egypt.”
The sighting took place some 500km north of the known range of spotted hyena in neighbouring Sudan. The researchers theorized that a regional, decadal weather cycle, part of the Active Red Sea Trough phenomenon, could have resulted in increased rainfall and plant growth, opening up a migration corridor for the hyena where better grazing opportunities supported sufficient prey.
To test this idea, they used a normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) as a measure of precipitation and corresponding pastoral grazing opportunity, with NDVI values obtained from Landsat 5 and 7 satellite images between 1984 and 2022. Analysis revealed multi-year droughts with shorter relatively wet periods. The last five years had higher NVDI values than the previous two decades, suggesting increased plant growth could support prey for a curious spotted hyena on the move.
“The fact that the corridor area has become less environmentally harsh, offering easier passage along ‘the highway’, may explain how the hyena reached this far north,” says Nagy. “However, the motivation for its extensive journey into Egypt is still a mystery that demands further research.”
Spotted hyenas are successful pack predators, usually found in a variety of habitats in sub-Saharan Africa. They can travel up to 27km in a day, shadowing semi-nomadic, human-managed livestock migrations and subsisting on occasional kills.
The individual described in this study killed two goats herded by people in Wadi Yahmib in the Elba Protected Area, and was subsequently tracked, spotted, chased and killed in late February 2024. The kill was photographed and geolocated, giving animal ecologists the opportunity to follow up the sighting.
The study’s findings force a rethink of the agreed distribution of spotted hyenas and add to the available data on how regional climate change can affect animal migration.
The paper can be found here: https://doi.org/10.1515/mammalia-2024-0031
De Gruyter
Mauricio Quiñones
Communications
Tel: +49 30 260 05 164
mauricio.quinones@degruyter.com
www.degruyter.com
De Gruyter publishes first-class scholarship and has done so for more than 270 years. An international, independent publisher headquartered in Berlin -- and with further offices in Boston, Beijing, Basel, Vienna, Warsaw and Munich -- it publishes over 1,300 new book titles each year and more than 900 journals in the humanities, social sciences, medicine, mathematics, engineering, computer sciences, natural sciences, and law. The publishing house also offers a wide range of digital media, including open access journals and books. The group includes the imprints De Gruyter Akademie Forschung, Birkhäuser, De Gruyter Mouton, De Gruyter Oldenbourg, De Gruyter Saur, Düsseldorf University Press, Deutscher Kunstverlag (DKV) and Jovis Verlag, as well as the publishing services provider Sciendo. For more information, visit: www.degruyter.com
END
Spotted hyena found in Egypt for the first time in 5,000 years
Climatic factors, changing livestock grazing and human activity in the area may have supported an ill-fated odyssey
2025-01-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
SignGPT – Project awarded £8.45m to build a sign language AI model for the Deaf community
2025-01-21
A large-language model (LLM) built to meet the needs of the Deaf community, translating between signed and spoken language, is the aim of a new project led by the University of Surrey.
SignGPT: Building Generative Predictive Transformers for Sign Language has been awarded £8.45m from the UK Engineering & Physical Sciences Research Council. The five-year project will build tools to allow spoken language to be automatically translated into photo-realistic sign language and video of sign language to be translated into spoken language – a complex translation problem that is yet to be solved.
Surrey ...
Garden ponds: Hidden gems of urban biodiversity conservation
2025-01-21
Urbanisation is rapidly transforming landscapes worldwide, becoming a key driver of global biodiversity loss. It often impacts biodiversity negatively by creating selective environments that limit species diversity in urban compared to natural habitats. Amidst this challenge, understanding and enhancing urban blue-green infrastructure is critical. Garden ponds are small yet significant water features that are increasingly common in urban areas. They offer numerous ecosystem services, like aesthetic purposes, microclimate regulation, and habitats for ornamental species. However, their role in supporting ...
Epigenetic aging and DNA-methylation as tumor markers for breast cancer
2025-01-21
“Our study contributes to the development of a DNAm biomarker that integrates conventional BC risk factors to better reflect the risk for BC subtypes, promoting epigenetically targeted preventive interventions tailored to aged individuals with high risk.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 21, 2025 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) on December 5, 2024, Volume 16, ...
Salt deposit ring inside your pasta pan?
2025-01-21
WASHINGTON, Jan. 21, 2025 – If you’ve ever tossed a generous pinch of salt into your pasta pan’s water for flavor or as an attempt to make it boil faster, you’ve likely ended up with a whitish ring of deposits inside the pan.
A group of scientists from the University of Twente in the Netherlands and the French National Institute for Agriculture, Food, and Environment (INRAE), inspired by this observation during an evening of board games and pasta dinner, wondered what it ...
First fast radio burst traced to old, dead, elliptical galaxy
2025-01-21
For the first time, astronomers have traced a fast radio burst (FRB) to the outskirts of an ancient, dead, elliptical galaxy — an unprecedented home for a phenomenon previously associated with much younger galaxies.
Detailed in two complementary studies led by Northwestern University and McGill University, the discovery shatters assumptions that FRBs solely emanate from regions of active star formation. The new observational evidence, instead, hints that the origins of these mysterious cosmic events might be more diverse than ...
We can make fertilizer more efficiently under the surface of the Earth
2025-01-21
Instead of relying on energy-hungry reactors to generate high temperatures and pressure, researchers are looking underground at Earth’s natural heat and forces to cook up ammonia for fertilizer. In a proof-of-concept study, published January 21 in the Cell Press journal Joule, researchers generated ammonia by mixing nitrogen-laced water with iron-rich rocks—without any energy input or CO2 emission. This new recipe may lead to a more sustainable alternative to current methods, theoretically churning out enough ammonia for 2.42 million years.
The idea stems from an unusual geological phenomenon observed in the 1980s in Mali, West Africa. Locals discovered a well ...
What's behind preterm birth? Scientists just found a big clue
2025-01-21
What's Behind Preterm Birth? Scientists Just Found a Big Clue
UCSF researchers discovered a molecular timer that gets activated in the first days of pregnancy and influences when mice give birth.
A typical human pregnancy lasts 40 weeks, but most parents know this number is only a rough estimate.
Babies are born on a seemingly unpredictable timeline, with a normal pregnancy ranging from 38 to 42 weeks. And 10 percent of all births are preterm, meaning they occur before 37 weeks of gestation, which puts babies at risk of a host of complications.
Now, UC San Francisco researchers have discovered a molecular timer in mice that plays a role in controlling ...
The importance of eco-friendly sensors in global food supply
2025-01-21
WASHINGTON, Jan. 21, 2025 – Greenhouses and open farms that welcome visitors to purchase locally grown produce and meat have become increasingly important to food productivity. Not only are farmers looking for ways to monitor conditions to help improve greenhouse crop growth and yield, but keeping harvested food fresh in storage conditions is also a major concern. Smart sensor technology, monitoring and controlling temperature and humidity, plays an essential role in producing enough food to meet the ever-increasing demand ...
Brain immune cells may also be from Mars and Venus
2025-01-21
A collision happens. Someone is hurt, a head injury, a concussion. Just as the first responders arrive to help the person, inside the brain, another “crew” of responders is busy clearing debris and repairing injured tissue.
This crew is called the microglia - the immune cells of the central nervous system. Microglia are imperative to maintaining neuronal function by clearing toxins in the brain and central nervous system. But if they are overactive, they can damage neurons instead and, in some cases, have been found to promote the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
During ...
Effect of pediatric obesity treatment on long-term health
2025-01-21
About The Study: This cohort study demonstrated that good response to pediatric obesity treatment was associated with reduced long-term morbidity, such as type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension. Additionally, a link between pediatric obesity treatment effectiveness and lower incidences of mortality in young adulthood was observed; however, effective pediatric obesity treatment was not associated with adult depression or anxiety, highlighting their distinct nature despite frequent coexistence.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Emilia Hagman, PhD, email emilia.hagman@ki.se
To access the embargoed study: Visit our ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy may help prevent preeclampsia
Menopausal hormone therapy not linked to increased risk of death
Chronic shortage of family doctors in England, reveals BMJ analysis
Booster jabs reduce the risks of COVID-19 deaths, study finds
Screening increases survival rate for stage IV breast cancer by 60%
ACC announces inaugural fellow for the Thad and Gerry Waites Rural Cardiovascular Research Fellowship
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
Colonists dredged away Sydney’s natural oyster reefs. Now science knows how best to restore them.
[Press-News.org] Spotted hyena found in Egypt for the first time in 5,000 yearsClimatic factors, changing livestock grazing and human activity in the area may have supported an ill-fated odyssey